Abstract
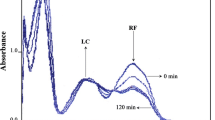
The photolysis of formylmethylflavin (FMF), a major intermediate in the photodegradation sequence of riboflavin, has been carried out in water (pH 7.0) and in several organic solvents. FMF produces lumichrome (LC) in organic solvents and LC and lumiflavin (LF) in aqueous solution. FMF and its photoproducts have been analysed using a specific multicomponent spectrophotometric method. FMF undergoes a bimolecular redox reaction on photolysis. The second-order rate constants for the reaction range from 0.66 (chloroform) to 2.44 M−1 s−1 (water) and are a linear function of the solvent dielectric constant. A plot of ln k against 1/e is linear for the reactions in 1-butanol, 1-propanol, ethanol, methanol, acetonitrile and water (e ~ 17–79) and non-linear in chloroform and dichloroethane (e ~ 5–10) suggesting a change in reaction mechanism in the two regions. This may be explained on the basis of the existence of a dipolar intermediate along the reaction pathway. The rate of photolysis is governed by the solvation of the intermediate and is thus influenced by the dielectric constant of the medium. The solvent effect on the rate of photolysis of FMF has been expressed in terms of the solvent acceptor number. A linear relationship has been found between ln k and the solvent acceptor number.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. C. Smith, and D. E. Metzler, The photochemical degradation of riboflavin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1963, 85, 3285–3288.
W. M. Moore, J. T. Spence, F. A. Raymond, and S. D. Colson, Photochemistry of riboflavin. 1. The hydrogen transfer process in the anaerobic photobleaching of flavins, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1963, 85, 3367–3372.
W. L. Cairns, and D. E. Metzler, Photochemical degradation of flavins. VI. A new photoproduct and its use in studying the photolytic mechanism, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1971, 93, 2772–2777.
P. F. Heelis, The photophysical and photochemical properties of flavins (isoalloxazines), Chem. Soc. Rev., 1982, 11, 15–39.
I. Ahmad, Q. Fasihullah, A. Noor, I. A. Ansari, Q. N. M. Ali, Photolysis of riboflavin in aqueous solution: a kinetic study, Int. J. Pharm., 2004, 280, 199–208.
I. Ahmad, Q. Fasihullah, F. H. M. Vaid, A study of simultaneous photolysis and photoaddition reactions of riboflavin in aqueous solution, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B, 2004, 75, 13–20.
I. Ahmad, Q. Fasihullah, F. H. M. Vaid, Effect of phosphate buffer on photodegradation reactions of riboflavin in aqueous solution, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B, 2005, 78, 229–234.
P. S. Song, and D. E. Metzler, Photochemical degradation of flavins. IV. Studies, on the anaerobic photolysis of riboflavin, Photochem. Photobiol., 1967, 6, 691–709.
G. E. Treadwell, W. L. Cairns, and D. E. Metzler, Photochemical degradation of flavins. V. Chromatographic studies of the products of photolysis of riboflavin, J. Chromatogr., 1968, 35, 376–388.
I. Ahmad, H. D. C. Rapson, Multicomponent spectrophotometric assay of riboflavin and photoproducts, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 1990, 8, 217–223.
W. M. Moore, and R. C. Ireton, The photochemistry of riboflavin - V. The, photodegradation of isoalloxazines in alcoholic solvents, Photochem. Photobiol., 1977, 25, 347–356.
I. Ahmad, H. D. C. Rapson, P. F. Heelis, and G. O. Phillips, Alkaline hydrolysis of 7,8-dimethyl-10-(formylmethyl) isoalloxazine. A kinetic study, J. Org. Chem., 1980, 45, 731–733.
P. F. Heelis, G. O. Phillips, I. Ahmad, H. D. C. Rapson, The photodegradation of formylmethylflavin - a steady state and laser flash photolysis study, Photobiochem. Photobiophys., 1980, 1, 125–130.
H. Heitele, Dynamic solvent effects on electron transfer reactions, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2003, 32, 359–377.
A. J. Parker, Rates of reaction in protic and dipolar aprotic solvents, Chem. Rev., 1969, 69, 1–32.
E. Buncel, R. A. Stairs and and H. Wilson, The Role of the Solvent in Chemical Reactions, Oxford University Press, New York, 2003.
A. Pross, Theoretical and Physical Principles of Organic Reactivity, Wiley, New York, 1995, pp. 196–218.
C. Reichardt, Solvents and Solvent Effects in Organic Chemistry, VCH Publishers, New York, 2nd edn, 1988.
K. J. Laidler, Chemical Kinetics, Harper & Row, New York, 3rd edn, 1987, pp. 183–195.
R. Schmidt and V. N. Sapunov, Non-Formal Kinetics, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, 1982, pp. 123–154.
E. S. Amis and J. F. Hinton, Solvent Effects on Chemical Phenomena, Academic Press, New York, 1973.
E. M. Kosower, An Introduction to Physical Organic Chemistry, Wiley, New York, 1968, pp. 259–386.
F. Wilkinson, Chemical Kinetics and Reaction Mechanisms, Van Nostrand Reinhold, London, 1980, pp. 142–143.
M. M. Amiji and B. J. Sandmann, Applied Physical Pharmacy, McGraw-Hill, New York, 2003, pp. 262–264.
Martin’s Physical Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, ed. P. J. Sinko, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, 2006, 4th edn, pp. 415–416.
J. T. Carstensen, Drug Stability Principles and Practices, Marcel Dekker, 1990, pp. 79–80.
K. A. Connors, G. L. Amidon and V. J. Stella, Chemical Stability of Pharmaceuticals, Wiley, New York, 2nd edn, 1986, pp. 38–41.
I. Racz, Drug Formulation, Wiley, New York, 1989, pp. 134–142.
P. S. Song, in Flavins and Flavoproteins, ed. H. Kamin, University Park Press, Baltimore, 1971, pp. 37–61.
M. Green, and G. Tollin, Flash photolysis of flavins.1. Photoreduction in non-aqueous solvents, Photochem. Photobiol., 1968, 7, 129–143.
W. E. Kurtin, M. A. Latino, and P. S. Song, A study of photochemistry of flavins in pyridine and with a donor, Photochem. Photobiol., 1967, 6, 247–259.
V. Szczesna and J. Koziol, in Flavins and Flavoproteins-Physicochemical Properties and Function, ed. W. Ostrowski, Polish Scientific Publishers, Warsaw, 1977, pp. 117–126.
I. Ahmad, and G. Tollin, Solvent effects on flavin electron reactions, Biochemistry, 1982, 20, 5925–5928.
H. H. Fall, and H. G. Petering, Metabolic inhibitors. 1. 6,7-Dimethyl-9-formylmethylisoalloxazine, 6,7-dimethyl-9-(2-hydroxyethyl)-isoalloxazine and derivatives, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1956, 78, 377–381.
C. Fukumachi, and Y. Sakurai, Vitamin B2 photolysis. V. The, photolytic formation of 6,7-dimethylflavin-9-acetic acid ester from riboflavin, Vitamins (Kyoto), 1954, 7, 939–943.
I. Ahmad, Q. Fasihullah, F. H. M. Vaid, Effect of light intensity and wavelengths on photodegradation reactions of riboflavin in aqueous solution, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B, 2006, 82, 21–27.
C. G. Hatchard, and C. A. Parker, A new sensitive chemical actinimeter. II. Potassium, ferrioxalate as a standard chemical actinometer, Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A, 1956, A 235, 518–536.
E. Sikorska, D. R. Worrall, J. I. Bourdelande, and M. Sikorski, Photophysics of lumichrome and its analogs, Pol. J. Chem., 2003, 77, 65–73.
Pharmaceutics The Science of Dosage Form Design, ed. M. E. Aulton, Churchill Livigstone, London, 2nd edn, 2002, pp. 104–105.
V. Guttman, The Donor–Acceptor Approach to Molecular Interactions, Plenum Press, New York, 1978.
M. M. McBride, and D. E. Metzler, Photochemical degradation of flavins. III. Hydroxyethyl, and formylmethyl analogs of riboflavin, Photochem. Photobiol., 1967, 6, 113–123.
M. M. McBride, and W. M. Moore, The photochemistry of riboflavin. II. Polarographic, studies on the hydroxyethyl and formylmethyl analogs of riboflavin, Photochem. Photobiol., 1967, 6, 103–113.
W. M. Moore, C. Baylor, Jr., Photochemistry of riboflavin. IV. Photobleaching of some nitrogen-9-substituted isoalloxazines and flavines, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1969, 91, 7170–7179.
B. G. Barman, and G. Tollin, Kinetics and equilibriums in partially reduced flavin solutions, Biochemistry, 1972, 11, 4760–4765.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, I., Fasihullah, Q. & Vaid, F.H.M. Photolysis of formylmethylflavin in aqueous and organic solvents. Photochem Photobiol Sci 5, 680–685 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1039/b602917e
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b602917e