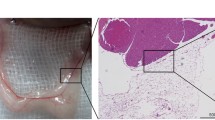
Abstract
Mechanistic studies of acute pancreatitis require animal models because clinical material is generally not available during the early phases of the disease. Here we describe a protocol to induce biliary pancreatitis by retrogradely infusing bile acids into the pancreatic duct of anesthetized mice. The resulting model replicates events believed to be responsible for the onset of clinical biliary (i.e., gallstone) pancreatitis and creates highly reproducible pancreatitis with a severity that depends on the concentration of infused bile acid. Pancreatitis reaches its maximal level of severity within 24 h of induction, and it resolves over the subsequent week. This protocol enables the investigator to use genetically modified strains of mice, and it requires only relatively simple and easily learned techniques of small animal surgery. With practice and gentle technique, the surgery (from induction of anesthesia to completion of the infusion) can be completed within 25 min per animal.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta, M.J. & Ledesma, C.L. Gallstone migration as a cause of acute pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 290, 484–487 (1974).
Opie, E.L. The etiology of acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis. Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp. 12, 182–192 (1901).
Opie, E.L. The relationship of cholelithiasis to disease of the pancreas and fat necrosis. Am. J. Med. Surg. 12, 27–40 (1901).
Lerch, M.M. et al. Pancreatic duct obstruction triggers acute necrotizing pancreatitis in the opossum. Gastroenterology 104, 853–861 (1993).
Sherman, S. & Lehman, G.A. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography- and endoscopic sphincterotomy-induced pancreatitis. In The Pancreas: An Integrated Textbook of Basic Science, Medicine, and Surgery (eds, Berger, H.G., Warshaw, A., Buchler, M.W., Kozarek, R., Lerch, M.M., Neoptolemos, J., Shiratori, K. & Whitcomb, D.) 291–310 (Blackwell, Oxford, 1998).
Lampel, M. & Kern, H.F. Acute interstitial pancreatitis in the rat induced by excessive doses of a pancreatic secretagogue. Virchows Arch. A Pathol. Anat. Histol. 373, 97–117 (1977).
Dawra, R. et al. Development of a new mouse model of acute pancreatitis induced by administration of L-arginine. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 292, G1009–G1018 (2007).
Tashiro, M., Schafer, C., Yao, H., Ernst, S.A. & Williams, J.A. Arginine induced acute pancreatitis alters the actin cytoskeleton and increases heat shock protein expression in rat pancreatic acinar cells. Gut 49, 241–250 (2001).
Lombardi, B., Estes, L.W. & Longnecker, D.S. Acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis (massive necrosis) with fat necrosis induced in mice by DL-ethionine fed with a choline-deficient diet. Am. J. Pathol. 79, 465–480 (1975).
Aho, H.J., Koskensalo, S.M. & Nevalainen, T.J. Experimental pancreatitis in the rat. Sodium taurocholate-induced acute haemorrhagic pancreatitis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 15, 411–416 (1980).
Aho, H.J. & Nevalainen, T.J. Experimental pancreatitis in the rat. Ultrastructure of sodium taurocholate-induced pancreatic lesions. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 15, 417–424 (1980).
Laukkarinen, J.M., van Acker, G.J., Weiss, E.R., Steer, M.L. & Perides, G.A. Mouse model of acute biliary pancreatitis induced by retrograde pancreatic duct infusion of Na-taurocholate. Gut 56, 1590–1598 (2007).
Wittel, U.A. et al. Taurocholate-induced pancreatitis: a model of severe necrotizing pancreatitis in mice. Pancreas 36, e9–e21 (2008).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by an NIH Grant DM31396 to M.L.S. and by the Sigrid Juselius Foundation Fellowship to J.M.L.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The surgery was first performed by G.J.D.v.A. and further refined by J.M.L. Surgeries to obtain the pictures in this article were performed by G.P. The surgery in the video was performed by G.J.D.v.A. G.P., J.M.L. and G.J.D.v.A., and M.L.S. evaluated the results. M.L.S. wrote the article and G.J.D.v.A., J.M.L., G.P. and M.L.S. edited it.
Corresponding authors
Supplementary information
Supplementary Movie
Retrograde pancreatic duct infusion with sodium taurocholate. (WMV 118274 kb)
The movie shows the surgery on a C57Bl mouse.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perides, G., van Acker, G., Laukkarinen, J. et al. Experimental acute biliary pancreatitis induced by retrograde infusion of bile acids into the mouse pancreatic duct. Nat Protoc 5, 335–341 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2009.243
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2009.243
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Decreased syntaxin17 expression contributes to the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis in murine models by impairing autophagic degradation
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2023)
-
Thiopurines impair the apical plasma membrane expression of CFTR in pancreatic ductal cells via RAC1 inhibition
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)
-
Influence of Intestinal Lymphatic Ligation on Pulmonary Injury in Rats with Severe Acute Pancreatitis
Current Medical Science (2022)
-
Hypertriglyceridemia Acute Pancreatitis: Animal Experiment Research
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (2022)
-
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate severe acute pancreatitis by inhibiting oxidative stress in rats
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2022)