Abstract
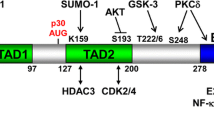
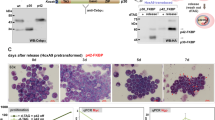
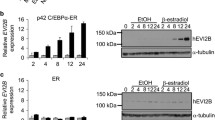
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α (C/EBPα) transactivates target genes dependent upon DNA binding via its basic region-leucine zipper domain and slows G1 progression by interaction with E2F, cdk2, or cdk4. E2F interacts with the non-DNA-binding surface of the C/EBPα basic region and C/EBPα residues 1–70 are required for repressing E2F targets, while cdk2 and cdk4 bind residues 177–191. C/EBPα-ER induces the 32D cl3 myeloblast cell line to differentiate to granulocytes. C/EBPα-ER variants incapable of binding DNA slowed G1, but did not induce early or late granulopoiesis, indicating that cell cycle inhibition as mediated by C/EBPα is not sufficient for differentiation. C/EBPα-ER variants lacking residues 11–70 or residues 11–70 and 178–200 both slowed the G1 to S transition. C/EBPα(GZ)-ER, containing the GCN4 rather than the C/EBPα leucine zipper, also slowed G1. In contrast, C/EBPα(BRM2)-ER, carrying mutations in the outer surface of the basic region required for interaction with E2F, did not slow G1. C/EBPα(BRM2)-ER induced early markers of granulopoiesis much less efficiently than C/EBPα-ER and did not direct terminal maturation. Inhibition of G1 progression using mimosine increased induction of late markers by G-CSF. Thus, both DNA binding and cell cycle arrest, mediated by opposite surfaces of the C/EBPα basic region, are required for granulopoiesis.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anfossi G, Gewirtz AM and Calabretta B . (1989). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 86, 3379–3383.
Antonson P and Xanthopoulos KG . (1995). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 215, 105–113.
Bies J, Mukhopadhyaya R, Pierce J and Wolff L . (1995). Cell. Growth Differ., 6, 59–68.
Birkenmeier EH, Gwyenn B, Howard S, Jerry J, Gordon JI, Landschulz WH and McKnight SL . (1989). Genes Dev., 3, 1146–1156.
Britos-Bray M and Friedman AD . (1997). Mol. Cell. Biol., 17, 5127–5135.
Cao W, Britos-Bray M, Claxton DF, Kelley CA, Speck NA, Liu PP and Friedman AD . (1997). Oncogene, 15, 1315–1327.
Chandrasekaran C and Gordon JI . (1993). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 8871–8875.
Chen PL, Riley DJ, Chen-Kiang S and Lee WH . (1996). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 93, 465–469.
Clarke MF, Kukowska LJ, Westin E, Smith M and Prochownik EV . (1988). Mol. Cell. Biol. 8, 884–892.
Crescenzi M, Fleming TP, Lassar AB, Weintraub H and Aaronson SA . (1990). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 87, 8442–8446.
Danos O and Mulligan RC . (1988). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 85, 6460–6464.
Friedman AD . (2002a). Oncogene, 21, 3377–3390.
Friedman AD . (2002b). J. Cell. Biochem., 86, 624–629.
Friedman AD, Landschulz WH and McKnight SL . (1989). Genes Dev., 3, 1314–1322
Friedman AD and McKnight SL . (1990). Genes Dev., 4, 1416–1426.
Gewirtz AM, Anfossi G, Venturelli D, Valpreda S, Sims R and Calabretta B . (1989). Science, 245, 180–183.
Hagemeier C, Bannister AJ, Cook A and Kouzarides T . (1993). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 1580–1584.
Hsu W, Kerpola TK, Chen P-L, Curran T and Chen-Kiang S . (1994). Mol. Cell. Biol., 14, 268–276.
Johansen LM, Iwama A, Lodie TA, Sasaki K, Felsher DW, Golub TR and Tenen DG . (2001). Mol. Cell. Biol., 21, 3789–3806.
Johnson PF, Landschulz, Graves BJ and McKnight SL . (1987). Genes Dev., 1, 133–146.
Kato J-Y and Sherr CJ . (1993). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 11513–11517.
Landschulz WH, Johnson PF and McKnight SL . (1989). Science, 246, 1681–1688.
Liu M, Lee M-H, Cohen M, Bommakanti M and Freedman LP . (1996). Genes Dev., 10, 142–153.
Lou J, Cao W, Bernardin F, Ayyanathan K, Rauscher III FJ and Friedman AD . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 2695–2703.
Muller C, alunni-Fabbroni M, Kowenz-Leutz E, Mo X, Tommasino M and Leutz A . (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 7276–7281.
Nerlov C and Ziff EB . (1994). Genes Dev., 8, 350–362.
Oelgeschläger M, Nuchprayoon I, Lüscher B and Friedman AD . (1996). Mol. Cell. Biol., 16, 4717–4725.
Pabst T, Mueller BU, Zhang P, Radomska HS, Narravula S, Schnittger S, Behre G, Hiddemann W and Tenen DG . (2001). Nat. Genet., 27, 263–270.
Porse BT, Pederson TA, Xu X, Lindberg B, Wewer UM, Friis-Hansen L and Nerlov C . (2001). Cell, 107, 247–258.
Radomska HS, Huettner CS, Zhang P and Tenen DG . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 4301–4314.
Scott LM, Civin CI, Rorth P and Friedman AD . (1992). Blood, 80, 1725–1735.
Slomiany BA, D'Arigo KL, Kelly MM and Kurtz DT . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 5986–5997.
Strom DK, Cleveland JL, Chellappan S, Nip J and Hiebert SW . (1998). Cell Growth Differ., 9, 59–69.
Timchenko NA, Wilde M and Darlington GJ . (1999). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 2936–2945.
Umek RM, Friedman AD and McKnight SL . (1991). Science, 251, 288–292.
Valtieri M, Tweardy DJ, Caracciolo D, Johnson K, Mavilio F, Altman S, Snatoli D and Rovera G . (1987). J. Immunol., 138, 3829–3835.
Vinson CR, Sigler PB and McKnight SL . (1989). Science, 246, 911–916.
Wang ND, Finegold MJ, Bradley A, Ou CN, Abdelsayed SV, Wilde MD, Taylor LR, Wilson DR and Darglington DG . (1995). Science, 269, 1108–1112.
Wang Q and Friedman AD . (2002). Blood, 99, 2776–2785.
Wang H, Iakova P, Wilde M, Welm A, Goode T, Roesler WJ and Timchenko NA . (2001). Cell, 8, 817–828.
Wang G, Miskimins R and Miskimins WK . (2000). Exp. Cell Res., 254, 64–71.
Wang X, Scott E, Sawyers CL and Friedman AD . (1999). Blood, 94, 560–571.
Zhang D-E, Zhang P, Wang N-D, Hetherington CJ, Darlington GJ and Tenen DG . (1997). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 569–574.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants R01 HL62274 and HL62274 to ADF. ADF is a Leukemia and Lymphoma Society Scholar and is also supported by the Children's Cancer Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, QF., Cleaves, R., Kummalue, T. et al. Cell cycle inhibition mediated by the outer surface of the C/EBPα basic region is required but not sufficient for granulopoiesis. Oncogene 22, 2548–2557 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206360
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206360
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Expression level of CEBPA gene in acute lymphoblastic leukemia individuals
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
CUGBP1 promotes cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis via down-regulating C/EBPα in human non-small cell lung cancers
Medical Oncology (2015)
-
C/EBPα in normal and malignant myelopoiesis
International Journal of Hematology (2015)
-
Pharmacological targeting of the Wdr5-MLL interaction in C/EBPα N-terminal leukemia
Nature Chemical Biology (2015)
-
Elevated PIN1 expression by C/EBPα-p30 blocks C/EBPα-induced granulocytic differentiation through c-Jun in AML
Leukemia (2010)