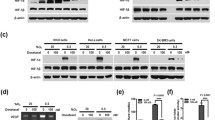
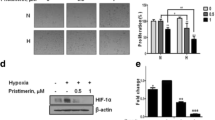
Abstract
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1), a transcription factor that is critical for tumor adaptation to microenvironmental stimuli, represents an attractive chemotherapeutic target. YC-1 is a novel antitumor agent that inhibits HIF-1 through previously unexplained mechanisms. In the present study, YC-1 was found to prevent HIF-1α and HIF-1β accumulation in response to hypoxia or mitogen treatment in PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Neither HIF-1α protein half-life nor mRNA level was affected by YC-1. However, YC-1 was found to suppress the PI3K/Akt/mTOR/4E-BP pathway, which serves to regulate HIF-1α expression at the translational step. We demonstrated that YC-1 also inhibited hypoxia-induced activation of nuclear factor (NF)-κB, a downstream target of Akt. Two modulators of the Akt/NF-κB pathway, caffeic acid phenethyl ester and evodiamine, were observed to decrease HIF-1α expression. Additionally, overexpression of NF-κB partly reversed the ability of wortmannin to inhibit HIF-1α-dependent transcriptional activity, suggesting that NF-κB contributes to Akt-mediated HIF-1α accumulation during hypoxia. Overall, we identify a potential molecular mechanism whereby YC-1 serves to reduce HIF-1 expression.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayala GE, Dai H, Ittmann M, Li R, Powell M, Frolov A et al. (2004). Growth and survival mechanisms associated with perineural invasion in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 64: 6082–6090.
Bilton RL, Booker GW . (2003). The subtle side to hypoxia inducible factor (HIFalpha) regulation. Eur J Biochem 270: 791–798.
Brown JM, Wilson WR . (2004). Exploiting tumour hypoxia in cancer treatment. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 437–447.
Chen EY, Mazure NM, Cooper JA, Giaccia AJ . (2001). Hypoxia activates a platelet-derived growth factor receptor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway that results in glycogen synthase kinase-3 inactivation. Cancer Res 61: 2429–2433.
Chiang PC, Chien CL, Pan SL, Chen WP, Teng CM, Shen YC et al. (2005). Induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis by a marine prostanoid in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 43: 679–686.
Chun YS, Yeo EJ, Choi E, Teng CM, Bae JM, Kim MS et al. (2001). Inhibitory effect of YC-1 on the hypoxic induction of erythropoietin and vascular endothelial growth factor in Hep3B cells. Biochem Pharmacol 61: 947–954.
Domingo-Domenech J, Mellado B, Ferrer B, Truan D, Codony-Servat J, Sauleda S et al. (2005). Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB in human prostate carcinogenesis and association to biochemical relapse. Br J Cancer 93: 1285–1294.
Figueroa YG, Chan AK, Ibrahim R, Tang Y, Burow ME, Alam J et al. (2002). NF-kappaB plays a key role in hypoxia-inducible factor-1-regulated erythropoietin gene expression. Exp Hematol 30: 1419–1427.
Fradet V, Lessard L, Begin LR, Karakiewicz P, Masson AM, Saad F . (2004). Nuclear factor-kappaB nuclear localization is predictive of biochemical recurrence in patients with positive margin prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10: 8460–8464.
Funasaka T, Yanagawa T, Hogan V, Raz A . (2005). Regulation of phosphoglucose isomerase/autocrine motility factor expression by hypoxia. FASEB J 19: 1422–1430.
Haddad JJ, Olver RE, Land SC . (2000). Antioxidant/pro-oxidant equilibrium regulates HIF-1alpha and NF-kappa B redox sensitivity. Evidence for inhibition by glutathione oxidation in alveolar epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 275: 21130–21139.
Hockel M, Vaupel P . (2001). Tumor hypoxia: definitions and current clinical, biologic, and molecular aspects. J Natl Cancer Inst 93: 266–276.
Huang DM, Guh JH, Huang YT, Chueh SC, Chiang PC, Teng CM . (2005a). Induction of mitotic arrest and apoptosis in human prostate cancer pc-3 cells by evodiamine. J Urol 173: 256–261.
Huang YT, Pan SL, Guh JH, Chang YL, Lee FY, Kuo SC et al. (2005b). YC-1 suppresses constitutive nuclear factor-kappaB activation and induces apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 4: 1628–1635.
Hudson CC, Liu M, Chiang GG, Otterness DM, Loomis DC, Kaper F et al. (2002). Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression and function by the mammalian target of rapamycin. Mol Cell Biol 22: 7004–7014.
Isaacs JS, Jung YJ, Neckers L . (2004). Aryl hydrocarbon nuclear translocator (ARNT) promotes oxygen-independent stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by modulating an Hsp90-dependent regulatory pathway. J Biol Chem 279: 16128–16135.
Jaakkola P, Mole DR, Tian YM, Wilson MI, Gielbert J, Gaskell SJ et al. (2001). Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von Hippel–Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science 292: 468–472.
Jung YJ, Isaacs JS, Lee S, Trepel J, Neckers L . (2003). IL-1beta-mediated up-regulation of HIF-1alpha via an NFkappaB/COX-2 pathway identifies HIF-1 as a critical link between inflammation and oncogenesis. FASEB J 17: 2115–2117.
Kallio PJ, Pongratz I, Gradin K, McGuire J, Poellinger L . (1997). Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha: posttranscriptional regulation and conformational change by recruitment of the Arnt transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 5667–5672.
Kaluzova M, Kaluz S, Lerman MI, Stanbridge EJ . (2004). DNA damage is a prerequisite for p53-mediated proteasomal degradation of HIF-1alpha in hypoxic cells and downregulation of the hypoxia marker carbonic anhydrase IX. Mol Cell Biol 24: 5757–5766.
Karni R, Dor Y, Keshet E, Meyuhas O, Levitzki A . (2002). Activated pp60c-Src leads to elevated hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha expression under normoxia. J Biol Chem 277: 42919–42925.
Kim I, Kim CH, Kim JH, Lee J, Choi JJ, Chen ZA et al. (2004). Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate and zinc inhibit proteasome-dependent proteolysis. Exp Cell Res 298: 229–238.
Ko FN, Wu CC, Kuo SC, Lee FY, Teng CM . (1994). YC-1, a novel activator of platelet guanylate cyclase. Blood 84: 4226–4233.
Koong AC, Chen EY, Giaccia AJ . (1994). Hypoxia causes the activation of nuclear factor kappa B through the phosphorylation of I kappa B alpha on tyrosine residues. Cancer Res 54: 1425–1430.
Kung AL, Wang S, Klco JM, Kaelin WG, Livingston DM . (2000). Suppression of tumor growth through disruption of hypoxia-inducible transcription. Nat Med 6: 1335–1340.
Lang KJ, Kappel A, Goodall GJ . (2002). Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha mRNA contains an internal ribosome entry site that allows efficient translation during normoxia and hypoxia. Mol Biol Cell 13: 1792–1801.
Laughner E, Taghavi P, Chiles K, Mahon PC, Semenza GL . (2001). HER2 (neu) signaling increases the rate of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) synthesis: novel mechanism for HIF-1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor expression. Mol Cell Biol 21: 3995–4004.
Lessard L, Begin LR, Gleave ME, Mes-Masson AM, Saad F . (2005). Nuclear localisation of nuclear factor-kappaB transcription factors in prostate cancer: an immunohistochemical study. Br J Cancer 93: 1019–1023.
Lessard L, Mes-Masson AM, Lamarre L, Wall L, Lattouf JB, Saad F . (2003). NF-kappa B nuclear localization and its prognostic significance in prostate cancer. BJU Int 91: 417–420.
Mabjeesh NJ, Escuin D, LaVallee TM, Pribluda VS, Swartz GM, Johnson MS et al. (2003). 2ME2 inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis by disrupting microtubules and dysregulating HIF. Cancer Cell 3: 363–375.
Manna SK, Aggarwal BB . (2000). Wortmannin inhibits activation of nuclear transcription factors NF-kappaB and activated protein-1 induced by lipopolysaccharide and phorbol ester. FEBS Lett 473: 113–118.
McCarty MF . (2004). Targeting multiple signaling pathways as a strategy for managing prostate cancer: multifocal signal modulation therapy. Integr Cancer Ther 3: 349–380.
McEleny K, Coffey R, Morrissey C, Fitzpatrick JM, Watson RW . (2004). Caffeic acid phenethyl ester-induced PC-3 cell apoptosis is caspase-dependent and mediated through the loss of inhibitors of apoptosis proteins. BJU Int 94: 402–406.
Moeller BJ, Cao Y, Li CY, Dewhirst MW . (2004). Radiation activates HIF-1 to regulate vascular radiosensitivity in tumors: role of reoxygenation, free radicals, and stress granules. Cancer Cell 5: 429–441.
Mottet D, Dumont V, Deccache Y, Demazy C, Ninane N, Raes M et al. (2003). Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha protein level during hypoxic conditions by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/glycogen synthase kinase 3beta pathway in HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem 278: 31277–31285.
Nieminen AL, Qanungo S, Schneider EA, Jiang BH, Agani FH . (2005). Mdm2 and HIF-1alpha interaction in tumor cells during hypoxia. J Cell Physiol 204: 364–369.
Pan SL, Guh JH, Peng CY, Wang SW, Chang YL, Cheng FC et al. (2005). YC-1 [3-(5′-hydroxymethyl-2′-furyl)-1-benzyl indazole] inhibits endothelial cell functions induced by angiogenic factors in vitro and angiogenesis in vivo models. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 314: 35–42.
Powis G, Kirkpatrick L . (2004). Hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha as a cancer drug target. Mol Cancer Ther 3: 647–654.
Rapisarda A, Uranchimeg B, Sordet O, Pommier Y, Shoemaker RH, Melillo G . (2004). Topoisomerase I-mediated inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor 1: mechanism and therapeutic implications. Cancer Res 64: 1475–1482.
Ross JS, Kallakury BV, Sheehan CE, Fisher HA, Kaufman Jr RP, Kaur P et al. (2004). Expression of nuclear factor-kappa B and I kappa B alpha proteins in prostatic adenocarcinomas: correlation of nuclear factor-kappa B immunoreactivity with disease recurrence. Clin Cancer Res 10: 2466–2472.
Ryan HE, Lo J, Johnson RS . (1998). HIF-1 alpha is required for solid tumor formation and embryonic vascularization. EMBO J 17: 3005–3015.
Semenza GL, Wang GL . (1992). A nuclear factor induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol 12: 5447–5454.
Takada Y, Kobayashi Y, Aggarwal BB . (2005). Evodiamine abolishes constitutive and inducible NF-kappaB activation by inhibiting IkappaBalpha kinase activation, thereby suppressing NF-kappaB-regulated antiapoptotic and metastatic gene expression, upregulating apoptosis, and inhibiting invasion. J Biol Chem 280: 17203–17212.
Tang TT, Lasky LA . (2003). The forkhead transcription factor FOXO4 induces the down-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha by a von Hippel–Lindau protein-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem 278: 30125–30135.
Treins C, Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Murdaca J, Semenza GL, Van OE . (2002). Insulin stimulates hypoxia-inducible factor 1 through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/target of rapamycin-dependent signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 277: 27975–27981.
Yeo EJ, Chun YS, Cho YS, Kim J, Lee JC, Kim MS et al. (2003). YC-1: a potential anticancer drug targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Natl Cancer Inst 95: 516–525.
Zhong H, Chiles K, Feldser D, Laughner E, Hanrahan C, Georgescu MM et al. (2000). Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression by the epidermal growth factor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/AKT/FRAP pathway in human prostate cancer cells: implications for tumor angiogenesis and therapeutics. Cancer Res 60: 1541–1545.
Zhong H, Hanrahan C, Van der PH, Simons JW . (2001). Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and 1beta proteins share common signaling pathways in human prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 284: 352–356.
Zhong H, Semenza GL, Simons JW, De Marzo AM . (2004). Up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is an early event in prostate carcinogenesis. Cancer Detect Prev 28: 88–93.
Zhou J, Callapina M, Goodall GJ, Brune B . (2004a). Functional integrity of nuclear factor kappaB, phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase, and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling allows tumor necrosis factor alpha-evoked Bcl-2 expression to provoke internal ribosome entry site-dependent translation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Cancer Res 64: 9041–9048.
Zhou J, Schmid T, Brune B . (2003). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha causes accumulation of a ubiquitinated form of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha through a nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent pathway. Mol Biol Cell 14: 2216–2225.
Zhou J, Schmid T, Frank R, Brune B . (2004b). PI3K/Akt is required for heat shock proteins to protect hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha from pVHL-independent degradation. J Biol Chem 279: 13506–13513.
Zundel W, Schindler C, Haas-Kogan D, Koong A, Kaper F, Chen E et al. (2000). Loss of PTEN facilitates HIF-1-mediated gene expression. Genes Dev 14: 391–396.
Acknowledgements
We thank Yu-Chun Huang, Yi-Fan Ma, Paul Yueh-Jen Hsu and Po-Cheng Chiang for valuable discussion of experimental technique. We also thank Shu-Hui Chiang for providing us with critical reagents that made this work possible. This work was supported by a research grant from Yung-Shin Pharmaceutical Industry Co. Ltd. and NSC 94-2320-B002-038 from the National Science Council of the Republic of China, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, HL., Liu, YN., Huang, YT. et al. YC-1 inhibits HIF-1 expression in prostate cancer cells: contribution of Akt/NF-κB signaling to HIF-1α accumulation during hypoxia. Oncogene 26, 3941–3951 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210169
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210169
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Efficient targeting of HIF-1α mediated by YC-1 and PX-12 encapsulated niosomes: potential application in colon cancer therapy
Journal of Biological Engineering (2023)
-
The role of hypoxia on prostate cancer progression and metastasis
Molecular Biology Reports (2023)
-
Hypoxia-induced PPFIA4 accelerates the progression of ovarian cancer through glucose metabolic reprogramming
Medical Oncology (2023)
-
Chemotherapy: a double-edged sword in cancer treatment
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2022)
-
Intracellular prostaglandin E2 contributes to hypoxia-induced proximal tubular cell death
Scientific Reports (2021)