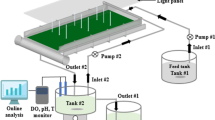
Immobilized biofilms are effective in heavy metal removal. The current studies investigated the use of rotating biological contactor (RBC) biofilms in treatment of a wastewater containing cadmium, copper and zinc, each at a concentration of 100 mg L−1. In particular, the influence of hydraulic retention time (HRT) on metal accumulation was studied. Longer HRTs (>12 h) were associated with greater metal removal than short HRTs, particularly with regard to cadmium and zinc. The system was also shown to operate successfully over an extended period of time, at an HRT of 24 h, with removal efficiencies of approximately 34%, 85% and 57% for Cd2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ respectively after 5–8 weeks contact. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology (2000) 24, 244–250.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 28 July 1999/ Accepted in revised form 21 December 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costley, S., Wallis, F. Effect of flow rate on heavy metal accumulation by rotating biological contactor (RBC) biofilms. J Ind Microbiol Biotech 24, 244–250 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.2900812
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.2900812