Abstract
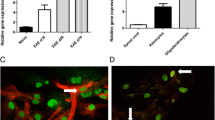
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their inhibitors (TIMPs) known to be fundamental to normal physiological processes, also contribute to several pathologies associated with uncontrolled tissue degradation. Recent observation of MMPs and TIMPs in the central nervous system suggest they could play a role in the neurodegenerative process following viral infection. We have investigated the expression of these molecules in human and rat glial cells infected with retrovirus HTLV-I, the causative agent of HTLV-I associated myelopathy (TSP/HAM). We report that cytokines secreted by infected glial cells are responsible for the increased expression of MMP-3, MMP-9 and TIMP-3, while MMP-2, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 remained stable. The role of dysregulated MMPs/TIMPs in the pathogenesis of TSP/HAM may be related to various functions of these proteases, namely degradation of the blood–brain barrier, myelin constituent cleavage and conversion of inactive TNF-precursor to active form.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giraudon, P., Buart, S., Bernard, A. et al. Cytokines secreted by glial cells infected with HTLV-I modulate the expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their natural inhibitor (TIMPs): possible involvement in neurodegenerative processes. Mol Psychiatry 2, 107–110 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000218
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000218
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
HAM/TSP-derived HTLV-1-infected T cell lines promote morphological and functional changes in human astrocytes cell lines: possible role in the enhanced T cells recruitment into Central Nervous System
Virology Journal (2015)
-
In vivo molecular target assessment of matrix metalloproteinase inhibition
Nature Medicine (2001)