Abstract
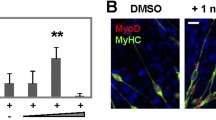
The results reported here indicate that retinoic acid (RA) induces growth arrest and differentiation only in MyoD-expressing muscle cells. Transient transfection assays reveal a functional interaction between MyoD, a key myogenic regulator and RA-receptors, principal mediators of RA actions. Interestingly, we demonstrate that RXR-MyoD-containing complexes are recruited at specific MyoD DNA-binding sites in muscle cells. Furthermore, we also demonstrate that RA-receptors and the muscle basic helix–loop–helix (b-HLH) proteins interact physically. Mutational analysis suggests that this interaction occurs via the basic region of muscle b-HLH proteins and the DNA-binding domain of RA-receptors and is important for functional interactions between these two families of transcription factors. In conclusion, these results highlight novel interactions between two distinct groups of regulatory proteins that influence cell growth and differentiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Froeschlé, A., Alric, S., Kitzmann, M. et al. Retinoic acid receptors and muscle b-HLH proteins: partners in retinoid-induced myogenesis. Oncogene 16, 3369–3378 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201894
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201894
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Genome-wide Twist1 occupancy in endocardial cushion cells, embryonic limb buds, and peripheral nerve sheath tumor cells
BMC Genomics (2014)
-
Retinoic acid enhances skeletal muscle progenitor formation and bypasses inhibition by bone morphogenetic protein 4 but not dominant negative β-catenin
BMC Biology (2009)
-
Inhibition of autocrine secretion of myostatin enhances terminal differentiation in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells
Oncogene (2003)