Abstract
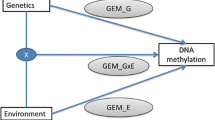
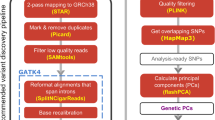
Identifying interactions between genetics and the environment (GxE) remains challenging. We have developed EAGLE, a hierarchical Bayesian model for identifying GxE interactions based on associations between environmental variables and allele-specific expression. Combining whole-blood RNA-seq with extensive environmental annotations collected from 922 human individuals, we identified 35 GxE interactions, compared with only four using standard GxE interaction testing. EAGLE provides new opportunities for researchers to identify GxE interactions using functional genomic data.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flint, J. & Mackay, T.F.C. Genome Res. 19, 723–733 (2009).
Eichler, E.E. et al. Nat. Rev. Genet. 11, 446–450 (2010).
Battle, A. et al. Genome Res. 24, 14–24 (2014).
GTEx Consortium. Science 348, 648–660 (2015).
Bray, M.S. et al. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 294, H1036–H1047 (2008).
Glass, D. et al. Genome Biol. 14, R75 (2013).
Fairfax, B.P. et al. Science 343, 1246949 (2014).
Lee, M.N. et al. Science 343, 1246980 (2014).
Barreiro, L.B. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 1204–1209 (2012).
Brown, A.A. et al. eLife 3, e01381 (2014).
Buil, A. et al. Nat. Genet. 47, 88–91 (2015).
van de Geijn, B., McVicker, G., Gilad, Y. & Pritchard, J.K. Nat. Methods 12, 1061–1063 (2015).
Degner, J.F. et al. Bioinformatics 25, 3207–3212 (2009).
Biondi, O. et al. Am. J. Pathol. 182, 2298–2309 (2013).
Jacobo-Albavera, L. et al. PLoS One 7, e49818 (2012).
Schadt, E.E. et al. Nat. Genet. 37, 710–717 (2005).
Bu˚žková, P., Lumley, T. & Rice, K. Ann. Hum. Genet. 75, 36–45 (2011).
Hussin, J.G. et al. Nat. Genet. 47, 400–404 (2015).
Hodgkinson, A. et al. Science 344, 413–415 (2014).
Burgess, J.L. et al. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 46, 1013–1022 (2004).
Pejnovic, N.N. et al. Diabetes 62, 1932–1944 (2013).
Wang, C. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 32, 926–932 (2014).
Kersten, S. Mol. Metab. 3, 354–371 (2014).
Mostafavi, S. et al. PLoS One 8, e68141 (2013).
Panousis, N.I., Gutierrez-Arcelus, M., Dermitzakis, E.T. & Lappalainen, T. Genome Biol. 15, 467 (2014).
Kim, D. et al. Genome Biol. 14, R36 (2013).
Li, H. et al. Bioinformatics 25, 2078–2079 (2009).
Harvey, C.T. et al. Bioinformatics 31, 1235–1242 (2015).
Castel, S.E., Levy-Moonshine, A., Mohammadi, P., Banks, E. & Lappalainen, T. Genome Biol. 16, 195 (2015).
Kumasaka, N., Knights, A.J. & Gaffney, D.J. Nat. Genet. 48, 206–213 (2016).
Knowles, D.A. & Minka, T. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 24, 1701–1709 (2011).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank J. Leek for helpful comments and S. Kersten for providing the graphic from which the PPARα network figure was adapted. D.A.K. is supported by NIH U54CA149145. M.-J.F. is supported by a CIHR Neuroinflammation fellowship. P.A. is supported by the Ontario Ministry of Research and Innovation. A.B. and S.B.M. are supported by NIH R01MH101814 and NIH R01HG008150. A.B. is supported by the Searle Scholars Program, NIH R01MH101820, NIH 1R01MH109905-01, and NIH 1R01GM120167-010. S.B.M. is supported by the Edward Mallinckrodt Jr. Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.A.K., S.B.M. and A.B. conceived the project and wrote the manuscript. D.A.K. and A.B. developed the method. D.A.K. implemented the software and performed the main analyses. J.R.D. and A.R. performed additional statistical analyses. X.Z., J.B.P., M.M.W., J.S., S.M. and D.F.L. gave input regarding the DGN cohort. Supervised by P.A. and M.-J.F., H.E. ran EAGLE on the CARTaGENE replication cohort. S.B.M. and A.B. supervised the project.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–14, Supplementary Tables 1–4 and Supplementary Notes 1–11. (PDF 3649 kb)
Supplementary Software
Source code for EAGLE software. (ZIP 36 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knowles, D., Davis, J., Edgington, H. et al. Allele-specific expression reveals interactions between genetic variation and environment. Nat Methods 14, 699–702 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4298
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4298
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
SURGE: uncovering context-specific genetic-regulation of gene expression from single-cell RNA sequencing using latent-factor models
Genome Biology (2024)
-
A landscape of gene expression regulation for synovium in arthritis
Nature Communications (2024)
-
SEESAW: detecting isoform-level allelic imbalance accounting for inferential uncertainty
Genome Biology (2023)
-
The transcriptional legacy of developmental stochasticity
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Allele-specific expression reveals genes with recurrent cis-regulatory alterations in high-risk neuroblastoma
Genome Biology (2022)