Abstract
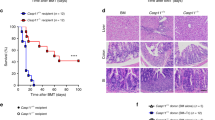
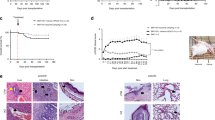
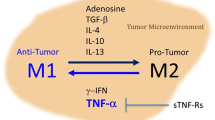
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and Fas ligand (FasL) have been implicated in the pathogenesis of graft- versus-host disease (GVHD), which is a major complication after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. We have examined the ameliorating effect of a metalloproteinase inhibitor (KB-R7785) that inhibits TNF-α and FasL release in a murine acute GVHD model after bone marrow transplantation. Administration of KB-R7785 to irradiated (BALB/c × C57BL/6) F1 mice that received C57BL/6 bone marrow cells and spleen cells reduced the mortality and weight loss in association with minimal signs of GVHD pathology in the liver, intestine, and hematopoietic tissues. The KB-R7785 treatment did not affect hematopoietic reconstitution by donor cells. Therefore, KB-R7785 could be a potent therapeutic agent for GVHD after bone marrow transplantation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hattori, K., Hirano, T., Ushiyama, C. et al. A metalloproteinase inhibitor prevents acute graft-versus-host disease in mice after bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 23, 1283–1289 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1701792
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1701792
- Springer Nature Limited