Thermomyces lanuginosus
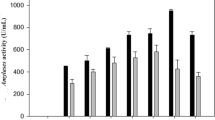
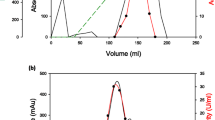
was subjected to three cycles of mutagenesis (UV/NTG) and a selection procedure to develop amylase-hyperproducing, catabolite-repression-resistant and partially constitutive strains. One of the selected derepressed mutant strain III51, produced ∼7- and 3-fold higher specific activity of α-amylase (190 U/mg protein) and glucoamylase (105 U/mg protein), respectively, compared to a wild-type parental strain. Further, the effect of production parameters on mutant strain III51 was studied using a Box–Behnken design. The regression models computed showed significantly high R 2 values of 96 and 97% for α-amylase and glucoamylase activities, respectively, indicating that they are appropriate for predicting relationships between corn flour, soybean meal and pH with α-amylase and glucoamylase production. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology (2002) 29, 70–74 doi:10.1038/sj.jim.7000270
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 05 July 2001/ Accepted in revised form 16 April 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubinder, K., Chadha, B., Singh, N. et al. Amylase hyperproduction by deregulated mutants of the thermophilic fungus Thermomyces lanuginosus . J Ind Microbiol Biotech 29, 70–74 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.7000270
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.7000270