Abstract
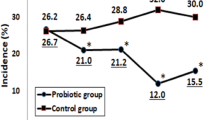
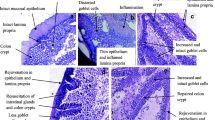
Malnutrition is associated with a significant impairment of cell-mediated immunity, phagocyte function, immunoglobulin A concentrations and cytokine production. This situation—which is unfortunately very frequent in infants and children from developing countries—leads to a high risk of infection, and often to episodes of diarrhoea, hence aggravating the nutritional status. Fermented milks are known to exert a beneficial influence on the host's health. They act by modulating gut microflora, regulating any alteration of gut mucosa and stimulating immune response. A number of studies have shown that probiotics shorten the duration of diarrhoea and prevent recurrence of other episodes. Furthermore, probiotics can prevent diarrhoea from infection in infants with malnutrition. In addition, it has been shown that cytokines could be used as biological markers of both impaired immune system and the immune stimulation of probiotics. The aim of this review is to update the effect of fermented milks in situations of malnutrition and diarrhoea as a consequence of infection as well as the role of cytokines produced by fermented milks in these deficient conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solis, B., Samartín, S., Gómez, S. et al. Probiotics as a help in children suffering from malnutrition and diarrhoea. Eur J Clin Nutr 56 (Suppl 3), S57–S59 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601488
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601488
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Fecal bacteria and metabolite responses to dietary lysozyme in a sow model from late gestation until lactation
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Effects of probiotics on child growth: a systematic review
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition (2015)
-
The art of targeting gut microbiota for tackling human obesity
Genes & Nutrition (2015)
-
Consumption of pasteurized human lysozyme transgenic goats’ milk alters serum metabolite profile in young pigs
Transgenic Research (2010)
-
Consumption of milk from transgenic goats expressing human lysozyme in the mammary gland results in the modulation of intestinal microflora
Transgenic Research (2006)