Abstract
OBJECTIVE: Hyperactivity of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis is frequently found in hyperinsulinemic subjects, such as patients with diabetes or abdominal obesity. Here, the question has been posed as to whether hyperinsulinemia increases HPA secretory activity.
METHODS: We performed paired—euglycemic and stepwise hypoglycemic (76–66–56–46 mg/dl)—clamp experiments in two groups (each of 15 healthy men) at different insulin infusions rates, ie, 1.5 mU/min/kg (low-insulin condition) and 15.0 mU/min/kg (high-insulin condition).
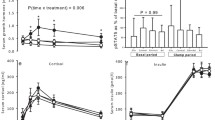
RESULTS: During the euglycemic clamp, the high rate insulin infusion increased plasma ACTH levels, whereas plasma ACTH levels remained essentially unchanged during the low-insulin condition (condition by time interaction, P=0.008). Likewise, serum cortisol levels were higher during the high- vs low-insulin condition (condition by time interaction, P=0.004). During the hypoglycemic clamp, plasma ACTH levels did not differ between the low- vs high-insulin condition, while serum cortisol levels were higher during the high- vs low-insulin condition at the beginning of the clamp (plasma glucose ∼76 mg/dl; P=0.032).
CONCLUSION: Data indicate that hyperinsulinemia acutely increases HPA secretory activity in healthy men. This finding appears to be relevant to the pathogenesis of many clinical abnormalities associated which diabetes and abdominal adiposity, often referred to as the metabolic syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fruehwald-Schultes, B., Kern, W., Born, J. et al. Hyperinsulinemia causes activation of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis in humans. Int J Obes 25 (Suppl 1), S38–S40 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801695
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801695
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
GDF15 and Cortisol Response to Meal Tolerance Test in Post-Sleeve Gastrectomy Patients with Weight Regain
Obesity Surgery (2022)
-
Intranasal Insulin: a Treatment Strategy for Addiction
Neurotherapeutics (2020)
-
Intranasal Treatment of Central Nervous System Dysfunction in Humans
Pharmaceutical Research (2013)
-
Brain Insulin Signaling and Alzheimer's Disease: Current Evidence and Future Directions
Molecular Neurobiology (2012)
-
Functional State of Adrenocortical System in Rats with Manifest Alloxan-Induced Diabetes Mellitus
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine (2008)