Abstract
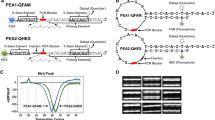
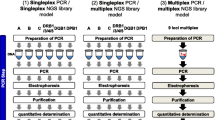
Large numbers of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are being identified by several laboratories for the purpose of developing dense genetic maps. Single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) analysis has been widely used as a method for detecting novel sequence variations in PCR products. Differences in migration of single-stranded DNA can be used not only to find mutations, but to genotype SNPs in large sample populations. Using PCR with fluorescent labeling and automated capillary electrophoresis SSCP (CE-SSCP), we have developed a panel of 15 functional candidate SNPs. With an automated single capillary instrument, relatively rapid and low cost CE-SSCP SNP genotyping using currently available technology is feasible for 135 000 genotypes per year. With parallel multiple array capillary electrophoresis, more genotypes per year may be attainable.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonen, D., Veenstra-VanderWeele, J., Yang, Z. et al. High throughput fluorescent CE-SSCP SNP genotyping. Mol Psychiatry 4, 339–343 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000564
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000564
- Springer Nature Limited