Abstract
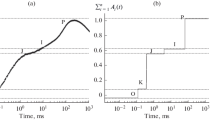
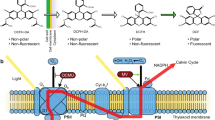
The induction (sudden dark-to-light transition) of fluorescence of photosynthetic bacteria has proved to be sensitive tool for early detection of mercury (Hg2+) contamination of the culture medium. The major characteristics of the induction (dark, variable and maximum fluorescence levels together with rise time) offer an easier, faster and more informative assay of indication of the contamination than the conventional techniques. The inhibition of Hg2+ is stronger in the light than in the dark and follows complex kinetics. The fast component (in minutes) reflects the damage of the quinone acceptor pool of the RC and the slow component (in hours) is sensitive to the disintegration of the light harvesting system including the loss of the structural organization and of the pigments. By use of fluorescence induction, the dependence of the diverse pathways and kinetics of the mercury-induced effects on the age and the metabolic state of the bacteria were revealed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Barregard, E. Fabricius-Lagging, T. Lundh, J. Mölne, M. Wallin, M. Olausson, C. Modigh and G. Sallsten, Cadmium, mercury, and lead in kidney cortex of living kidney donors: Impact of different exposure sources, Environ. Res., 2010, 110, 47–54.
F. Borsetti, P. L. Martelli, R. Casadio and D. Zannoni, Metals and Metalloids in Photosynthetic Bacteria: Interactions, Resistance and Putative Homeostasis Revealed by Genome Analysis, The Purple Phototrophic Bacteria, Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009, pp. 655–689.
A. Malik, Metal bioremediation through growing cells, Environ. Int., 2004, 30, 261–278.
S. Silver, Bacterial resistances to toxic metal ions—a review, Gene, 1996, 179, 9–19.
F. Pisani, F. Italiano, F. de Leo, R. Gallerani, S. Rinalducci, L. Zolla, A. Agostiano, L. R. Ceci and M. Trotta, Soluble proteome investigation of cobalt effect on the carotenoidless mutant of Rhodobacter sphaeroides, J. Appl. Microbiol., 2009, 106, 338–349.
A. Buccolieri, F. Italiano, A. Dell’Atti, G. Buccolieri, L. Giotta, A. Agostiano, F. Milano and M. Trotta, Testing the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides as heavy metal removal tool, Ann. Chim., 2006, 96, 195–204.
F. Italiano, A. Buccolieri, L. Giotta, A. Agostiano, L. Valli, F. Milano and M. Trotta, Response of the carotenoidless mutant Rhodobacter sphaeroides growing cells to cobalt and nickel exposure, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 2009, 63, 948–957.
J. F. Imhoff, Anoxygenic Photosynthetic Bacteria, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995.
W. R. Sistrom, The Kinetics of the Synthesis of Photopigments in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides, J. Gen. Microbiol., 1962, 28, 607–616.
P. Maróti, Kinetics and yields of bacteriochlorophyll fluorescence: redox and conformation changes in reaction center of Rhodobacter sphaeroides, Eur. Biophys. J., 2008, 37, 1175–1184.
D. Bina, R. Litvin and F. Vacha, Kinetics of in vivo bacteriochlorophyll fluorescence yield and the state of photosynthetic apparatus of purple bacteria, Photosynth. Res., 2009, 99, 115–125.
H.-W. Trissl, Antenna organization in purple bacteria investigated by means of fluorescence induction curves, Photosynth. Res., 1996, 47, 175–185.
E. Asztalos, P. Maróti, Export or recombination of charges in reaction centers in intact cells of photosynthetic bacteria, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Bioenerg., 2009, 1787, 1444–1450.
M. Koblizek, J. D. Shih, S. I. Breitbart, E. C. Ratcliffe, Z. S. Kolber, C. N. Hunter and R. A. Niederman, Sequential assembly of photosynthetic units in Rhodobacter sphaeroides as revealed by fast repetition rate analysis of variable bacteriochlorophyll a fluorescence, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Bioenerg., 2005, 1706, 220–231.
M. H. Zwietering, I. Jongenburger, F. M. Rombouts, K. van’t Riet, Modeling of the Bacterial Growth Curve, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1990, 56, 1875–1881.
M. H. Zwietering, F. M. Rombouts, K. van’t Riet, Comparison of definitions of the lag phase and the exponential phase in bacterial growth, J. Appl. Bacteriol., 1992, 72, 139–145.
S. H. Kim and R. P. Sharma, Mercury-induced apoptosis and necrosis in murine macrophages: role of calcium-induced reactive oxygen species and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 2004, 196, 47–57.
N. Fernandez and R. Beiras, Combined toxicity of dissolved mercury with copper, lead and cadmium on embryogenesis and early larval growth of the Paracentrotus lividus sea-urchin, Ecotoxicology, 2001, 10, 263–271.
Q. Wang, B. Liu, H. Yang, X. Wang and Z. Lin, Toxicity of lead, cadmium and mercury on embryogenesis, survival, growth and metamorphosis of Meretrix meretrix larvae, Ecotoxicology, 2009, 18, 829–837.
H. Clijsters and F. Assche, Inhibition of photosynthesis by heavy metals, Photosynth. Res., 1985, 7, 31–40.
M. Gadallah, Interactive effect of heavy metals and temperature on the growth, and chlorophyll, saccharides and soluble nitrogen contents in Phaseolus plants, Biol. Plant., 1994, 36, 373–382.
K.-N. Lars, The Effect of Deleterious Concentrations of Mercury on the Photosynthesis and Growth of Chlorella pyrenoidosa, Physiol. Plant., 1971, 24, 556–561.
C. M. Lu, C. W. Chau and J. H. Zhang, Acute toxicity of excess mercury on the photosynthetic performance of cyanobacterium, S. platensis - assessment by chlorophyll fluorescence analysis, Chemosphere, 2000, 41, 191–196.
S. Murthy and P. Mohanty, Mercury ions inhibit photosynthetic electron transport at multiple sites in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus 6301, J. Biosci., 1993, 18, 355–360.
M. Patra and A. Sharma, Mercury toxicity in plants, Bot. Rev., 2000, 66, 379–422.
X. Du, Y. G. Zhu, W. J. Liu and X. S. Zhao, Uptake of mercury (Hg) by seedlings of rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown in solution culture and interactions with arsenate uptake, Environ. Exp. Bot., 2005, 54, 1–7.
D. W. Boening, Ecological effects, transport, and fate of mercury: a general review, Chemosphere, 2000, 40, 1335–1351.
L. Giotta, A. Agostiano, F. Italiano, F. Milano and M. Trotta, Heavy metal ion influence on the photosynthetic growth of Rhodobacter sphaeroides, Chemosphere, 2006, 62, 1490–1499.
R. J. Cogdell and J. P. Thomber, Light-harvesting pigment—protein complexes of purple photosynthetic bacteria, FEBS Lett., 1980, 122, 1–8.
C. Rafferty, J. Bolt, K. Sauer and R. Clayton, Photooxidation of antenna bacteriochlorophyll in chromatophores from carotenoidless mutant Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides and the attendant loss of dimeric exciton interaction, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1979, 76, 4429–4432.
M. Bernier and R. Carpentier, The action of mercury on the binding of the extrinsic polypeptides associated with the water oxidizing complex of photosystem II, FEBS Lett., 1995, 360, 251–254.
F. Šeršeň, K. Král’ová, A. Bumbálová, Action of Mercury on the Photosynthetic Apparatus of Spinach Chloroplasts, Photosynthetica, 1998, 35, 551–559.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asztalos, E., Italiano, F., Milano, F. et al. Early detection of mercury contamination by fluorescence induction of photosynthetic bacteria. Photochem Photobiol Sci 9, 1218–1223 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1039/c0pp00040j
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c0pp00040j