Abstract
Objective: To compare the efficacy, tolerability, and safety of once-daily therapy with amlodipine 5 mg/benazepril 10 mg vs amlodipine 5 mg, benazepril 10 mg, and placebo.
Design: Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicentre trial.
Setting: Twenty-two clinical centres, including private practice groups and academic research clinics.
Patients: A total of 530 patients between 21 and 80 years of age with essential hypertension were screened for the study, and 454 were randomised to treatment with amlodipine 5 mg/benazepril 10 mg, amlodipine 5 mg, benazepril 10 mg, or placebo for 8 weeks.
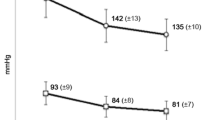
Results: Amlodipine 5 mg/benazepril 10 mg produced greater reductions from baseline in sitting diastolic blood pressure than amlodipine 5 mg (P < 0.03), benazepril 10 mg (P < 0.001), and placebo (P < 0.001). The response rate in the amlodipine 5-mg/benazepril 10-mg treatment group (66.4%) was better than that observed in the amlodipine 5-mg (50.0% P < 0.02), benazepril 10-mg (38.3% P < 0.001), and placebo (24.4% P < 0.001) groups. There was no significant difference in heart rate among the four groups. The incidence of oedema in the amlodipine 5-mg/benazepril 10-mg (1.7%) group was somewhat less than that in the amlodipine 5-mg (4.5%) group.
Conclusions: Therapy with amlodipine 5 mg/benazepril 10 mg was well tolerated and was superior to amlodipine 5 mg, benazepril 10 mg, and placebo in reducing sitting diastolic blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frishman WH et alComparison of amlodipine and benazepril monotherapy to amlodipine plus benazepril inpatients with systemic hypertension: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. The Benazepril/Amlodipine Study Group J Clin Pharmacol 1995 35 1060–1066
Frishman WH, Landau A, Cretkovic A Combination drug therapy with calcium-channel blockers in the treatment of systemic hypertension J Clin Pharmacol 1993 33 752–755
White WB, Viadero JJ, Lane TJ, Podesla S Effects of combination therapy with captopril and nifedipine in severe or resistant hypertension Clin Pharmacol Ther 1986 39 43–48
Guazzi MD et alCalcium-channel blockade with nifedipine and angiotensin coverting-enzyme inhibition with captopril in the therapy ofpatients with severe primary hypertension Circulation 1984 70 279–284
1989 guidelines for the management of mild hypertension: memorandum from a WHO/ISH meeting J Hypertens 1989 7 689–693
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a research grant from Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, East Hanover, NJ 07936.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pool, J., Kaihlanen, P., Lewis, G. et al. Once-daily treatment of patients with hypertension: a placebo-controlled study of amlodipine and benazepril vs amlodipine or benazepril alone. J Hum Hypertens 15, 495–498 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001217
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001217
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The central mechanism underlying hypertension: a review of the roles of sodium ions, epithelial sodium channels, the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system, oxidative stress and endogenous digitalis in the brain
Hypertension Research (2011)
-
Effects of Calcium Channel and Renin-Angiotensin System Blockade on Intravascular and Neurohormonal Mechanisms of Hypertensive Vascular Disease
American Journal of Hypertension (2008)
-
Antihypertensive treatment in the elderly
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research (2002)