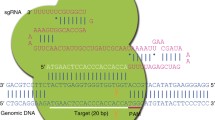
Abstract
Animal models with genetic modifications under temporal and/or spatial control are invaluable to functional genomics and medical research. Here we report the generation of tissue-specific knockout rats via microinjection of zinc-finger nucleases (ZFNs) into fertilized eggs. We generated rats with loxP-flanked (floxed) alleles and a tyrosine hydroxylase promoter–driven cre allele and demonstrated Cre-dependent gene disruption in vivo. Pronuclear microinjection of ZFNs, shown by our data to be an efficient and rapid method for creating conditional knockout rats, should also be applicable in other species.

Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
Change history
26 August 2013
In the version of this article initially published, a name was misspelled in the Acknowledgements section. The error has been corrected in the HTML and PDF versions of the article.
References
Geurts, A.M. et al. Science 325, 433 (2009).
Cui, X. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 29, 64–67 (2011).
Tesson, L. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 29, 695–696 (2011).
Gu, H., Marth, J.D., Orban, P.C., Mossmann, H. & Rajewsky, K. Science 265, 103–106 (1994).
Chen, F. et al. Nat. Methods 8, 753–755 (2011).
McCoy, A., Besch-Williford, C.L., Franklin, C.L., Weinstein, E.J. & Cui, X. Dis. Model. Mech. 6, 269–278 (2013).
Taniguchi, H. et al. Neuron 71, 995–1013 (2011).
Forrest, D. et al. Neuron 13, 325–338 (1994).
Zhou, Q.Y., Quaife, C.J. & Palmiter, R.D. Nature 374, 640–643 (1995).
Chinta, S.J. & Andersen, J.K. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 37, 942–946 (2005).
Witten, I.B. et al. Neuron 72, 721–733 (2011).
Bai, G. & Hoffman, P.W. in Biology of the NMDA Receptor (ed. Van Dongen, A.M.) Ch. 5 (CRC Press, 2009).
Weber, T., Schönig, K., Tews, B. & Bartsch, D. PLoS ONE 6, e28283 (2011).
Sato, Y. et al. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 319, 1197–1202 (2004).
Rabbitts, T.H. Nature 372, 143–149 (1994).
Zheng, B. et al. Nat. Genet. 22, 375–378 (1999).
Glaser, S., Anastassiadis, K. & Stewart, A.F. Nat. Genet. 37, 1187–1193 (2005).
Acknowledgements
We thank A. Lambowitz for critical advice, F. Urnov, D. Carroll and G. Davis for valuable comments on the manuscript, J. Huang (Cold Spring Harbor Lab) for providing IRES-cre sequence, K. Watsek for animal husbandry, L. Little for technical assistance and G. Zhao for suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.C. designed the experiments and analyzed the data; A.J.B. and D.A.F. carried out experiments; A.J.B., Y.W. and J.W. did microinjections; R.H., D.J., A.C. and W.S. did part of the genotyping; E.K. and K.F. performed qRT-PCR; A.M. did western blots; and X.C. and E.J.W. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All authors are full-time employees of SAGE Labs, Inc., which sells genetically engineered rats and provides custom model creation services.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–10, Supplementary Tables 1–5 and Supplementary Note (PDF 1425 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brown, A., Fisher, D., Kouranova, E. et al. Whole-rat conditional gene knockout via genome editing. Nat Methods 10, 638–640 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2516
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2516
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
Establishment of a Cre-rat resource for creating conditional and physiological relevant models of human diseases
Transgenic Research (2021)
-
PKCζ facilitates lymphatic metastatic spread of prostate cancer cells in a mice xenograft model
Oncogene (2019)
-
CLICK: one-step generation of conditional knockout mice
BMC Genomics (2018)
-
From engineering to editing the rat genome
Mammalian Genome (2017)
-
Genome editing revolutionize the creation of genetically modified pigs for modeling human diseases
Human Genetics (2016)