Abstract
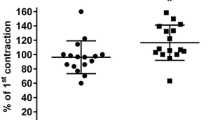
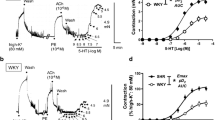
Isometric tension measurement using a selective Rho-kinase inhibitor (+)- (R)-trans4-(1-aminoethyl)-N-(4-pyridyl)cyclohexanecarboxamide (Y-27632) and a selective myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) inhibitor 1-(5-iodonaphthalene-1-sulfonyl)-1H-hexahydro-1,4-diazepine hydrochloride (ML7) were used in rabbit clitoral cavernosum smooth muscle (CSM). NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) was used to evaluate the relationship between NO release and Rho-kinase. Y-27632 significantly attenuated contractions induced by ANG II, dose-dependently. However, ML7 did not affect the contractile response to ANG II except in the high concentrations of ML7. Y-27632 inhibited contraction with phenylephrine (PhE), but ML7 did not inhibit contraction with PhE. Nitric oxide synthase inhibitor (NAME) did not affect the Y-27632-induced relaxation in the pre-contracted strip with PhE. The present study demonstrates that G-protein-coupled increase in myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity mediated through the RhoA/Rho-kinase signal pathway is involved in the control by ANG II of the clitoral CSM tone. RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway acts in the ANG II-induced contraction independently of the NO pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Timmermans PB et al. Angiotension II receptor subtypes Am J Hypertens 1992; 5: 406–410.
Park JK et al. Renin angiotensin system in rabbit corpus cavernosum: functional characterization of angiotensin II receptors J Urol 1997; 158: 653–658.
Park JK et al. Renin angiotensin system of rabbit clitoral cavernosum: interaction with nitric oxide J Urol 2000; 164: 556–561.
Kifor I et al. Tissue angiotensin II as a modulator of erectile function. I. Angiotensin peptide content, secretion and effects in the corpus cavernosum J Urol 1997; 157: 1920–1925.
Leiblum SR, Baume RM, Croog SH . The sexual functioning of elderly hypertensive women J Sex Marital Ther 1994; 20: 250–270.
Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV . Signal transduction and regulation in smooth muscle Nature 1994; 372: 231–236.
Kitazawa T, Masuo M, Somlyo AP . G protein-mediated inhibition of myosin light-chain phosphatase in vascular smooth muscle Proc Natl Acad Sci 1991; 88: 9307–9310.
Nakahara T et al. Y-27632 potentiates relaxant effects of beta 2-adrenoceptor agonists in bovine tracheal smooth muscle Eur J Pharmac 2000; 389: 103–106.
Chitaley K et al. Antagonism of Rho-kinase stimulates rat penile erection via a nitric oxide-independent pathway Nat Med 2001; 7: 119–122.
Kimura K et al. Regulation of myosin phosphatase by Rho and Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase) Science 1996; 273: 245–248.
Boivin D, Bilodeau D, Beliveau R . Regulation of cytoskeletal functions by Rho small GTP-binding proteins in normal and cancer cells Can J Physiol Pharmac 1996; 74: 801–810.
Takaishi K et al. Translocation of activated Rho from the cytoplasm to membrane ruffling area, cell-cell adhesion sites and cleavage furrows Oncogene 1995; 11: 39–48.
Karnam P et al. Activation and translocation of Rho (and ADP ribosylation factor) by insulin in rat adipocytes. Apparent involvement of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 6136–6140.
Uehata M et al. Calcium sensitization of smooth muscle mediated by a Rho-associated protein kinase in hypertension Nature 1997; 389: 990–994.
Goldstein I, Berman JR . Vasculogenic female sexual dysfunction: vaginal engorgement and clitoral erectile insufficiency syndromes Int J Impot Res 1998; 10: S84–S90.
Kureishi Y et al. Rho-associated kinase directly induces smooth muscle contraction through myosin light chain phosphorylation J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 12257–12260.
Navar LG et al. Paracrine regulation of the renal microcirculation Physiol Rev 1996; 76: 425–536.
Freeman EJ, Tallant EA . Vascular smooth-muscle cells contain AT1 angiotensin receptors coupled to phospholipase D activation Biochem J 1994; 304: 543–548.
Yamakawa T et al. Involvement of Rho-kinase in angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy of rat vascular smooth muscle cells Hypertension 2000; 35: 313–319.
Fu X et al. The effects of the Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 on arachidonic acid-, GTPgammaS-, and phorbol ester-induced Ca2+-sensitization of smooth muscle FEBS Lett 1998; 440: 183–187.
Cellek S, Moncada S . Nitrergic control of peripheral sympathetic responses in the human corpus cavernosum: a comparison with other species Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 8226–8231.
Chitaley K, Webb RC . Nitric oxide induces dilation of rat aorta via inhibition of Rho-kinase signaling Hypertension 2002; 39: 438–442.
Mills TM, Chitaley K, Lewis RW, Webb RC . Nitric oxide inhibits RhoA/Rho-kinase signaling to cause penile erection Eur J Pharmac 2002; 439: 173–174.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the Institute of Clinical Medicine of Chonbuk National University Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J., Lee, S., Kim, Y. et al. Role of rho-kinase activity in angiotensin II-induced contraction of rabbit clitoral cavernosum smooth muscle. Int J Impot Res 14, 472–477 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900911
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900911
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Local renin–angiotensin systems in the genitourinary tract
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2012)
-
Real-time monitoring of angiotensin II-induced contractile response and cytoskeleton remodeling in individual cells by atomic force microscopy
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2009)
-
Surface Plasmon Resonance Monitoring of Cell Monolayer Integrity: Implication of Signaling Pathways Involved in Actin-Driven Morphological Remodeling
Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering (2008)