Abstract
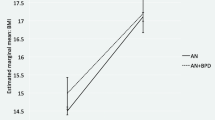
This study explores the relationship between obesity and borderline personality symptomatology in two clinical settings: a psychiatric vs primary care setting. The body mass indices (BMI) of 48 women from a psychiatric outpatient setting and 83 women from a primary care setting were calculated. Each participant completed the borderline personality scale of the Personality Diagnostic Questionnaire-Revised (PDQ-R). While BMI and PDQ-R were moderately related in the psychiatric sample (r=0.43, P<0.01), there was a lack of association between these variables in the primary care sample (r=0.04, P>0.05). In conclusion, women's increasing body weight appears to have some degree of correlation to borderline personality symptomatology among psychiatric patients, whereas it apparently does not among primary care patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sansone RA, Sansone LA, Wiederman MW . The comorbidity, relationship, and treatment implications of borderline personality and obesity J Psychosom Res 1997 43: 541–543.
Hyler SE, Rieder RO . Personality Diagnostic Questionnaire-Revised (PDQ-R). New York State Psychiatric Institute: New York 1987.
Garrow JS, Webster J . Quetelet's index (W/H2) as a measure of fatness Int J Obes 1985 9: 147–153.
Najjar MF, Rowland M . Anthropometric reference data and prevalence of overweight: United States, 1976–1980. Vital and Health Statistics, series 11, no. 238, PHS Publication No. 87-1688 Department of Health and Human Services: Hyattsville, MD 1987.
Harwell M . Misinterpreting interaction effects in analysis of variance Measurement Eval Counsel Dev 1998 31: 125–136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sansone, R., Wiederman, M., Sansone, L. et al. Obesity and borderline personality symptomatology: comparison of a psychiatric versus primary care sample. Int J Obes 25, 299–300 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801514
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801514
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Body self-evaluation and physical scars in patients with borderline personality disorder: an observational study
Borderline Personality Disorder and Emotion Dysregulation (2014)
-
Major depression, borderline personality disorder, and visceral fat content in women
European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience (2011)