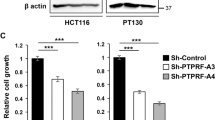
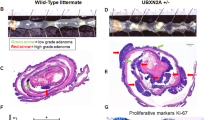
Abstract
Altered expression of receptor tyrosine kinases contributes to tumorigenic behaviors of epithelial cancers. In this study, the pathogenic roles of receptor tyrosine kinase RON (recepteur d'origine nantais) in regulating oncogenic phenotypes in colorectal epithelial cells were studied. Increased expression of RON and its variants resulted in colony formation and motile activities of colonic epithelial AA/C1 cells as evident in soft-agar and migration assays, respectively. These results suggest that overexpression of wild-type RON mediates the transformed phenotypes in immortalized colon epithelial cells. In colorectal cancer cells (HT-29, HCT116, and SW620) that naturally express RON, the RON gene expression was silenced by RNA interference. The introduction of RON-specific small interfering (si) RNA significantly affected cancer cell proliferation, motility, and led to increased apoptotic cell death. Focus-forming activities and anchorage-independent growth of colon cancer cells were also dramatically reduced. Moreover, it was demonstrated in tumor growth assays that silencing RON gene expression significantly reduces tumorigenic activities of SW620 cells in vivo. By analysing signaling proteins involved in colon carcinogenesis, we found that the effect of RON-specific siRNA is associated with diminished expression of β-catenin, a critical component in the Wnt signaling pathway. Taken together, our results demonstrate that altered expression of RON in colon cancer cells is required to maintain tumorigenic phenotypes. Thus, silencing RON gene expression could have potential to reverse malignant activities of colon tumors in vivo.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angeloni D, Danilkovitch A, Ivanov SV, Breathnach R, Johnson BE, Leonard EJ and Lerman MI . (2000). Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 29, 147–156.
Bienz M and Clevers H . (2000). Cell, 103, 311–320.
Birchmeier W, Brinkmann V, Niemann C, Meiners S, DiCesare S, Naundorf H and Sachs M . (1997). Ciba Found. Symp., 212, 230–240.
Bogenrieder T and Herlyn M . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 6524–6536.
Bright-Thomas RM and Hargest R . (2003). Eur. J. Surg. Oncol., 29, 107–117.
Chen Y-Q, Zhou Y-Q, Angeloni-Andreazzoli D, Kurtz AL, Qiang X-Z and Wang M-H . (2000). Exp. Cell Res., 261, 229–238.
Chen Y-Q, Zhou Y-Q, Fisher JH and Wang M-H . (2002a). Oncogene, 21, 6382–6386.
Chen Y-Q, Zhou Y-Q, Fu L-H, Wang D and Wang M-H . (2002b). Carcinogenesis, 23, 1811–1891.
Collesi C, Santoro MM, Gaudino G and Comoglio PM . (1996). Mol. Cell. Biol., 16, 5518–5526.
Comoglio PM and Trusolino L . (2002). J. Clin. Invest., 109, 857–862.
Crawford JM . (1994). Pathological Basis of Disease: The Gastrointestinal Tract Cotran RZ, Kumar V, Robbins SL (eds). WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, pp. 755–829.
Danilkovitch-Miagkova A, Miagkov A, Skeel A, Nakaigawa N, Zbar B and Leonard EJ . (2001). Mol. Cell. Biol., 21, 5857–5868.
Dorudi S and Hart IR . (1993). Curr. Opin. Oncol., 5, 130–135.
Earp HS, Calvo BF and Sartor CI . (2003). Trans. Am. Clin. Assoc., 114, 315–333.
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Weber K and Tuschl Y . (2002). Methods, 26, 199–213.
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE and Mello CC . (1998). Nature, 391, 806–811.
Fogh J, Fogh JM and Orfeo T . (1977). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 59, 221–226.
Gaudino G, Follenzi A, Naldini L, Collesi C, Santoro M, Gallo KA, Godowski PJ and Comoglio PM . (1994). EMBO J., 13, 3524–3532.
Han S, Stuart LA and Degen SJF . (1991). Biochemistry, 30, 9768–9780.
He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, Hermeking H, Zawel L, da Costa LT, Morin PJ, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW . (1998). Science, 281, 1509–1512.
Humphreys RC and Hennighausen L . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 1085–1091.
Jackson AL, Bartz SR, Schelter J, Kobayashi SV, Burchard J, Mao M, Li B, Cavet G and Linsley PS . (2003). Nat. Biotechnol., 21, 635–637.
Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B . (1998). The Genetic Basis of Human Cancer: Colorectal Tumors Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW (eds). McGraw-Hill: New York, pp. 565–587.
Maggiora P, Marchio S, Stella MC, Giai M, Belfiore A, De Bortoli M, Di Renzo MF, Costantino A, Sismondi P and Comoglio PM . (1998). Oncogene, 16, 2927–2933.
McManus MT and Sharp PA . (2002). Nat. Rev.Genet., 3, 737–747.
Montero-Julian FA, Dauny I, Flavetta S, Ronsin C, Andre F, Xerri L, Wang M-H, Marvaldi J, Breathnach R and Brailly H . (1998). Hybridoma, 17, 541–551.
Okino T, Egami H, Ohmachi H, Takai E, Tamori Y, Nakagawa K, Nakano S, Akagi J, Sakamoto O, Suda T and Ogawa M . (1999). Intern. J. Oncol., 15, 709–714.
Oving IM and Clevers HC . (2002). Eur. J. Clin. Invest., 32, 448–457.
Peace BE, Hughes MJ, Degen SJF and Waltz SE . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 6142–6151.
Persengiev SP, Zhu X and Green MR . (2004). RNA, 10, 12–18.
Portera Jr CA, Berman RS and Ellis LM . (1998). Surg. Oncol., 7, 183–195.
Ronsin C, Muscatelli F, Mattei MG and Breathnach R . (1993). Oncogene, 8, 1195–1202.
Rubin JS, Bottaro DP and Aaronson SA . (1993). Biochem. Biophys. Acta, 1155, 357–371.
Santoro MM, Collesi C, Grisendi S, Gaudino G and Comoglio PM . (1996). Mol. Cell. Biol., 16, 7072–7083.
Santoro MM, Penengo L, Minetto M, Orecchia S, Cilli M and Gaudino G . (1998). Oncogene, 17, 741–749.
Skeel A, Yoshimura T, Showalter SD, Tanaka S, Appella E and Leonard EJ . (1991). J. Exp. Med., 173, 1227–1234.
Vande Woude GF, Jeffers M, Cortner J, Alvord G, Tsarfaty I and Resau J . (1997). Ciba Found. Symp., 212, 119–130.
Wang M-H, Dlugosz AA, Sun Y, Suda T, Skeel A and Leonard EJ . (1996). Exp. Cell Res., 226, 39–46.
Wang M-H, Kurtz AL and Chen Y-Q . (2000). Carcinogenesis, 21, 1507–1512.
Wang M-H, Ronsin C, Gesnel MC, Coupeym L, Skeel A, Leonard EJ and Breathnach R . (1994). Science, 266, 117–119.
Wang M-H, Wang D and Chen Y-Q . (2003). Carcinogenesis, 24, 1291–1300.
Williams AC, Harper SJ and Paraskeva C . (1990). Cancer Res., 50, 4724–4730.
Williams TA, Longati P, Pugliese L, Gual P, Bardelli A and Michieli P . (1999). J. Cell. Physiol., 181, 507–514.
Yokota J . (2000). Carcinogenesis, 21, 497–503.
Zhou Y-Q, He C, Chen Y-Q, Wang D and Wang M-H . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 186–197.
Acknowledgements
This work was performed in part at the University of Colorado School of Medicine. We thank Drs C Gespach (Hôpital Saint-Antoine, Paris, France) for AA/C1 cells; G Gaudino (Universita di Torino, Novara, Italy) for the RONm1254t cDNA; and EJ Leonard (National Cancer Institute, Frederick, MD, USA) for human MSP. We also thank Dr JS Lindsey (Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center) for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by NIH Grants R01 CA91980, Amarillo Area Foundation, and Foundation of Cheung Kong Scholars Program from the Ministry of Education, PR China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, XM., Wang, D., Shen, Q. et al. RNA-mediated gene silencing of the RON receptor tyrosine kinase alters oncogenic phenotypes of human colorectal carcinoma cells. Oncogene 23, 8464–8474 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207907
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207907
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MET and RON receptor tyrosine kinases in colorectal adenocarcinoma: molecular features as drug targets and antibody-drug conjugates for therapy
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2020)
-
Splice variants of the extracellular region of RON receptor tyrosine kinase in lung cancer cell lines identified by PCR and sequencing
BMC Cancer (2017)
-
Elevated RON protein expression in endometriosis and disease-associated ovarian cancers
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics (2017)
-
Strategies of targeting the extracellular domain of RON tyrosine kinase receptor for cancer therapy and drug delivery
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2016)
-
MSP–RON signalling in cancer: pathogenesis and therapeutic potential
Nature Reviews Cancer (2013)