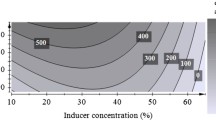
Whole cells of the phytopathogenic Erwinia chrysanthemi strains were immobilized in k-carrageenan and grown in high-calcium Xanthomonas campestris medium containing sodium polypectate as carbon source. All the strains used survived immobilization into k-carrageenan beads. Immobilized E. chrysanthemi strains displayed higher pectolytic and proteolytic enzyme activities than free cells in liquid suspension. Carrageenan immobilization techniques could provide a system to mimic the conditions of E. chrysanthemi cells in the infected plant tissue. This could prompt a thorough study of the factors governing the biosynthesis of virulence factors by this bacterium. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology (2001) 27, 215–219.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 04 April 2001/ Accepted in revised form 12 June 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muyima, N., Zamxaka, M. & Mazomba, N. Comparative evaluation of pectolytic and proteolytic enzyme production by free and immobilized cells of some strains of the phytopathogenic Erwinia chrysanthemi . J Ind Microbiol Biotech 27, 215–219 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.7000172
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.7000172