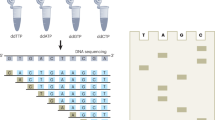
Abstract
We synthesized reversible terminators with tethered inhibitors for next-generation sequencing. These were efficiently incorporated with high fidelity while preventing incorporation of additional nucleotides, and we used them to sequence canine bacterial artificial chromosomes in a single-molecule system that provided even coverage for over 99% of the region sequenced. This single-molecule approach generated high-quality sequence data without the need for target amplification and thus avoided concomitant biases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kahvejian, A., Quackenbush, J. & Thompson, J.F. Nat. Biotechnol. 26, 1125–1133 (2008).
Mardis, E.R. Trends Genet. 24, 133–141 (2008).
Dohm, J.C., Lottaz, C., Borodina, T. & Himmelbauer, H. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, e105 (2008).
Braslavsky, I., Hebert, B., Kartalov, E. & Quake, S.R. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 3960–3964 (2003).
Harris, T.D. et al. Science 320, 106–109 (2008).
Bentley, D.R. et al. Nature 456, 53–59 (2008).
Ju, J. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 19635–19640 (2006).
Wu, W. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 6339–6349 (2007).
Kuchta, R.D. et al. Biochemistry 26, 8410–8417 (1987).
Bebenek, K., Joyce, C.M., Fitzgerald, M.P. & Kunkel, T.A. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 13878–13887 (1990).
Acknowledgements
We thank all of the past and present colleagues at Helicos who have contributed to this work. This work was made possible by grant number R01 HG004144 from the National Human Genetics Research Institute (NHGRI) at the US National Institutes of Health. Contents of this paper are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of NHGRI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.M., J.W.E., E.K.-O., S.M., A.R. and S.M.S. synthesized and/or designed new compounds. J.B., E.B. and P.M. designed and executed biochemical assays. M.C., M.J., L.K., G.M.L., A.P. and K.S. sequenced DNA samples. M.C., M.J., L.K., D.L., G.M.L. and A.P. analyzed sequencing data. J.B., J.M., E.K.-O., S.M.S. and J.F.T. wrote the manuscript. J.B., P.R.B., M.C., J.W.E., M.J. and S.M.S. supervised and managed the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
J.B, J.M., E.B., P.R.B., M.C., J.W.E., M.J., E.K.-O., L.K., D.L., G.M.L., S.M., P.M., A.P., A.R., S.M.S., K.S. and J.F.T. are present or former employees of Helicos BioSciences.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–4, Supplementary Tables 1–3, Supplementary Note (PDF 592 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bowers, J., Mitchell, J., Beer, E. et al. Virtual terminator nucleotides for next-generation DNA sequencing. Nat Methods 6, 593–595 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1354
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1354
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
Biological big-data sources, problems of storage, computational issues, and applications: a comprehensive review
Knowledge and Information Systems (2024)
-
DNA synthesis technologies to close the gene writing gap
Nature Reviews Chemistry (2023)
-
Development of a sequencing system for spatial decoding of DNA barcode molecules at single-molecule resolution
Communications Biology (2020)
-
DNA sequencing using nanopores and kinetic proofreading
Quantitative Biology (2020)