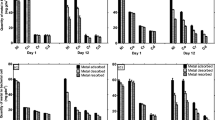
Accumulation of heavy metals by Pseudomonas fluorescens 4F39 was rapid and pH-dependent. The affinity series for bacterial accumulation of metal cations decreased in the order Ni>>Hg>U>>As>Cu>Cd>Co>Cr>Pb. Metal cations were grouped into those whose accumulation increased as the pH increased, with a maximum accumulation at the pH before precipitation (Ni, Cu, Pb, Cd, Co), and those whose maximum accumulation was not associated with precipitation (Cr, As, U, Hg). High Ni2+ accumulation was studied. Electron microscopy indicated that at pH 9, Ni2+ accumulated on the cell surface as needle and hexagon-like precipitates, whose crystalline structure was confirmed by electron diffraction analysis and corresponded to two different orientations of the nickel hydroxide crystals. Crystals on cells showed marked anisotropy by X-ray powder diffraction, which differentiated them from crystals observed in nickel solution at pH 10 and 11 and from commercial nickel hydroxide. Nickel biosorption by Pseudomonas fluorescens 4F39 was a microprecipitation consequence of an ion exchange. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology (2000) 24, 146–151.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 22 June 1999/ Accepted in revised form 04 December 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
López, A., Lázaro, N., Priego, J. et al. Effect of pH on the biosorption of nickel and other heavy metals by Pseudomonas fluorescens 4F39. J Ind Microbiol Biotech 24, 146–151 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.2900793
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.2900793