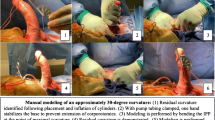
Abstract
Peyronie’s patients are candidates for surgical treatment when the acute phase has resolved. The choice of surgical treatment modality, either reconstructive procedure or implantation of penile prosthesis, largely depends on the type and degree of the deformity and the penile vascular status of the patient. We present the results of ou1 Effects of inhibitors and rmTNF-α on FMLP-induced O2 production by mouse leukocytesr experience with incision and venous patch technique in Peyronie’s disease.
Incision and venous patch technique was performed in 20 patients with a mean duration of the disease of 26.1±19.8 months.
Complete straightening was achieved in 15 (75%) patients after a mean followup of 13.2±9.4 (3–27) months. Postoperative residual curvature (<20°) was observed in 4 (20%) patients. Bulging at the graft site was noted in 1 (5%) patient. Potency was preserved in all patients except one.
Incision and venous patch technique, with its satisfactory results, should be considered in Peyronie’s patients having an adequate penile vascular system during chronic stable phase of the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kadioğlu, A., Tefekli, A., Usta, M. et al. Surgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease with incision and venous patch technique. Int J Impot Res 11, 75–81 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900375
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900375
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Plaque incision and grafting represents the best surgical approach to the Peyronie’s disease patient: Con
Current Sexual Health Reports (2006)
-
Surgical management: saphenous vein grafts
International Journal of Impotence Research (2002)