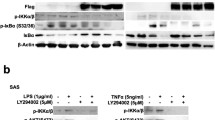
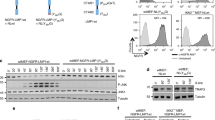
Abstract
Marginal zone mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) B-cell lymphoma is the most common extranodal non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The t(11;18)(q21;q21) translocation occurs frequently in MALT lymphomas and creates a chimeric NF-κB-activating protein containing the baculoviral IAP repeat (BIR) domains of c-IAP2 (inhibitor of apoptosis protein 2) fused with portions of the MALT1 protein. The BIR1 domain of c-IAP2 interacts directly with TRAF2 (TNFα-receptor-associated factor–2), but its role in NF-κB activation is still unclear. Here, we investigated the role of TRAF2 in c-IAP2/MALT1-induced NF-κB activation. We show the BIR1 domain of c-IAP2 is essential for NF-κB activation, whereas BIR2 and BIR3 domains are not. Studies of c-IAP2/MALT1 BIR1 mutant (E47A/R48A) that fails to activate NF-κB showed loss of TRAF2 binding, but retention of TRAF6 binding, suggesting that interaction of c-IAP2/MALT1 with TRAF6 is insufficient for NF-κB induction. In addition, a dominant-negative TRAF2 mutant or downregulation of TRAF2 achieved by small interfering RNA inhibited NF-κB activation by c-IAP2/MALT1 showing that TRAF2 is indispensable. Comparisons of the bioactivity of intact c-IAP2/MALT1 oncoprotein and BIR1 E47A/R48A c-IAP2/MALT1 mutant that cannot bind TRAF2 in a lymphoid cell line provided evidence that TRAF2 interaction is critical for c-IAP2/MALT1-mediated increases in the NF-κB activity, increased expression of endogenous NF-κB target genes (c-FLIP, TRAF1), and resistance to apoptosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi T, Motegi M, Tamura A, Suzuki R, Hosokawa Y, Suzuki H et al. (1999). A novel gene, MALT1 at 18q21, is involved in t(11;18) (q21;q21) found in low-grade B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Oncogene 18: 5785–5794.
Akira S, Takeda K . (2004). Toll-like receptor signaling. Nat Rev Immunol 4: 499–511.
Chu ZL, McKinsey TA, Liu L, Gentry JJ, Malim MH, Ballard DW . (1997). Suppression of tumor necrosis factor-induced cell death by inhibitor of apoptosis c-IAP2 is under NF-κB control. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 10057–10062.
Dierlamm JM, Baens I, Wlodarska M, Stefanova-Ouzounova M, Hernandez JM, Hossfeld DK et al. (1999). The apoptosis inhibitor gene API2 and a novel 18q gene, MLT, are recurrently rearranged in the t(11;18)(q21;q21) associated with mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas. Blood 93: 3601–3609.
Eckelman BP, Salvesen GS, Scott FL . (2006). Human inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: why XIAP is the black sheep of the family. EMBO Rep 7: 988–994.
Habelhah H, Takahashi S, Cho SG, Kadoya T, Watanabe T, Ronai Z . (2004). Ubiquitination and translocation of TRAF2 is required for activation of JNK but not of p38 or NF-κB. EMBO 23: 322–332.
Kreuz S, Siegmund D, Scheurich P, Wajant H . (2001). NF-κB inducers upregulate cFLIP, a cycloheximide-sensitive inhibitor of death receptor signaling. Mol Cell Biol 21: 3964–3973.
Lucas PC, Yonezumi M, Inohara N, McAllister-Lucas LM, Abazeed ME, Chen FF et al. (2001). Bcl10 and MALT1, independent targets of chromosomal translocation in malt lymphoma, cooperate in a novel NF-êB signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 276: 19012–19019.
Lucas PC, Kuffa P, Gu S, Kohrt D, Kim DS, Siu K et al. (2007). A dual role for the API2 moiety in API2-MALT1-dependent NF-κB activation: heterotypic oligomerization and TRAF2 recruitment. Oncogene 26: 5643–5654.
Micheau O, Lens S, Gaide O, Alevizopoulos K, Tschopp J . (2001). NF-κB signals induce the expression of c-FLIP. Mol Cell Biol 21: 5299–5305.
Micheau O, Tschopp J . (2003). Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell 114: 181–190.
Morgan J, Yin Y, Borowsky A, Kuo F, Nourmand N, Koontz JI et al. (1999). Breakpoints of the t(11;18)(q21;q21) in mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma lie within or near the previously undescribed gene MALT1 in chromosome 18. Cancer Res 59: 6205–6213.
Noels H, van Loo G, Hagens S, Broeckx V, Beyaert R, Marynen P et al. (2007). A Novel TRAF6 binding site in MALT1 defines distinct mechanisms of NF-κB activation by API2MALT1 fusions. J Biol Chem 282: 10180–10189.
Rothe M, Wong SC, Henzel WJ, Goeddel DV . (1994). A novel family of putative signal transducers associated with the cytoplasmic domain of the 75 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell 78: 681−–6692.
Rothe M, Pan MG, Henzel WJ, Ayres TM, Goeddel DV . (1995). The TNFR2–TRAF signaling complex contains two novel proteins related to baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis proteins. Cell 83: 1243–1252.
Salvesen GS, Duckett CS . (2002). IAP proteins: blocking the road to death's door. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3: 401–410.
Schimmer AD, Dalili S, Batey RA, Riedl SJ . (2006). Targeting XIAP for the treatment of malignancy. Cell Death Differ 13: 179–188.
Silverman N, Maniatis T . (2001). NF-êB signaling pathways in mammalian and insect innate immunity. Genes Dev 15: 2321–2342.
Streubel B, Lamprecht A, Dierlamm J, Cerroni L, Stolte M, Ott G et al. (2003). T(14;18)(q32;q21) involving IGH and MALT1 is a frequent chromosomal aberration in MALT lymphoma. Blood 101: 2335–2339.
Temesgen S, Welsh K, Lober T, Togo SH, Zapata JM, Reed JC . (2006). Distinct BIR domains of cIAP1 mediate binding to and ubiquitination of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 and second mitochondrial activator of caspases. J Biol Chem 281: 1080–1090.
Thome M . (2004). CARMA1, BCL-10 and MALT1 in lymphocyte development and activation. Nat Rev Immunol 4: 348–359.
Varfolomeev E, Wayson SM, Dixit VM, Fairbrother WJ, Vucic D . (2006). The inhibitor of apoptosis protein fusion c-IAP2MALT1 stimulates NF-êB activation independently of TRAF1 AND TRAF2. J Biol Chem 281: 29022–29029.
Vega F, Medeiros LJ . (2001). Marginal-zone B-cell lymphoma of extranodal mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue type: molecular genetics provides new insights into pathogenesis. Adv Anat Pathol 8: 313–326.
Zhang Q, Siebert R, Yan M, Hinzmann B, Cui X, Xue L et al. (1999). Inactivating mutations and overexpression of BCL10, a caspase recruitment domain-containing gene, in MALT lymphoma with t(1;14)(p22;q32). Nat Genetics 22: 63–68.
Zhou H, Wertz I, O'Rourke K, Ultsch M, Seshagiri S, Eby M et al. (2004). Bcl10 activates the NF-êB pathway through ubiquitination of NEMO. Nature 427: 167–171.
Zhou H., Du MQ, Dixit VM . (2005). Constitutive NF-êB activation by the t(11;18)(q21;q21) product in MALT lymphoma is linked to deregulated ubiquitin ligase activity. Cancer Cell 7: 425–431.
Zucca E, Bertoni F, Roggero E, Cavalli F . (2000). The gastric marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of MALT type. Blood 96: 410–419.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garrison, J., Samuel, T. & Reed, J. TRAF2-binding BIR1 domain of c-IAP2/MALT1 fusion protein is essential for activation of NF-κB. Oncogene 28, 1584–1593 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.17
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.17
- Springer Nature Limited