Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To examine the relationships between four anthropometric measurements and cardiovascular risk factors in Taiwan.
DESIGN: The data was collected from four nationwide health screen centers in Taiwan from 1998 to 1999.
SUBJECTS: A total of 38 556 subjects: 18 280 men and 20 276 women, mean age=37.0±11.1 y. None had any known major systemic diseases or were currently on medication.
MEASUREMENTS: Individual body weight, height, waist circumference (WC), and cardiovascular risk factors (blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose, triglycerides, total cholesterol level, low-density and high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol level) were assessed and their relationships were examined.
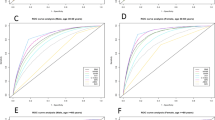
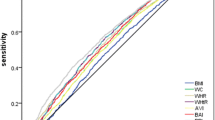
RESULTS: In both sexes, with increasing body mass index (BMI), WC, WHpR (waist-to-hip ratio) and WHtR (waist-to-height ratio), there were significantly higher risks of hypertension, impaired fasting glucose, diabetes and dyslipidemia (P<0.001) in almost all age groups. In the age groups older than 65, however, the relationships were statistically inconsistent.
CONCLUSIONS: In Taiwan, the four anthropometric indexes (BMI, WC, WHpR, WHtR) are closely related to cardiovascular risk factors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization. Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic WHO: Geneva 1998.
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kuczmarski RJ, Johnson CL . Overweight and obesity in the United States: prevalence and trends, 1960–1994 Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998 22: 39–47.
Kuczmarski RJ, Flegal KM, Campbell SM, Johnson CL . Increasing prevalence of overweight among US adults. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 1960 to 1991 JAMA 1994 272: 205–211.
Kopelman . Obesity as a medical problem Nature 2000 404: 635–643.
Pi-Sunyer X . Health implications of obesity Am J Clin Nutr 1991 53: 1595s–1603s.
Hubert HB, Feinleib M, McNamara PM, Castelli WP . Obesity as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease: a 26-year follow-up of participants in the Framingham Heart Study Circulation 1983 67: 968–977.
William BK, Ralph BD, Janet LC . Effect of weight on cardiovascular disease Am J Clin Nutr 1996 63: 419s–422s.
Seidell JC, Verschu Ren WM, Van Leer EM, Kromhout D . Overweight, underweight, and mortality. A prospective study of 48,187 men and women Arch Intern Med 1996 156: 958–963.
Björntorp P . Metabolic implications of body fat distribution Diabetes Care 1991 14: 1132–1143.
Larsson B, Svardsud K, Welin L, Wilhelmsen L, Bjorntorp P, Tibblin G . Abdominal adipose tissue distribution, obesity, and the risk of cardiovascular disease and death: 13-year follow up of participants in the study of men born in 1913 Br Med J 1984 288: 1401–1404.
Kissebah AH, Vydelingum N, Murray R, Evans DJ, Hartz AJ, Kalkhoff RK, Adams PW . Relation of body fat distribution to metabolic complications of obesity J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1982 54: 254–260.
Mazess RB, Barden HS, Bisek JP, Hanson J . Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for total body and regional bone mineral and soft tissue composition Am J Clin Nutr 1990 51: 1106–1112.
Lukaski HC . Methods for the assessment of human body composition: Traditional and new Am J Clin Nutr 1987 46: 537–556.
Friedl KE, Deluca JP, Marchitelli LJ, Vogel JA . Reliability of body-fat estimations from a four-compartment model by using density, body water, and bone mineral measurements Am J Clin Nutr 1992 55: 764–770.
Kushner RF, Schoeller DA, Fjeld CR, Danford L . Is the impedance index (H2/R) significant in predicting total body water Am J Clin Nutr 1992 56: 835–839.
Gallagher D, Visser M, Sepulveda D, Pierson RN, Harris T, Heymsfield SB . How useful is body mass index for comparison of body fatness across age, sex, and ethnic groups? Am J Epidemiol 1996 143: 228–239.
Deurenberg P, Yap M, van Staveren WA . Body mass index and percent body fat: a meta-analysis among different ethnic groups Int J Obes 1988 22: 1164–1171.
Pouliot MC, Despres JP, Lemieux S, Moorjani S, Bouchard C, Tremblay A, Nadeau A, Lupien PJ . Waist circumference and abdominal sagittal diameter: the best simple anthropometric indices of abdominal visceral adipose tissue accumulation and related cardiovascular risk in men and women Am J Cardiol 1994 73: 460–468.
Dospres J-P, Denis P, Marie C, Pouliot, Angelo T, Clande B . Estimate of deep abdominal adipose-tissue accumulation from single anthorpometric measurements in men Am J Clin Nutr 1991 54: 471–477.
Hsieh SD, Yoshinaga H . Abdominal fat distribution and coronary heart disease risk factors in men—waist/height ratio as a simple and useful predictor Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1995 19: 585–589.
Hsieh SD, Yoshinaga H . Waist/height ratio as a simple and useful predictor of coronary heart disease risk factors in women Intern Med 1995 34: 1147–1152.
Ko GTC, Chan JCN, Woo J, Lau E, Yeung VTF, Chow C-C, Wai HPS, Li JKY, So W-Y, Cockram CS . Simple anthropometric indexes and cardiovascular risk factors in the Chinese Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1997 21: 995–1001.
Hsieh SD, Yo Shinaga H, Muto T, Sakurai Y, Kosaka K . Health risks among Japanese men with moderate body mass index Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2000 24: 358–362.
Department of Health. Taiwan Public Health Report 1999 DOH: Taipei 1999.
World Health Organization. The Asia-Pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment WHO: Geneva 2000.
Wang J, Thornton JC, Russell M, Burastero S, Heymsfield S Jr, Pierson RN . Asians have lower body mass index (BMI) but higher percent body fat than do Caucasians: comparisons of anthropometric measurements Am J Clin Nutr 1994 60: 23–28.
Deurenberg-Yap M, Yian TB, Kai CS, Deurenberg P, van Staveren WA . Manifestation of cardiovascular risk factors at low levels of body mass index and waist-to-hip ratio in Singaporean Chinese subjects. Asia Pacific J Clin Nutr 1999 8: 177–183.
Wang J, Russell-Aulet M, Mazariegos M et al. Body fat by dual photon absorptiometry (DPA): comparisons with traditional methods in Asians, Blacks and Caucasians Am J Hum Biol 1992 4: 501–510.
Elandt-Johnson RC . Definition of rates: some remarks on their use and misuse Am J Epidemiol 1975 102: 267–271.
Patel S, Unwin N, Bhopal R, White M, Harland J, Ayis SAM, Watson W, Alberti KGMM . A comparison of proxy measures of abdominal obesity in Chinese, European and South Asian adults Diabetic Med 1999 16: 853–860.
Ko GTC, Chan JCN, Cockram CS, Woo J . Prediction of hypertension, diabetes or albuminuria using simple anthropometric indexes in Hong Kong Chinese Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999 23: 1136–1142.
Turcato E, Bosello O, Francesco VD, Harris TB, Zoico E, Bissoli L, Fracassi E, Zamboni M . Waist circumference and abdominal sagittal diameter as surrogates of body fat distribution in the elderly: their relation with cardiovascular risk factors Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2000 24: 1005–1010.
Fujioka S, Matsuzawa Y, Tokunaga K, Tarui S . Contribution of intra-abdominal fat accumulation to the impairment of glucose and lipid metabolism in human obesity Metabolism 1987 36: 54–59.
Lean MEJ, Han TS, Morrison CE . Waist circumference as a measure for indicating need for weight management Br Med J 1995 311: 158–161.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, KC., Lin, WY., Lee, LT. et al. Four anthropometric indices and cardiovascular risk factors in Taiwan. Int J Obes 26, 1060–1068 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802047
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802047
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Prevalence of canine obesity in the city of São Paulo, Brazil
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Association of wrist circumference with cardio-metabolic risk factors: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Eating and Weight Disorders - Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity (2020)
-
Waist-to-height ratio index for predicting incidences of hypertension: the ARIRANG study
BMC Public Health (2018)
-
Association between socioeconomic status and obesity in a Chinese adult population
BMC Public Health (2013)
-
Elevated ALT and GGT predict all-cause mortality and hepatocellular carcinoma in Taiwanese male: a case-cohort study
Hepatology International (2013)