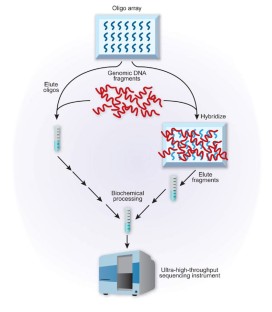
Methods relying on dense arrays of synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides to target specific subsets of the human genome may enable routine resequencing of all human exons or multi-megabase-pair chromosomal regions.
Kim Caesar
References
Porreca, J.G. et al. Nat. Methods 4, 931–936 (2007).
Okou, T.D. et al. Nat. Methods 4, 907–909 (2007).
Albert, T.J. et al. Nat. Methods 4, 903–905 (2007).
Shendure, J. et al. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5, 335–344 (2004).
Nilsson, M. et al. Science 265, 2085–2088 (1994).
Hardenbol, P. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 673–678 (2003).
Bashiardes, S. et al. Nat. Methods 2, 63–69 (2005).
Guo, Z. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 6964–6969 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olson, M. Enrichment of super-sized resequencing targets from the human genome. Nat Methods 4, 891–892 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth1107-891
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth1107-891
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
In-depth resistome analysis by targeted metagenomics
Microbiome (2018)
-
A systematic evaluation of hybridization-based mouse exome capture system
BMC Genomics (2013)
-
Inconsistencies of genome annotations in apicomplexan parasites revealed by 5'-end-one-pass and full-length sequences of oligo-capped cDNAs
BMC Genomics (2009)
-
Mutation screening in 86 known X-linked mental retardation genes by droplet-based multiplex PCR and massive parallel sequencing
The HUGO Journal (2009)
-
The beginning of the end for microarrays?
Nature Methods (2008)


