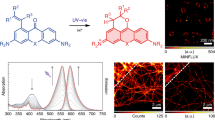
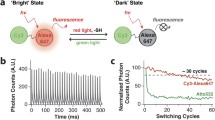
Abstract
Optical microscopes use visible light and an arrangement of lenses to provide us with magnified images of small samples. Combined with efficient fluorescent probes and highly sensitive fluorescence detection techniques they allow the non-invasive 3D study of subcellular structures even in living cells or tissue. However, optical microscopes are subject to diffraction of light which limits optical resolution to approximately 200 nm in the imaging plane. In the recent past, powerful methods emerged that enable fluorescence microscopy with subdiffraction optical resolution. Since most of these methods are based on the temporal control of fluorescence emission of fluorophores, photochromic molecules that can be switched reversibly between a fluorescent on- and a non-fluorescent off-state are the key for super-resolution imaging methods. Here, we present our approach to use spiropyran-fluorophore conjugates as efficient molecular optical switches (photoswitches). In these photochromic conjugates fluorescence emission of the fluorophore is controlled by the state of the spiropyran, which can be switched reversibly between a colorless spiropyran and a colored merocyanine form upon irradiation with light. Thus, the efficiency of energy transfer from the fluorophore to the spiropyran can be modulated by the irradiation conditions. We present ensemble data of the switching process of various spiropyrans and spiropyran-fluorophore conjugates and demonstrate photoswitching at the single-molecule level. Our data suggest that spiropyrans have to be immobilized in polymers to stabilize the merocyanine form in order to be useful for super-resolution fluorescence imaging based on precise localization of individual emitters. Special emphasis is put on photobleaching of donor fluorophores due to UV irradiation, i.e. photoswitching of the photochromic acceptor. Furthermore, we present a water soluble switchable spiropyran derivative and demonstrate the first intermolecular single-molecule photoswitching experiments in polymers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Abbe, Beiträge zur Theorie des Mikroskops und der mikroskopischen Wahrnehmung, Arch. Mikrosk. Anat., 1873, 9, 413–420.
S. W. Hell, Far-field optical nanoscopy, Science, 2007, 316, 1153–1158.
N. Ji, H. Shroff, H. Zhong and E. Betzig, Advances in the speed and resolution of light microscopy, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 2008, 18, 605–616.
M. Heilemann, P. Dedecker, J. Hofkens and M. Sauer, Photoswitches: Key molecules for subdiffraction-resolution fluorescence imaging and molecular quantification, Laser & Photonics Rev., 2009, 3, 180–202.
S. W. Hell and J. Wichmann, Breaking the diffraction resolution limit by stimulated emission: stimulated-emission-depletion fluorescence microscopy, Opt. Lett., 1994, 19, 780–783.
T. A. Klar, S. Jakobs, M. Dyba, A. Egner and S. W. Hell, Fluorescence microscopy with diffraction resolution barrier broken by stimulated emission, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2000, 97, 8206–8210.
C. Flors, J. Hotta, H. Uji-i, P. Dedecker, R. Ando, H. Mizuno, A. Miyawaki and J. Hofkens, Superresolution microscopy on the basis of engineered dark states, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 13970–13977.
E. Betzig, G. H. Patterson, R. Sougrat, O. W. Lindwasser, S. Olenych, J. S. Bonifacino, M. W. Davidson, J. Lippincott-Schwartz and H. F. Hess, Development and use of fluorescent protein markers in living cells, Science, 2006, 313, 1642–1645.
S. T. Hess, T. P. Girirajan and M. D. Mason, Ultra-high resolution imaging by fluorescence photoactivation localization microscopy, Biophys. J., 2006, 91, 4258–4272.
M. J. Rust, M. Bates and X. Zhuang, Sub-diffraction-limit imaging by stochastic reconstruction optical microscopy (STORM), Nat. Methods, 2006, 3, 793–795.
J. Fölling, M. Bossi, H. Bock, R. Medda, C. A. Wurm, B. Hein, S. Jakobs, C. Eggeling and S. W. Hell, Fluorescence nanoscopy by ground-state depletion and single-molecule return, Nat. Methods, 2008, 5, 943–945.
M. Heilemann, S. van de Linde, M. Schuttpelz, R. Kasper, B. Seefeldt, A. Mukherjee, P. Tinnefeld and M. Sauer, Subdiffraction-resolution fluorescence imaging with conventional fluorescent probes, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2008, 47, 6172–6176.
S. van de Linde, M. Sauer and M. Heilemann, Subdiffraction-resolution fluorescence imaging of proteins in the mitochondrial inner membrane with photoswitchable fluorophores, J. Struct. Biol., 2008, 164, 250–254.
C. Steinhauer, C. Forthmann, J. Vogelsang and P. Tinnefeld, Super-resolution microscopy on the basis of engineered dark states, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 16840–16841.
S. van de Linde, R. Kasper, M. Heilemann and M. Sauer, Photoswitching microscopy with standard fluorophores, Appl. Phys. B: Lasers Opt., 2008, 93, 725–731.
J. Vogelsang, T. Cordes, C. Forthmann, C. Steinhauer and P. Tinnefeld, Controlling the fluorescence of ordinary oxazine dyes for single-molecule switching and superresolution microscopy, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2009, 106, 8107–8112.
S. van de Linde, U. Endesfelder, A. Mukherjee, M. Schüttpelz, G. Wiebusch, S. Wolter, M. Heilemann and M. Sauer, Multicolor photoswitching microscopy for subdiffraction-resolution fluorescence imaging, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2009, 8, 465–469.
S. Wolter, M. Schüttpelz, M. Tscherepanow, S. van de Linde, M. Heilemann and M. Sauer, Real-time computation of subdiffraction-resolution fluorescence images, J. Microsc., 2010, 237, 12–22.
M. Heilemann, S. van de Linde, A. Mukherjee and M. Sauer, Super-resolution imaging with small organic fluorophores, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2009, 48, 6903–6908.
R. E. Thompson, D. R. Larson and W. W. Webb, Precise Nanometer Localization Analysis for Individual Fluorescent Probes, Biophys. J., 2002, 82, 2775–2783.
A. Yildiz, M. Tomishige, R. D. Vale and P. R. Selvin, Kinesin walks hand-over-hand, Science, 2004, 303, 676–678.
R. Ando, H. Mizuno and A. Miyawaki, Regulated fast nucleocytoplasmic shuttling observed by reversible protein highlighting, Science, 2004, 306, 1370–1373.
S. Habuchi, R. Ando, P. Dedecker, W. Verheijen, H. Mizuno, A. Miyawaki and J. Hofkens, Reversible single-molecule photoswitching in the GFP-like fluorescent protein Dronpa, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2005, 102, 9511–9516.
G. H. Patterson, J. Lippincott-Schwartz, A photoactivatable GFP for selective photolabeling of proteins and cells, Science, 2002, 297, 1873–1877.
J. Wiedenmann, S. Ivanchenko, F. Oswald, F. Schmitt, C. Röcker, A. Salih, K.-D. Spindler and G. U. Nienhaus, EosFP, a fluorescent marker protein with UV-inducible green-to-red fluorescence conversion, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2004, 101, 15905–15910.
K. A. Lukyanov, D. M. Chudakov, S. Lukyanov and V. V. Verkhusha, Photoactivatable fluorescent proteins, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2005, 6, 885–891.
G. Berkovic, V. Krongauz and V. Weiss, Spiropyrans and Spirooxazines for Memories and Switches, Chem. Rev., 2000, 100, 1741–1754.
M. Irie, Diarylethenes for memories and switches, Chem. Rev., 2000, 100, 1685–1716.
Y. Yokoyama, Fulgides for memories and switches, Chem. Rev., 2000, 100, 1717–1740.
M. Irie, T. Fukaminato, T. Sasaki, N. Tamai and T. Kawai, A digital fluorescent molecular photoswitch, Nature, 2002, 420, 759–760.
T. Fukaminato, T. Sasaki, T. Kawai, N. Tamai and M. Irie, Digital photoswitching of fluorescence based on the photochromism of diarylethene derivatives at a single-molecule level, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 14843–14849.
X. Sheng, A. Peng, H. Fu, Y. Liu, Y. Zhao, Y. Ma and J. Yao, Modulation of a fluorescence switch based on photochromic spirooxazine in composite organic nanoparticles, Nanotechnology, 2007, 18, 145707–145714.
Z. Tian, W. Wu and A. D. Q. Li, Photoswitchable fluorescent nanoparticles: preparation, properties and applications, ChemPhysChem, 2009, 10, 2577–2591.
S. Yamamoto, K. Matsuda and M. Irie, Absolute asymmetric photocyclization of a potochromic diarylethene derivative in single crystals, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2003, 42, 1636–1639.
T. Fukaminato, T. Umemoto, Y. Iwata, S. Yokojima, M. Yo-Neyama, S. Nakamura and M. Irie, Photochromism of diarylethene single molecules in polymer matrices, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 5932–5938.
S. F. Yan, V. Belov, M. Bossi and S. W. Hell, Switchable fluorescent and solvatochromic molecular probes based on 4-amino-N-methylphthalimide and a photochromic diarylethene, Eur. J. Org.Chem., 2008, 2531–2538.
Photochromism, ed. G. H. Brown, Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1971.
Photochromism: Molecules and Systems, ed. H. Dürr and H. Bouas-Laurent, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1990.
H. Duerr, Organische Photochromie, Angew. Chem., 2004, 116, 3404–4318.
A. Menju, K. Hayashi and M. Irie, Photoresponsive polymers. 3. Reversible solution viscosity change of poly(methacrylic acid) having spirobenzopyran pendant groups in methanol, Macromolecules, 1981, 14, 755–758.
V. I. Minkin, Photo-, thermo-, solvato- and electrochromic spiroheterocyclic compounds, Chem. Rev., 2004, 104, 2751–2776.
T. Minami, N. Tamai, T. Yamazaki and L. Yamazaki, Picosecond time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy of the photochromic reaction of spiropyran in Langmuir-Blodgett films, J. Phys. Chem., 1991, 95, 3988–3993.
J. L. Bahr, G. Kodis, L. de la Garza, S. Lin, A. L. Moore, T. A. Moore and D. Gust, Photoswitched singlet energy transfer in a porphyrin−spiropyran dyad, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2001, 123, 7124–7133.
M. Q. Zhu, L. Zhu, J. J. Han, W. Wu, J. K. Hurst and A. D. Q. Li, Spiropyran-based photochromic polymer nanoparticles with optically switchable luminescence, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 4303–4309.
L. Zhu, W. Wu, M. Q. Zhu, J. J. Han, J. K. Hurst and A. D. Q. Li, Reversibly photoswitchable dual-color fluorescent nanoparticles as new tools for live-cell imaging, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 3524–3526.
M. Bossi, V. Belov, S. Polyakova and S. W. Hell, Reversible red fluorescent molecular switch, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2006, 45, 7462–7465.
J. Fölling, S. Polyakova, V. Belov and A. van Blaaderen, et al., Synthesis and characterization of photoswitchable fluorescent silica nanoparticles, Small, 2008, 4, 134–142.
A. S. Dvornikov and P. M. Rentzepis, Photochromism: non-linear picosecond kinetics and 3D computer memory, Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst., 1994, 246, 379–388.
M. Heilemann, E. Margeat, R. Kasper, M. Sauer and P. Tinnefeld, Carbocyanine dyes as efficient reversible single-molecule optical switch, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 3801–3806.
J. Vogelsang, T. Cordes and P. Tinnefeld, Single-molecule photophysics of oxazines on DNA and its application in a FRET switch, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2009, 8, 486–492.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is part of a themed issue on synthetic and natural photoswitches.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seefeldt, B., Kasper, R., Beining, M. et al. Spiropyrans as molecular optical switches. Photochem Photobiol Sci 9, 213–220 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1039/b9pp00118b
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b9pp00118b