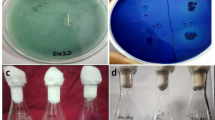
Biological oxidation of organic dyes is important for textile industry wastewater treatment. The aim of this work was to assess the biodegradation kinetics of a specific azo-dye, p-aminoazobenzene. The degradation of p-aminoazobenzene by Bacillus subtilis was examined through batch experiments in order to investigate the effect of p-aminoazobenzene on the bacterial growth rate and elucidate the mechanism of dye degradation. The results proved that B. subtilis cometabolizes p-aminoazobenzene in the presence of glucose as carbon source, producing aniline and p-phenylenediamine as the nitrogen–nitrogen double bond is broken. The azo-dye was found to act as an inhibitor to microbial growth. A mathematical model was developed that describes cellular growth, glucose utilization, p-aminoazobenzene degradation and product formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 26 July 1996/ Accepted in revised form 14 May 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zissi, U., Lyberatos, G. & Pavlou, S. Biodegradation of p-aminoazobenzene by Bacillus subtilis under aerobic conditions. J Ind Microbiol Biotech 19, 49–55 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.2900418
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.2900418