Abstract
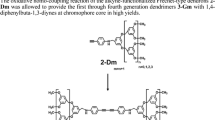
A new poly(amidoamine) dendrimer from second generation whose periphery comprises sixteen fluorescent 4-N,N-dimethylaminoethylamino-1,8-naphthalimide units has been synthesized and characterized. In DMF, the dendrimer shows sensitivity to the presence of Cu2+, Fe3+ and protons. The changes in the fluorescence intensity of the material are in opposite directions if acids or metals are present. Fluorescence enhancements (FE from 5 to 9 depending on solvent) are recorded when the photoinduced electron transfer (PET) originating from the donating amine to the electron accepting naphthalimide is inhibited by the protonation of the N,N-dimethylamino groups. In the case of Cu2+ cations, a fluorescence quenching (FQ of 6) is first observed, followed by fluorescence partial restoration. In the Fe3+ case, the same behaviour is observed with a final FE of 2. The successive complexations of these cations by the dendrimer core and by the external rim of the dendrimer may explain the results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Fischer, F. Vögtle, Dendrimers: from design to application - a progress report Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 1999 38 885–905 and references therein.
K. K. Inoue, Functional dendrimers, hyperbranched and star polymers Prog. Polym. Sci. 2000 25 453–571 and references therein.
F. Vögtle, S. Gesterman, R. Hesse, H. Schwierz and B. Windisch, Functional dendrimers Prog. Polym. Sci. 2000 25 987–1041 and references therein.
M. W. P. L. Baars and E. W. Meijer, Host-guest chemistry in dendritic molecules, Top. Curr. Chem., 2000, 210, pp. 131–182 and references therein.
V. Balzani, P. Ceroni, M. Maestri, Ch. Saudan, Luminescent dendrimers, recent advances Top. Curr. Chem. 2003 228 159–191 and references therein.
R. M. Crooks, B. I. Lemmon III, L. Sun, L. Yeung and M. Zhao, Dendrimer-encapsulated metals and semi-conductors: caracterisation and applications Top. Curr. Chem. 2001 212 81–135 and references therein.
D. A. Tomalia, H. Baker, J. Dewald, M. Hall, G. Kallos, S. Martin, J. Roeck, J. Ryder and P. Smith, A new class of polymers: starburst-dendritic macromolecules Polymer J. 1985 17 117–132.
I. Grabchev, X. Qian, V. Bojinov, Y. Xiao and W. Zhang, Synthesis and photophysical properties of 1,8-naphthalimide-labelled PAMAM as PET sensors of protons and transition metals Polymer 2002 43 5731–5736.
I. Grabchev, V. Bojinov, J.-M. Chovelon, Synthesis, photophysical and photochemical properties of fluorescent PAMAM dendrimers Polymer 2003 44 4421–4428.
I. Grabchev, J.-M. Chovelon and X. Qian, A polyamidoamine dendrimer with peripheral 1,8-naphthalimide groups capable of acting as a PET fluorescent sensor for metal cations New J. Chem. 2003 27 337–340.
I. Grabchev, J.-M. Chovelon, V. Bojinov and G. Ivanova, Poly(amidoamine) dendrimers peripherally modified by 4-ethylamino-1,8-naphthalimide Tetrahedron 2003 59 9591–9598.
I. Grabchev, X. Qian, Y. Xiao and W. Zhang, Heterogeneous PET fluorescent sensors selective for transition metal ions or protons:polymers labelled with naphthalimides New J. Chem. 2002 26 920–925.
E. Martin, R. Weigand and A. Pardo, Solvent dependence of the inhibition of intramolecular charge-transfer in N-substituted 1,8-naphthalimide derivatives as dye lasers J. Lumin. 1996 68 157–164.
V. Gruzinskii, A. Kukhto and G. Shakkah, Spectra of lasing efficiency in lasers with solutions of complex organic compounds J. Appl. Spectr. 1998 65 463–465.
S.-C. Chang, B. Archer, R. Utecht, D. Levis, M. Judy and J. Matthews, 4-alkylamino-3-bromo-N-alkyl-1,8-naphthalimides: new photochemically activable antiviral compounds Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1993 3 555–556.
A. D. Andricopulo, R. A. Yunes, F. Cechinel, C. Valdir, R. Correa, F. Willain, S. Arnaldo, R. S. Adair and R. J. Nunes, Synthesis and analgesic properties of cyclic imides: Naphthalimide and bis-Naphthalimide derivatives Acta Farm. Bonaerenes 1998 17 219–224.
I. Grabchev, I. Moneva, V. Bojinov and S. Guittonneau, Synthesis and properties of fluorescent 1,8-naphthalimide dyes for liquid crystals J. Mater. Chem 2000 10 1291–1296.
I. Grabchev and I. Moneva, Synthesis and properties of vinylic copolymers with fluorescent moieties as optical brighteners for liquid crystals J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999 74 151–157.
V. Bojinov and T. Konstantinova, Synthesis of polymerizable 1,8-naphthalimide dyes containing hindered amine fragment Dyes Pigm. 2002 54 239–245.
S. Yang, F. Meng, H. Tian and K. Chen, Photostability of novel copolymers functionalized with laser dyes based on modified rhodamine 6G and 1,8-naphthalimide Eur. Polym. J. 2002 38 911–919.
A. Kamal, B. S. Narayan Reddy, G. Reddy and G. Ramesh, Design and synthesis of C-8 linked pyrrolobenzodiazepine-naphthalimide hybrids as anti-tumour agents Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002 12 1933–1935.
A. P. de Silva, H. Q. N. Gunaratne, J.-L. Habib-Jiwan, C. P. McCoy, T. E. Rice, J. Ph. Soumillion, New fluorescent model compounds for the study of photoinduced electron transfer: the influence of molecular electric field in the excited state Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 1995 34 1728–1731.
K. A. Mitchell, R. G. Brown, Y. Dongwu, S.-C. Chang, R. Utecht and D. E. Lewis, A fluorescent sensor for Cu2+ at the sub-ppm level J. Photochem. Photobiol., A 1998 115 157–161.
B. Ramachamdram, N. B. Sankaran, R. Karmakar, S. Saha and A. Samanta, Fluorescence signalling of transition metal ions by multicomonent systemes comprising 4-chloro-1,8-naphthalimide as fluorophore Tetrahedron 2000 56 7041–7044.
A. P. de Silva and T. E. Rice, Small supramolecular system emulates unidirectional, path-selective photoinduced electron transfer (PET) of bacterial photosynthetic reaction center Chem. Commun. 2001 163–164.
T. Mayr, D. Wencel; and T. Werner, Fluorimetric determination of copper(ii) in aqueous solution using lucifer yellow CH as selective metal reagent Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem. 2001 371 44–48.
T. Gunnlaugsson, T. Clive Lee and R. Parkesh, A highly selective and sensitive fluorescent PET (photoinduced electron transfer) chemosensor for Zn(ii) Org. Biomol. Chem. 2003 1 3265–3267.
A. P. de Silva, A. Goligher, H. Q. N. Gunaratne and T. E. Rice, The pH-dependent fluorescence of pyridylmethyl-4-amino-1,8-naphthalimides ARKIVOC 2003 vii 229–243.
T. Gunnlaugsson, C. McCoy, R. J. Morrow, C. Phelan and F. Stomeo, Towards the development of controllable and reversible ‘on-off’ luminescence switching in soft-matter; synthesis and spectroscopic investigation of 1,8-naphthalimide-based PET (photoinduced electron transfer) chemosensors for pH in water-permeable hydrogels ARKIVOC 2003 vii 216–228.
A. W. Varnes, R. B. Dodson and E. L. Wehry, Interactions of transition-metal ions with photoexcited states of flavines. Fluorescence quenching studies J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972 94 946–950.
K. Rurack, U. Resch, M. Senoner and S. Daehne, A new fluorescence probe for trace metal ions: Cation-dependent spectroscopic properties J. Fluoresc. 1993 3 141–143.
J. A. Kemlo and T. M. Sheperd, Quenching of excited singlet states by metal ions Chem. Phys. Lett. 1977 47 158–162.
I. Grabchev, J. M. Chovelon and X. Qian, A copolymer of 4-N,N-dimethylaminoethylene N-allyl-1,8-naphthalimide with methylmethacrylate as selective fluorescent chemosensor in homogeneous systems for metal cations J. Photochem. Photobiol., A 2003 158 37–43.
Y. Xiao and X. Qian, Fluoroionophores with a peri effect and strong electron donating receptors: TICT promoted PET and signaling response to transition cations Tetrahedron Lett. 2003 44 2087–2091.
D. Eaton, Reference materials for fluorescence measurements Pure Appl. Chem. 1998 60 1107–1114.
B. Ramachamdram, G. Saroja, N. B. Sankaran and A. Samanta, Unusually high fluorescence enhancement of 1,8-naphthalimides derivatives by transition metals J. Phys. Chem. B 2000 104 11824–11832.
T. C. Barros, P. Berci Filho, V. G. Toscano and M. J. Politi, Intramolecular excimer formation from 1,8-N-alkyldinaphthalimides J. Photochem. Photobiol., A 1995 89 141–146.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grabchev, I., Soumillion, JP., Muls, B. et al. Poly(amidoamine) dendrimer peripherally modified with 4-N,N-dimethylaminoethyleneamino-1,8-naphthalimide as a sensor of metal cations and protons. Photochem Photobiol Sci 3, 1032–1037 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1039/b412384k
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b412384k