Abstract
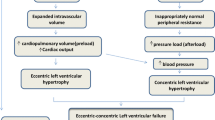
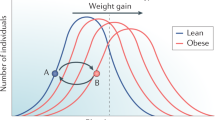
Obesity and arterial hypertension are important public health problems. Both overweight and hypertension predispose to cardiovascular diseases, such as myocardial infarction, stroke and renal failure. Moreover, overweight clearly predisposes to hypertension, and thus to an increased prevalence of cardiovascular diseases. This in turn favors inactivity and further weight gain, leading to an exacerbation of cardiovascular disorders. Obesity, hypertension and cardiovascular diseases thus contribute to three corners of a vicious triangle. It is within this conceptual framework that this paper reviews the pathogenesis of obesity-related hypertension, which is highly complex. Many factors act together to promote vasoconstriction and sodium retention. Leptin, free fatty acids and insulin, whose levels are increased in obesity, may act synergistically to stimulate sympathetic activity and vasoconstriction. In addition, obesity-induced insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction may operate as amplifiers of the vasoconstrictor response. Finally, increased renal tubular reabsorption of sodium may also occur, caused by an increased renal sympathetic nerve activity, the direct effect of insulin, hyperactivity of the renin–angiotensin system and possibly by an alteration of intrarenal physical forces. All together, these factors will lead to sustained hypertension. Because the prevalence of obesity was steadily increasing in the last decades, leading to an increased prevalence of hypertension and cardiovascular disorders, obesity and hypertension will most likely become the health challenges of the twenty-first century.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montani, JP., Antic, V., Yang, Z. et al. Pathways from obesity to hypertension: from the perspective of a vicious triangle. Int J Obes 26 (Suppl 2), S28–S38 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802125
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802125
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Temporal and mediation relations of weight loss, and changes in insulin resistance and blood pressure in response to 2-year weight-loss diet interventions: the POUNDS Lost trial
European Journal of Nutrition (2022)
-
Long-Term Changes in Leptin, Chemerin, and Ghrelin Levels Following Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy
Obesity Surgery (2020)
-
Role of the histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid in high-fat diet-induced hypertension via inhibition of HDAC1/angiotensin II axis
International Journal of Obesity (2017)
-
High-fat diet increases pain behaviors in rats with or without obesity
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Visceral adiposity syndrome
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome (2016)