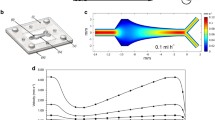
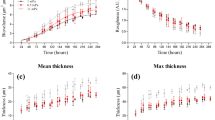
Biofilms of sulphate-reducing Desulfovibrio sp. EX265 were grown in square section glass capillary flow cells under a range of fluid flow velocities from 0.01 to 0.4 m/s (wall shear stress, τw, from 0.027 to 1.0 N/m2). In situ image analysis and confocal scanning laser microscopy revealed biofilm characteristics similar to those reported for aerobic biofilms. Biofilms in both flow cells were patchy and consisted of cell clusters separated by voids. Length-to-width ratio measurements (l c:w c) of biofilm clusters demonstrated the formation of more “streamlined” biofilm clusters (l c:w c=3.03) at high-flow velocity (Reynolds number, Re, 1200), whereas at low-flow velocity (Re 120), the l c:w c of the clusters was approximately 1 (l c:w c of 1 indicates no elongation in the flow direction). Cell clusters grown under high flow were more rigid and had a higher yield point (the point at which the biofilm began to flow like a fluid) than those established at low flow and some biofilm cell aggregates were able to relocate within a cluster, by travelling in the direction of flow, before attaching more firmly downstream.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 01 February 2002/ Accepted in revised form 16 July 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dunsmore, B., Jacobsen, A., Hall-Stoodley, L. et al. The influence of fluid shear on the structure and material properties of sulphate-reducing bacterial biofilms. J Ind Microbiol Biotech 29, 347–353 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.7000302
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.7000302