Abstract
Phytochrome (phy), a 124 kDa biliprotein, mediates plants’ perception of environmental light conditions including quantity, quality and duration of light. The complex phenomenology of phy function is connected with its polymorphism, the major phys being phyA and phyB. PhyA mediates irreversible photoresponses in the very low and high fluence ranges (VLFR and HIR) primarily in the far-red (FR) spectral region, whereas phyB mediates the ‘classical’ R/FR reversible responses in the low fluence range (LFR). This phyA specificity is determined at the level of (i) intramolecular events, (ii) turnover, phyA being light-labile, and (iii) nuclear–cytoplasmic partitioning and interaction with partner proteins. A unique feature of phyA is that two native isoforms, phyA′ and phyA″, comprise it, distinguished by spectroscopic and photochemical properties, localization and abundance in plant tissues, light stability, and other properties. They differ by the post-translational modification at the 6 kDa N-terminus, possibly phosphorylation, phyA′ being phosphorylated and phyA″ dephosphorylated. Both species participate in the light-induced nuclear–cytoplasmic partitioning. The light-labile phyA′ is responsible for de-etiolation (VLFR and HIR modes), whereas the relatively more light-stable phyA″ could be active throughout the whole life cycle. PhyA″ interferes with the action of phyA′ and this interaction may be part of the fine tuning mechanism of the phyA function. Finally, within the phyA′ pool there are different conformers in thermal equilibrium, that differ by the activation and kinetic parameters of the Pr → lumi-R photoreaction. This heterogeneity of phyA may account, at least partially, for the complex dynamics of its photoprocesses and the phenomenology of photoresponses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FL:
-
full-length phytochrome
- FR:
-
far-red light
- FRc:
-
constant FR
- FRp:
-
pulsed FR
- HIR:
-
high irradience responses
- GFP:
-
green fluorescent protein
- LFR:
-
low fluence responses
- lumi-R:
-
primary product of Pr photoexcitation
- NA:
-
N-terminally truncated phytochrome
- PCB:
-
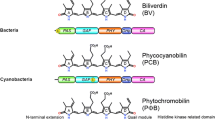
phycocyanobilin
- PΦB:
-
phytochromobilin
- phy:
-
phytochrome
- phyA:
-
phytochrome A
- phyA’ and phyA″:
-
isoforms of phyA
- phyB:
-
phytochrome B
- Pfr:
-
far-red light-absorbing phy form
- Pr:
-
red light-absorbing phy form
- Pr’:
-
Pr″
- Pr*:
-
Pr cycled through Pfr
- R:
-
red light
- Rc:
-
constant R
- Rp:
-
pulsed R
- VLFR:
-
very low fluence responses
- WT:
-
wild type.
References
Special issue, Photomorphogenesis, Plant Cell Environ., ed. H. Smith, 1997, 20, 657–844.
A. Cashmore, J. A. Jarillo, Y. J. Wu and D. Liu, Cryptochromes: blue light receptors for plants and animals, Science, 1999, 284, 760–765.
A. Batschauer, Light perception in higher plants, Cell Mol. Life Sci., 1999, 55, 153–166.
J. M. Christie and W. R. Briggs, Blue light sensing in higher plants, J. Biol. Chem., 2001, 276, 11457–11460.
M. Furuya and E. Schäfer, Photoperception and signaling of induction reactions by different phytochromes, Trends Plant Sci., 1996, 1, 301–307.
H. Smith, Phytochromes and light signal perception by plants–an emerging synthesis, Nature, 2000, 407, 585–591.
P. H. Quail, The phytochrome family: Dissection of functional roles and signaling pathways among family members, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London, Ser. B, 1998, 14, 257–271.
P. H. Quail, Phytochrome photosensory signaling networks, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2002, 3, 85–93.
J. J. Casal, Phytochromes, cryptochromes, phototropin: Photoreceptor interactions in plants, Photochem. Photobiol., 2000, 71, 1–11.
M. M. Neff, C. Fankhauser and J. Chory, Light: an indicator of time and place, Genes Dev., 2000, 14, 257–271.
C. Fankhauser, The phytochromes, a family of red/far-red absorbing photoreceptors, J. Biol. Chem., 2001, 276, 11453–11456.
P.-S. Song, Inter-domain signal transduction within the phytochromes, J. Biochem. Mol. Biol., 1999, 32, 215–225.
C.-M. Park, S.-H. Bhoo and P.-S. Song, Interdomain crosstalk in the phytochrome molecules, Semin. Cell Dev. Biol., 2000, 11, 449–456.
P. H. Quail, An emerging molecular map of the phytochromes, Plant Cell Environ., 1997, 20, 657–665.
T. Matsushita, M. Mochizuki, A. Nagatani, Dimers of the N-terminal domain of phytochrome B are functional in the nucleus, Nature, 2003, 424, 571–574.
W. Gärtner and S. E. Braslavsky, The phytochromes: spectroscopy and function, in Photoreceptors and Light Signalling, ed. A. Batschauer, Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, in press.
V. A. Sineshchekov, Photobiophysics and photobiochemistry of the heterogeneous phytochrome system, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1995, 1228, 125–164.
T. Shinomura, K. Uchida and M. Furuya, Elementary responses of photoperception by phytochrome A for high irradiance response of hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis thaliana, Plant Physiol., 2000, 122, 147–156.
K.-C. Yeh and J. C. Lagarias, Eukaryotic phytochromes: Light-regulated serine/threonine protein kinases with histidine kinase ancestry, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1998, 95, 13976–13981.
V. N. Lapko, X. Y. Jiang, D. L. Smith and P. S. Song, Mass spectrometric characterization of oat phytochrome A: isoforms and posttranslational modifications, Protein Sci., 1999, 8, 1032–1044.
H. G. Neuhaus, C. Bowler, R. Kern and N. H. Chua, Calcium/calmodulin-dependent and -independent phytochrome signal transduction pathways, Cell, 1993, 73, 937–952.
H. Okamoto, M. Matsui and X. W. Deng, Overexpression of the heterotrimeric G-protein alpha-subunit enhances phytochrome-mediated inhibition of hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis, Plant Cell, 2001, 13, 1639–1652.
H. Guo, T. Mockler, H. Duong and C. Lin, SUB1, an Arabidopsis Ca2+-binding protein involved in cryptochrome and phytochrome coaction, Science, 2001, 291, 487–490.
R. E. Kendrick and G. H. M. Kronenberg, Photomorphogenesis in Plants, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2nd edn., 1994.
R. Yamaguchi, M. Nakamura, N. Mochizuki, S. A. Kay and A. Nagatani, Light-dependent translocation of a phytochrome B-GFP fusion protein to the nucleus in transgenic Arabidopsis, J. Cell Biol., 1999, 145, 437–445.
F. Nagy, S. Kircher and E. Schäfer, Intracellular trafficking of photoreptors during light-induced signal transduction in plants, J. Cell Sci., 2000, 114, 475–480.
M. Ni, J. M. Tepperman and P. H. Quail, PIF3, a phytochrome-interacting factor necessary for normal photoinduced signal transduction, is a novel helix–loop–helix protein, Cell, 1998, 95, 657–667.
J. F. Martínez-García, E. Huq, P. H. Quail, Direct targeting of light signals to a promoter element-bound transcriptional factor, Science, 2000, 288, 859–863.
Y. Zhu, J. M. Tepperman, C. D. Fairchild and P. H. Quail, Phytochrome B binds with greater apparent affinity than phytochrome A to the basic helix–loop–helix factor PIF3 in a reaction requiring the PAS domain of PIF3, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2000, 97, 13419–13424.
P. H. Quail, Phytochrome-interacting factors, Semin. Cell Dev. Biol., 2000, 11, 457–466.
X.-W. Deng and P. H. Quail, Signaling in light-controlled development, Semin. Cell Dev. Biol., 1999, 10, 121–129.
C. Fankhauser and J. Chory, Light receptor kinases in plants!, Curr. Biol., 1999, 9, R123–R126.
H. Wang and X. W. Deng, Phytochrome Signaling Mechanism, The Arabidopsis Book ed. C. R. Somerville and E. M. Meyerowitz, American Society of Plant Biologists, Rockville, MD, 2002, pp. 1–30, DOI: 10.1199/tab.0009, http://www.aspb.org/publications/arabidopsis/.
H. Wang and X. W. Deng, Dissecting the phytochrome A-dependent signaling network in higher plants, Trends Plant Sci., 2003, 8, 172–178.
P. D. Cerdán, R. J. Staneloni, J. J. Casal and R. A. Sánchez, A 146 bp fragment of the tobacco Lhcb 1*2 promoter confers very-low-fluence, low-fluence and high-irradience responses of phytochrome to a minimal CaMV 35S promoter, Plant Mol. Biol., 1997, 33, 245–255.
J. Chory, M. Chatterjee, R. K. Cook, T. Elich, C. Fanhauserr, J. Li, P. Nagpal, M. Neff, A. Pepper, D. Poole, J. Reed and V. Vitart, From seed germination to flowering, light controls plant development via the pigment phytochrome, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1996, 93, 12066–12071.
J. Brockman and E. Schäfer, Analysis of Pfr destruction in Amarantus caudatus L.–evidence for two pools of phytochrome, Photochem. Photobiol., 1982, 35, 555–558.
L. H. Pratt, Distribution and localization of phytochrome within the plant, in Photomorphogenesis in Plants ed. R. E. Kendrick and G. H. M. Kronenberg, Martinus Nijhoff, Dordrecht, 1994, pp. 163–186.
J. G. Tokuhisa, S. M. Daniels and P. H. Quail, Phytochrome in green tissues: spectral and immunochemical evidence for two distinct molecular species of phytochrome in light-grown, Avena sativa L., Planta, 1985, 164, 321–332.
V. A. Sineshchekov and A. V. Sineshchekov, Fluorescence and absorption investigations of phytochrome in the cells of etiolated seedlings, Fiziol. Rast. (Russ.), 1987, 34, 730–741.
V. A. Sineshchekov and A. V. Sineshchekov, Fluorescence of phytochrome in the cells of dark-grown plants and its connection with the phototransformations of the pigment, Photochem. Photobiol., 1989, 49, 325–330.
R. A. Sharrock and P. H. Quail, Novel phytochrome sequences in Arabiddopsis thaliana: structure, evolution, and differential expression of a plant regulatory photoreceptor family, Genes Dev., 1989, 3, 1745–1757.
P. H. Quail, Phytochrome. A light-activated molecular switch that regulates plant gene expression, Ann. Rev. Genet., 1991, 25, 389–409.
R. C. Clough and R. D. Vierstra, Phytochrome degradation, Plant Cell Environ., 1997, 20, 713–721.
J. J. Casal and R. A. Sánchez, M. J. Yanovsky, The function of phytochrome A, Plant Cell Environ., 1997, 20, 813–819.
J. J. Casal, R. A. Sánchez and J. F. Botto, Modes of action of phytochromes, J. Exp. Bot., 1998, 49, 127–138.
J. J. Casal, S. J. Davis, D. Kirchenbauer, A. Viczian, M. J. Yanovsky, R. C. Clough, S. Kircher, E. T. Jordan-Beebe, E. Schäfer, F. Nagy and R. D. Vierstra, The serine-rich N-terminal domain of oat phytochrome A helps regulate light responses and subnuclear localization of the photoreceptor, Plant Physiol., 2002, 129, 1127–1137.
G. C. Whitelam and P. F. Devlin, Roles of different phytochromes in Arabidopsis photomorphogenesis, Plant Cell Environ, 1997, 20, 752–758.
P. H. Quail, M. T. Boylan, B. M. Parks, T. W. Short, Y. Xu and D. Wagner, Phytochromes: photosensory perception and signal transduction, Science, 1995, 268, 675–680.
T. Shinomura, A. Nagatani, H. Hanzawa, M. Kubota, M. Watanabe and M. Furuya, Action spectra for phytochrome A- and B-specific photoinduction of seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1996, 93, 8129–8133.
J. F. Botto, R. A. Sánchez, G. C. Whitelam and J. J. Casal, Phytochrome A mediates the promotion of seed germination by very low fluences of light and canopy shade light in Arabidopsis, Plant Physiol., 1996, 110, 439–444.
A. C. McCormac, H. Smith and G. C. Whitelam, Photoregulation of germination in seed of transgenic lines of tobacco and Arabidopsis which express an introduced cDNA encoding phytochrome A or phytochrome B, Planta, 1993, 191, 386–393.
J. J. Casal and R. A. Sánchez, Phytochromes and seed germination, Seed Sci. Res., 1998, 8, 317–329.
M. A. Mazzella, T. M. Alconada Magliano and J. J. Casal, Dual effect of phytochrome A on hypocotyl growth under continuous red light, Plant Cell Environ., 1997, 20, 261–267.
S. Jackson and B. Thomas, Photoreceptors and signals in the photoperiodic control of developments, Plant Cell Environ., 1997, 20, 790–795.
H. Smith and G. C. Whitelam, The shade avoidance syndrome: multiple responses mediated by multiple phytochromes, Plant Cell Environ., 1997, 20, 840–844.
R. P. Hangarter, Gravity, light and plant form, Plant Cell Environ., 1997, 20, 796–800.
B. M. Parks, P. H. Quail and R. P. Hangarter, Phytochrome A regulates red-light induction of phototropic enhancement in Arabidopsis, Plant Physiol., 1996, 110, 155–162.
A. K. Janoudi, W. R. Gordon, D. Wagner, P. Quail and K. L. Poff, Multiple phytochromes are involved in red-light-induced enhancement of first positive phototropism in Arabidopsis thaliana, Plant Physiol., 1997, 113, 975–979.
E. Adam, L. Kozma-Bognar, E. Schäfer and F. Nagy, Tobacco phytochromes: genes, structure and expression, Plant Cell Environ., 1997, 20, 678–684.
J. W. Reed, P. Nagpal, D. S. Poole, M. Furuya and J. Chory, Mutations in the gene for the red/far-red light receptor phytochrome B alter cell elongation and physiological responses throughout Arabidopsis development, Plant Cell, 1993, 5, 147–157.
B. M. Parks and E. P. Spalding, Sequential and coordinated action of phytochromes A and B during Arabidopsis stem growth revealed by kinetic analysis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1999, 96, 14142–14146. E. Spalding, personal communication.
M. Boylan and P. H. Quail, Phytochrome A overexpression inhibits hypocotyl elongation in transgenic Arabidopsis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1991, 88, 10806–10810.
R. J. Downs, Photorevesibility of flower initiation, Plant Physiol., 1956, 31, 279–284.
J. Chory and M. Furuya, The induction of seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana is regulated principally by phytochrome B and secondarily by phytochrome A, Plant Physiol., 1994, 104, 363–371.
M. M. Neff and J. Chory, Genetic interaction between phytochrome A, phytochrome B and cryptochrome 1 during Arabidopsis development, Plant Physiol., 1998, 118, 27–35.
H. Smith, Y. Xu and P. H. Quail, Antagonistic but complementary actions of phytochromes A and B allow optimum seedling de-etiolation, Plant Physiol., 1997, 114, 637–641.
P. F. Devlin, K. J. Halliday, N. P. Harber and G. C. Whitelam, The rosette habit of Arabidopsis thaliana is dependent upon phytochrome action: novel phytochromes control internode elongation and flowering time, Plant J., 1996, 10, 1127–1134.
C. D. Fairchild and P. H. Quail, The phytochromes: Photosensory perception and signal transduction, in Control of plant development: Genes and signals, ed. A. J. Greenland, E. M. Meyerowitz and M. W. Steer, Company of Biologists, Cambridge, 1998, pp. 85–92.
L. Hennig, C. Büche and E. Schäfer, Degradation of phytochrome A and the hight irradience response in Arabidopsis: a kinetic analysis, Plant Cell Environ., 2000, 23, 727–734.
C. D. Fairchild, M. A. Schumaker and P. H. Quail, HFR1 encodes an atypical bHLH protein that acts in phytochrome A signal transduction, Genes Dev., 2000, 14, 2377–2391.
D. Wagner, M. Koloszvari and P. H. Quail, Two small spatially distinct regions of phytochrome B are required for efficient signaling rates, Plant Cell, 1996, 8, 859–871.
R. C. Fry, J. Habashi, H. Okamoto and X. W. Deng, Characterization of a strong dominant phytochrome A mutation unique to phytochrome A signal propagation, Plant Physiol., 2002, 130, 457–465.
T. Kunkel, K. Tomizawa, R. Kern, M. Furuya and E. Schäfer, In vitro formation of a photoreversible adduct of phycocyanobilin and tobacco apophytochrome B, Eur. J. Biochem., 1993, 215, 587–594.
D. Wagner, J. M. Tepperman and P. H. Quail, Overexpression of phytochrome B induces a short hypocotyl phenotype in transgenic Arabidopsis, Plant Cell, 1991, 3, 1275–1288.
W. Gärtner, C. Hill, K. Worm, S. E. Braslavsky and K. Schaffner, Influence of expression system on chromophore binding and preservation of spectral properties in recombinant phytochrome A, Eur. J. Biochem., 1996, 236, 978–983.
T. Kunkel, G. Neuhaus, A. Batschauer, N.-H. Chua and E. Schäfer, Functional analysis of yeast-derived phytochrome A and B phycocyanobilin adducts, Plant J., 1996, 10, 625–636.
T. D. Elich and J. Chory, Biochemical characterization of Arabidopsis wild-type and mutant phytochrome B holoproteins, Plant Cell, 1997, 9, 2271–2280.
A. Remberg, A. Ruddat, S. E. Braslavsky, W. Gärtner and K. Schaffner, Chromophore incorporation, Pr to Pfr kinetics, and Pfr thermal reversion of recombinant N-terminal fragments of phytochrome A and B chromoproteins, Biochemistry, 1998, 37, 9983–9990.
A. Ruddat, P. Schmidt, C. Gatz, S. E. Braslavsky, W. Gärtner and K. Schaffner, Recombinant type A and B phytochromes from potato. Transient absorption spectroscopy, Biochemistry, 1997, 36, 103–111.
T. Kunkel, V. Speth, C. Büche and E. Schäfer, In vivo characterization of phytochrome-phycocyanin adducts in yeast, J. Biol. Chem., 1995, 270, 20193–202000.
M. Furuya, Molecular properties and biogenesis of phytochrome I and II, Adv. Biophys., 1989, 25, 133–167.
V. Sineshchekov, O. Ogorodnikova, A. Thiele and C. Gatz, Fluorescence and photochemical characterization of phytochromes A and B in transgenic potato expressing Arabidopsis phytochrome B, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol., 2001, 59, 139–146.
H. Hanzawa, T. Shinomura, K. Inomata, T. Kakiuchi, H. Kinoshita, K. Wada and M. Furuya, Structural requirement of bilin chromophore for the photosensory specificity of phytochromes A and B, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2002, 99, 4725–4729.
M. Ahmad, J. A. Jarillo, O. Smirnova and A. R. Cashmore, The CRY1 blue light receptor of Arabidopsis interacts with phytochrome A in vitro, Mol. Cell, 1998, 1, 939–948.
C. Fankhauser, K.-C. Yeh, J. C. Lagarias, H. Zhang, T. D. Elich and J. Chory, PKS1, a substrate phosphorylated by phytochrome that modulates light signaling in Arabidopsis, Science, 1999, 284, 1539–1541.
G. Choi, H. Yi, J. Lee, Y.-K. Kwon, M.-S. Soh, B. Shin, Z. Luka, T.-R. Hahn and P.-S. Song, Phytochrome signaling is mediated through nucleoside diphosphate kinase 2, Nature, 1999, 401, 610–613.
A. Colón-Carmona, D. L. Chen, K.-C. Yeh and S. Abel, Aux/IAA proteins are phosphorylated by phytochrome in vitro, Plant Physiol., 2000, 124, 1728–1738.
D.-H. Kim, J.-G. Kang, S.-S. Yang, K.-S. Chung, P.-S. Song and C.-M. Park, A phytochrome-associated protein phosphatase 2A modulates light signals in flowering time control in Arabidopsis, Plant Cell, 2002, 14, 3043–3056.
T. J. Campbell and E. Liscum, Plant Photobiology 2001, Plant Cell, 2001, 13, 1704–1710.
L. Kim, S. Kircher, R. Toth, E. Adam, E. Schäfer and F. Nagy, Light-induced nuclear import of phytochrome-A:GFP fusion proteins is differentially regulated in transgenic tobacco and Arabidopsis, Plant J., 2000, 22, 125–134.
J. Stockhaus, A. Nagatani, U. Halfter, S. Kay, M. Furuya and N. H. Chua, Genes Dev., 1992, 6, 2364–2372.
K. Emmler, J. Stockhaus, N.-H. Chua and E. Schäfer, An amino-terminal deletion of rice phytochrome A results in a dominant negative suppression of tobacco phytochrome A activity in transgenic tobacco seedlings, Planta, 1995, 197, 103–110.
E. T. Jordan, J. R. Cherry, J. M. Walker and R. D. Vierstra, The amino-terminus of phytochrome A contains two distinct functional domains, Plant J., 1995, 35, 660–664.
E. T. Jordan, J. M. Marita, R. C. Clough and R. D. Vierstra, Characterization of regions within the N-terminal 6-kilodalton domain of phytochrome A that modulate its biological activity, Plant Physiol., 1997, 115, 693–704.
K. Sakamoto and A. Nagatani, Nuclear localization activity of phytochrome B, Plant J., 1996, 10, 859–868.
S. Kircher, L. Kozma-Bognar, L. Kim, E. Adam, K. Harter, E. Schäfer and F. Nagy, Light quality-dependent nuclear import of the plant photoreceptors phytochrome-A and B, Plant Cell, 1999, 11, 1445–1456.
P. Gil, S. Kircher, E. Adam, E. Bury, L. Kozma-Bognar, E. Schäfer and F. Nagy, Photocontrol of subcellular partitioning of phytochrome-B:GFP fusion protein in tobacco seedlings, Plant J., 2000, 22, 135–145.
E. Huq, B. Al-Sady and P. Quail, Nuclear translocation of the photoreceptor phytochrome B is necessary for its biological function in seedling photomorphogenesis, Plant J., 2003, 35, 660–664.
A. Hisada, H. Hanzava, J. L. Weler, A. Nagatani, J. B. Reid and M. Furuya, Light-induced nuclear translocation of endogenous pea phytochrome A visualized by immunocytochemical procedures, Plant Cell, 2000, 12, 1063–1078.
F. Nagy and E. Schäfer, Phytochromes control photomorphogenesis by differentially regulated, interacting signaling pathways in higher plants, Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 2002, 53, 329–355.
M. J. Yanovsky, J. P. Luppi, D. Kirchbauer, O. B. Ogorodnikova, V. A. Sineshchekov, E. Adam, S. Kircher, R. J. Stanelini, E. Schäfer, F. Nagy, and J. J. Casal, Missense mutation in the PAS2 domain of phytochrome A impairs subnuclear localization and a subset of responses, Plant Cell, 2002, 14, 1591–1603.
K. Eichenberg, T. Kunkel, T. Kretsch, V. Speth and E. Schäfer, In vivo characterization of chimeric phytochromes in yeast, J. Biol. Chem., 1999, 274, 354–359.
R. C. Clough, E. T. Jordan-Beebe, K. N. Lohman, J. M. Marita, J. M. Walker, C. Gatz and R. D. Vierstra, Sequences within both the N- and C-terminal domains of phyA are required for Pfr ubiquitination and degradation, Plant J., 1999, 17, 155–67.
F. R. Cantón and P. H. Quail, Both phyA and phyB mediate light-imposed repression of PHYA gene expression in Arabidopsis, Plant Physiol., 1999, 121, 1207–1216.
M. J. Yanovsky, J. J. Casal and J. P. Luppi, The VLF loci, polymorphic between ecotypes Landsberg erecta and Columbia, dissected two branches of phytochrome A signaling pathways that correspond to the very-low fluence and high-irradience responses of phytochrome, Plant J., 1997, 12, 659–667.
M. J. Yanovsky, G. C. Whitelam and J. J. Casal, fhy3-1 retains inductive responses of phytochrome A, Plant Physiol., 2000, 123, 235–242.
J. J. Casal, M. J. Yanovsky and J. P. Luppi, Two photobiological pathways of phytochrome A activity, only one of which shows dominant negative suppression by phytochrome B, Photochem. Photobiol., 2000, 71, 481–486.
P. D. Cerdán, M. J. Yanovsky, F. C. Reymundo, A. Nagatani, R. J. Staneloni, G. C. Whitelam and J. J. Casal, Regulation of phytochrome B signaling by phytochrome A and FHY1 in Arabidopsis thaliana, Plant J., 1999, 18, 499–507.
P. D. Cerdán, R. J. Staneloni, J. Ortega, M. M. Bunge, M. J. Rodriguez-Batiller, R. A. Sánchez and J. J. Casal, Sustained but not transient phytochrome A signaling targets a region of an Lhcb1*2 promoter not necessary for phytochrome B action, Plant Cell, 2000, 12, 1203–1211.
M. Boylan, N. Douglas and P. H. Quail, Dominant negative suppression of Arabidopsis photoresponses by mutant phytochrome-A sequences identifies spatially discrete regulatory domains in the photoreceptor, Plant Cell, 1994, 6, 449–460.
V. Sineshchekov, O. Belyaeva and A. Sudnitsin, Phytochrome A positively regulates biosynthesis of the active protochlorophyllide in dicots under far-red light, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B: Biol., 2004, 74, 47–54.
P. Lariguet, H. E. Boccalandro, J. M. Alonso, J. R. Ecker, J. Chory, J. J. Casal and C. Fankhauser, A growth regulatory loop that provides homeostasis to phytochrome A signaling, Plant Cell, 2003, 12, 2966–2978.
M. Ahmad, J. A. Jarillo, O. Smirnova and A. R. Cashmore, The CRY1 blue light photoreceptor of Arabidopsis interacts with phytochrome A in vitro, Mol. Cell, 1998, 1, 939–948.
T. Hamasa, N. Tanaka, T. Noguchi, N. Kimura and K. Hasunuma, Phytochrome regulates phosphorylation of a protein with characteristics of a nucleoside diphosphate kinase in the crude membrane fraction from stem sections of etiolated pea seedlings, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B: Biol., 1996, 33, 143–151.
N. Tanaka, T. Ogura, T. Noguchi, H. Hirano, N. Yabe and K. Hasunuma, Phytochrome-mediated light signals are transduced to nucleoside diphoshate kinase in Pisum sativum L. cv. Alaska, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B: Biol., 1998, 45, 113–121.
T. Ogura, N. Tanaka, N. Yabe, S. Komatsu and K. Hasunuma, Characterization of protein complexes containing nucleoside diphosphate kinase with characteristics of light signal transduction through phytochrome in etiolated pea seedlings, Photochem. Photobiol., 1999, 69, 397–403.
J. Kim, H. Yi, J. Choi, B. Shin, P.-S. Song and J. Choi, Functional characterization of phytochrome interacting factor 3 in phytochrome mediated light signal transduction, Plant Cell, 2003, 15, 2399–2407.
C. Fankhauser and J. Chory, RSF1, an Arabidopsis locus implicated in phytochrome A signaling, Plant Physiol., 2000, 124, 39–45.
M. Hudson, C. Ringli, M. T. Boylan and P. H. Quail, The FAR1 locus encodes a novel nuclear protein specific to phytochrome A signaling, Genes Dev., 1999, 13, 2017–2027.
U. Hoecker, Y. Xu and P. H. Quail, SPA1: a new genetic locus involved in phytochrome A-specific signal transduction, Plant Cell, 1998, 10, 19–33.
U. Hoecker, J. M. Tepperman and P. H. Quail, SPA, a WD-repeat protein specific to phytochrome A signal transduction, Science, 1999, 284, 496–499.
Y. C. Zhou, M. Dieterle, C. Buche and T. Kretsch, The negatively acting factors EID1 and SPA1 have distinct functions in phytochrome A-specific light signaling, Plant Physiol., 2002, 128, 1098–108.
U. Hoecker, L. Baumgardt and S. Laubinder, Investigation of the functions of the SPA gene family, Plant Photobiology Meeting, Phillips-Universität, Marburg, 2003, Abstract 6.4.
M. Dieterle, Y.-C. Zhou, E. Schäfer, M. Funk and T. Kretsch, EID1, an F-box protein involved in phytochrome A-specific light signaling, Genes Dev., 2001, 15, 939–944.
X. L. Liu, M. F. Covington, C. Fankhauser, J. Chory and D. R. Wagner, ELF3 encodes a circadian clock-regulated nuclear protein that functions in an Arabidopsis PHYB signal transduction pathway, Plant Cell, 2001, 13, 1293–1304.
C. Fankhauser and D. Staiger, Photoreceptors in Arabidopsis thaliana: light perception, signal transduction and entrainment of the endogenous clock, Planta, 2002, 216, 1–16.
V. A. Sineshchekov, The system of phytochromes: photobiophysics and photobiochemistry in vivo, Membr. Cell Biol., 1998, 12, 691–720.
V. A. Sineshchekov, Phytochromes: molecular structure, photoreceptor process and physiological function, in Concepts in Photobiology: Photosynthesis and Photomorphogenesis, ed. G. S. Singhal, G. Renger, S. K. Sopory, K.-D. Irrgang, and Govindjee, Kluwer Acad. Publ., Boston–Dordrecht–London; Narosa Publ. House, Delhi–Madras–Calcutta–London; 1999, pp. 755–795.
V. A. Sineshchekov and A. V. Sineshchekov, Different photoactive states of the red phytochrome form in the cells of etiolated pea and oat seedlings, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B: Biol., 1990, 5, 197–217.
V. A. Sineshchekov, Two spectroscopically and photochemically distinguishable phytochromes in etiolated seedlings of monocots and dicots, Photochem. Photobiol., 1994, 59, 77–86.
V. A. Sineshchekov, Evidence for the existence of two phytochrome A populations, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B: Biol., 1995, 28, 53–55.
V. A. Sineshchekov, S. Frances and M. J. White, Fluorescence and photochemical characterization of phytochrome in de-etiolated pea mutant lip, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B: Biol., 1995, 28, 47–51.
V. A. Sineshchekov, A. G. Heyer and C. Gatz, Phytochrome states in transgenic potato plants with altered phyA levels, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B: Biol., 1996, 34, 137–142.
V. A. Sineshchekov, O. B. Ogorodnikova, P. F. Devlin and G. C. Whitelam, Fluorescence spectroscopy and photochemistry of phytochromes A and B in wild-type, mutant and transgenic strains of Arabidopsis thaliana, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B: Biol., 1997, 42, 133–142.
V. A. Sineshchekov, O. B. Ogorodnikova and J. L. Weller, Fluorescence and photochemical properties of phytochromes A and B in etiolated pea seedlings, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B: Biol., 1999, 49, 204–211.
V. Sineshchekov, L. Koppel’, L. Shlumukov, F. Barro, P. Barcelo, P. Lazzeri and H. Smith, Fluorescence and photochemical properties of phytochromes in wild-type wheat and a transgenic line over-expressing an oat phytochrome A (PHYA) gene: functional implications, Plant Cell Environ., 2001, 24, 289–1297.
V. Sineshchekov, J. Hughes, E. Hartmann and T. Lamparter, Fluorescence and photochemistry of recombinant phytochrome from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis, Photochem. Photobiol., 1998, 67, 263–267.
V. Sineshchekov, L. Koppel’, B. Esteban, J. Hughes and T. Lamparter, Fluorescence and photochemical investigations of the full-length (Cph1) and C-terminally truncated (Cph1delta2) recombinant phytochrome from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B: Biol., 2002, 67, 39–50.
V. Sineshchekov, L. Koppel’, J. Hughes, T. Lamparter and M. Zeidler, Recombinant phytochrome of the moss Ceratodon purpureus (CP2): fluorescence spectroscopy and photochemistry, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B. Biol., 2000, 56, 145–153.
L. Koppel’, H. Okamoto, M. Wada and V. Sineshchekov, Phytochrome in transgenic Arabidopsis overexpressing the fern Adiantum capillus-veneris PHY1: fluorescence spectroscopy and photochemistry, Program and Abstracts of European Symposium on Photomorphogenesis, P-25, Freie Universität Berlin, Berlin, March 21–26, 1999.
V. A. Sineshchekov and V. V. Akhobadze, Phytochrome states in etiolated pea seedlings: fluorescence and primary photoreactions at low temperatures, Photochem. Photobiol., 1992, 56, 743–749.
V. A. Sineshchekov, R. C. Clough, E. T. Jordan-Beebe and R. D. Vierstra, Fluorescence analysis of oat phyA deletion mutants expressed in tobacco suggests that the N-terminal domain determines the photochemical and spectroscopic distinctions between phyA′ and phyA″, Photochem. Photobiol., 1999, 69, 728–732.
V. Sineshchekov, L. Hennig, T. Lamparter, J. Hughes, W. Gärtner and E. Schäfer, Recombinant phytochrome A in yeast differs by its spectroscopic and photochemical properties from the major phyA′ and is close to the minor phyA″: evidence for post-translational modification of the pigment in plants, Photochem. Photobiol., 2001, 73, 692–696.
L. Koppel’ and V. Sineshchekov, Effect of a non-specific phosphatase inhibitor, PMSF, on the two phyA populations in roots of maize, Plant Photobiology Meeting, Phillips-Universität, Marburg, 2003, Abstract P10.
V. Sineshchekov and C. Fankhauser, PKS1 and PKS2 affect phyA state in etiolated Arabidopsis seedlings, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2004, 3 10.1039/b315431a/.
V. Sineshchekov, T. Lamparter and E. Hartmann, Evidence for the existence of membrane-associated phytochrome in the cell, Photochem. Photobiol., 1994, 60, 516–520.
A. Sudnitsin, E. Adam, F. Nagy, E. Schäfer and V. Sineshchekov, phyA-GFP is spectroscopically and photochemically close to phyA and comprises both phyA′ and phyA″, Plant Photobiology Meeting, Phillips-Universität, Marburg, 2003, Abstract P9.
A. G. Heyer, D. Mozley, V. Landschutze, B. Thomas and C. Gatz, Function of phytochrome A in Solanum tuberosum as revealed through the study of transgenic plants, Plant Physiol., 1995, 109, 53–61.
L. Shlumukov, F. Barro, P. Barcelo, P. Lazzeri and H. Smith, Establishment of far-red high irradiance responses in wheat through transgenic expression of an oat phytochrome A gene, Plant Cell Environ., 2001, 24, 703–712.
V. A. Sineshchekov and J. L. Weller, Two modes of the light-induced phytochrome A decline–with and without changes in the relative content of its native pools (phyA′ and phyA″): evidence from in situ fluorescence investigations of wild-type and mutant phyA-3D pea, J. Photochem. Photobiol., submitted.
J. L. Weller, S. L. Batge, J. J. Smith, L. H. J. Kerckhoffs, V. A. Sineshchekov, I. C. Murfet and J. B. Reid, A dominant mutation in the pea PHYA gene impairs light-dependent PHYA degradation, Plant Physiol., in press.
A. R. Hozwarth, E. Venuti, S. E. Braslavsky and K. Schaffner, The phototransformation process in Phytochrome. I. Ultrafast fluorescence component and kinetic models for the initial Pr → Pfr transformation steps in native phytochrome, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1992, 1140, 59–68.
M. E. Lippitsch, H. Riegler, F. R. Aussenegg, G. Hermann and E. Muller, Picosecond absorption and fluorescence studies on large phytochrome from rye, Biochem. Physiol. Pflanz., 1988, 183, 1–6.
P.-S. Song, B. R. Singh, N. Tamaui, T. Yamazaki, I. Yamazaki, S. Tokutomi and M. Furuya, Primary photoprocesses of phytochrome. Picosecond fluorescence kinetics of oat and pea phytochromes, Biochemistry, 1989, 28, 3265–3271.
M. J. Terry, J. L. Hall and B. Thomas, The association of type I phytochrome with wheat leaf plasma membranes, J. Plant Physiol., 1992, 140, 691–698.
T. Lamparter, P. Lutterbuse, H. A. W. Schneider-Poetsch and R. Hertel, A study of membrane-associated phytochrome: hydrophobicity test and native size determination, Photochem. Photobiol., 1992, 56, 697–707.
P. Schmidt, T. Gensch, A. Remberg, W. Gärtner, S. E. Braslavsky and K. Schaffner, The complexity of the Pr to Pfr phototransformation kinetics is an intrinsic property of native phytochrome, Photochem. Photobiol., 1998, 68, 754–761.
I. Michler and S. E. Braslavsky, Time-Resolved Thermodynamic Analysis of the Oat Phytochrome A Phototransformation. A Photothermal Beam Deflection Study, Photochem. Photobiol., 2001, 74, 624–635.
V. Sineshchekov, A. Sudnitsin, E. Adam, F. Nagy and E. Schäfer, unpublished results.
V. Sineshchekov and T. Lamparter, unpublished results.
L. Koppel’ and V. Sineshchekov, unpublished results.
V. Sineshchekov, O. Belyaeva and A. Sudnitsin, unpublished results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sineshchekov, V.A. Phytochrome A: functional diversity and polymorphism. Photochem Photobiol Sci 3, 596–607 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1039/b315430k
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b315430k