Abstract
Background:
The worldwide incidence of diabetes mellitus is rapidly increasing. There is recent interest in the influence of glucose metabolism on oncogenesis. We investigated the role of diabetes mellitus and the metabolic syndrome (MS) on prostate cancer development.
Methods:
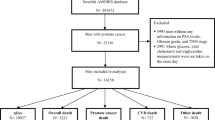
This study consisted of 11 541 men with coronary heart disease screened to participate in a secondary cardiac prevention trial. MS was defined according to modified NCEP/ATP III criteria. Multivariable regression analysis accounting for competing risks was performed using a modified Cox proportional hazard model in order to assess the association between diabetes, the MS and the subsequent development of prostate cancer.
Results:
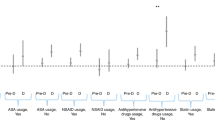
At baseline, subjects were classified into one of the four groups: (1) 6119 (53%) with neither diabetic mellitus nor MS, (2) 3376 (29%) with the MS but without diabetes, (3) 560 (5%) with diabetes mellitus but without MS and (4) 1486 (13%) with both conditions. Median follow-up was 12.7 years (range 0–15.7 years). During follow-up, 459 new cases of prostate cancer were recorded. The age-adjusted hazard ratio (HR) for prostate cancer was reduced in diabetic patients compared with those without diabetes, 0.54 and 95% confidence interval of 0.40–0.73. No significant association was noted between the presence of MS and prostate cancer development. On multivariate analysis, diabetes mellitus continued to protect against the development of prostate cancer, this was more pronounced in the absence of MS (HR=0.43, P=0.01 for diabetes in the absence of MS; HR=0.64, P=0.08 in the presence of MS).
Conclusions:
The results of this study indicate an inverse association between type 2 diabetes mellitus and prostate cancer risk.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kris MG, Benowitz SI, Adams S, Diller L, Ganz P, Kahlenberg MS et al. Clinical cancer advances 2010: annual report on progress against cancer from the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 5327–5347.
Ahmed RL, Schmitz KH, Anderson KE, Rosamond WD, Folsom AR . The metabolic syndrome and risk of incident colorectal cancer. Cancer 2006; 107: 28–36.
Stocks T, Lukanova A, Johansson M, Rinaldi S, Palmqvist R, Hallmans G et al. Components of the metabolic syndrome and colorectal cancer risk; a prospective study. Int J Obes 2008; 32: 304–314.
Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ . The metabolic syndrome. Lancet 2005; 365: 1415–1428.
Bjorge T, Stocks T, Lukanova A, Tretli S, Selmer R, Manjer J et al. Metabolic syndrome and endometrial carcinoma. Am J Epidemiol 2010; 171: 892–902.
Kabat GC, Kim M, Chlebowski RT, Khandekar J, Ko MG, McTiernan A et al. A longitudinal study of the metabolic syndrome and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2009; 18: 2046–2053.
Coughlin S . Diabetes mellitus as a predictor of cancer mortality in a large cohort of US adults. Am J Epidemiol 2004; 159: 1160–1167.
Wolf I, Sadetzki S, Catane R, Karasik A, Kaufman B . Diabetes mellitus and breast cancer. Lancet Oncol 2005; 6: 103–111.
Kasper JS, Giovannucci E . A meta-analysis of diabetes mellitus and the risk of prostate cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2006; 15: 2056–2062.
Bonovas S, Filioussi K, Tsantes A . Diabetes mellitus and risk of prostate cancer: a meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2004; 47: 1071–1078.
Hsing AW, Sakoda LC, Chua S . Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and prostate cancer. Am J Clin Nutr 2007; 86: s843–s857.
MacInnis RJ, English DR . Body size and composition and prostate cancer risk: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Cancer Causes Control 2006; 17: 989–1003.
Secondary prevention by raising HDL cholesterol and reducing triglycerides in patients with coronary artery disease: the Bezafibrate Infarction Prevention (BIP) study. Circulation 2000; 102: 21–27.
Goldbourt U, Behar S, Reicher-Reiss H, Agmon J, Kaplinsky E, Graff E et al. Rationale and design of a secondary prevention trial of increasing serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and reducing triglycerides in patients with clinically manifest atherosclerotic heart disease (the Bezafibrate Infarction Prevention Trial). Am J Cardiol 1993; 71: 909–915.
Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001; 285: 2486–2497.
Barchana M, Liphshitz I, Rozen P . Trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality in the Israeli Jewish ethnic populations. Fam Cancer 2004; 3: 207–214.
Gooley TA, Leisenring W, Crowley J, Storer BE . Estimation of failure probabilities in the presence of competing risks: new representations of old estimators. Stat Med 1999; 18: 695–706.
Fine JP, Gray RJ . A proportional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk. J Am Stat Assoc 1999; 94: 496–509.
Kohl M, Heinze G . PSHREG: A SASr macro for proportional and nonproportional substribution hazards regression with competing risk data. Vienna, 2012; Technical Report.
Kasper J, Giovannucci EA . Meta-analysis of diabetes mellitus and the risk of prostate cancer. Cancer Epidem Biomarker Prev 2006; 15: 2056–2062.
Southern DA, Faris PD, Brant R, Galbraith PD, Norris CM, Knudtson ML et al. Kaplan-Meier methods yielded misleading results in competing risk scenarios. J Clin Epidemiol 2006; 59: 1110–1114.
Bonovas S, Filioussi K, Tsantes A . Diabetes mellitus and risk of prostate cancer: a meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2004; 47: 1–8.
Bansal D, Bhansali A, Kapil G, Undela K, Tiwari P . Type 2 diabetes and risk of prostate cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2012; (e-pub ahead of print 2 October 2012).
Zhang F, Yang Y, Skrip L, Hu D, Wang Y, Wong C et al. Diabetes mellitus and risk of prostate cancer: an updated meta-analysis based on 12 case-control and 25 cohort studies. Acta Diabetol 2012; 49, (Suppl): 235–246.
Long XJ, Lin S, Sun YN, Zheng ZF . Diabetes mellitus and prostate cancer risk in Asian countries: a meta-analysis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2012; 13: 4097–4100.
Noto H, Goto A, Tsujimoto T, Noda M . Cancer risk in diabetic patients treated with metformin: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2012; 7: e33411.
Marshall JG, Cowell JM, Campbell ES, McNaughton DB . Regional variations in cancer screening rates found in women with diabetes. Nurs Res 2010; 59: 34–41.
Kraja AT, Borecki IB, North K, Tang W, Myers RH, Hopkins PN et al. Longitudinal and age trends of metabolic syndrome and its risk factors: the Family Heart Study. Nutr Metab 2006; 3: 41.
Laakso M, Pyorala K . Age of onset and type of diabetes. Diabetes Care 1985; 8: 114–117.
Various. Entry ‘Metabolic syndrome’. Wikipedia, 2012 (accessed 29 November 2012).
Vazquez G, Duval S, Jacobs DR, Silventoinen K . Comparison of body mass index, waist circumference, and waist/hip ratio in predicting incident diabetes: a meta-analysis. Epidemiol Rev 2007; 29: 115–128.
Decensi A, Puntoni M, Goodwin P, Cazzaniga M, Gennari A, Bonanni B et al. Metformin and cancer risk in diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Prev Res 2010; 3: 1451–1461.
Roddam AW, Allen NE, Appleby P, Key TJ . Endogenous sex hormones and prostate cancer: a collaborative analysis of 18 prospective studies. J Natl Cancer Inst 2008; 100: 170–183.
Roddam AW, Allen NE, Appleby P, Key TJ, Ferrucci L, Carter HB et al. Insulin-like growth factors, their binding proteins, and prostate cancer risk: analysis of individual patient data from 12 prospective studies. Ann Intern Med 2008; 149: W483–468.
Laukkanen JA, Laaksonen DE, Niskanen L, Pukkala E, Hakkarainen A, Salonen JT . Metabolic syndrome and the risk of prostate cancer in Finnish men: a population-based study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2004; 13: 1646–1650.
Lund Haheim L, Wisloff TF, Holme I, Nafstad P . Metabolic syndrome predicts prostate cancer in a cohort of middle-aged Norwegian men followed for 27 years. Am J Epidemiol 2006; 164: 769–774.
Tande AJ, Platz EA, Folsom AR . The metabolic syndrome is associated with reduced risk of prostate cancer. Am J Epidemiol 2006; 164: 1094–1102.
Martin R, Vatten L, Gunnell D, Romundstad P, Nilsen T . Components of the metabolic syndrome and risk of prostate cancer: the HUNT 2 cohort, Norway. Cancer Causes Control 2009, 1–12.
Wallner LP, Morgenstern H, McGree ME, Jacobson DJ, Sauver JL, Jacobsen SJ et al. The effects of metabolic conditions on prostate cancer incidence over 15 years of follow-up: results from the Olmsted County Study. BJU Int 2011; 107: 929–935.
Grundmark B, Garmo H, Loda M, Busch C, Holmberg L, Zethelius B . The metabolic syndrome and the risk of prostate cancer under competing risks of death from other causes. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2010; 19: 2088–2096.
Beebe-Dimmer JL, Dunn RL, Sarma AV, Montie JE, Cooney KA . Features of the metabolic syndrome and prostate cancer in African-American men. Cancer 2007; 109: 875–881.
Tuohimaa P, Tenkanen L, Syvala H, Lumme S, Hakulinen T, Dillner J et al. Interaction of factors related to the metabolic syndrome and vitamin D on risk of prostate cancer. Cancer Epidem Biomarker Prev 2007; 16: 302–307.
Beebe-Dimmer JL, Nock NL, Neslund-Dudas C, Rundle A, Bock CH, Tang D et al. Racial differences in risk of prostate cancer associated with metabolic syndrome. Urology 2009; 74: 185–190.
De Nunzio C, Freedland SJ, Miano R, Trucchi A, Cantiani A, Carluccini A et al. Metabolic syndrome is associated with high grade gleason score when prostate cancer is diagnosed on biopsy. Prostate 2011.
Esposito K, Chiodini P, Colao A, Lenzi A, Giugliano D . Metabolic syndrome and risk of cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2012; 35: 2402–2411.
Acknowledgements
Supported in part by a grant from the Israeli Cancer Association (to YRL).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lawrence, Y., Morag, O., Benderly, M. et al. Association between metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus and prostate cancer risk. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 16, 181–186 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2012.54
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2012.54
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Peri-prostatic adipose tissue measurements using MRI predict prostate cancer aggressiveness in men undergoing radical prostatectomy
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation (2021)
-
Association of type 2 diabetes mellitus and antidiabetic medication with risk of prostate cancer: a population-based case-control study
BMC Cancer (2020)
-
Association between blood pressure and risk of cancer development: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Meta-analysis of metabolic syndrome and prostate cancer
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2017)
-
Diabetes, prostate cancer screening and risk of low- and high-grade prostate cancer: an 11 year historical population follow-up study of more than 1 million men
Diabetologia (2016)