Abstract
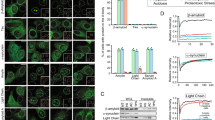
Recent reports suggest that some commonly used nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) unexpectedly shift the cleavage products of amyloid precursor protein (APP) to shorter, less fibrillogenic forms, although the underlying mechanism remains unknown. We now demonstrate, using a fluorescence resonance energy transfer method, that Aβ42-lowering NSAIDs specifically affect the proximity between APP and presenilin 1 and alter presenilin 1 conformation both in vitro and in vivo, suggesting a novel allosteric mechanism of action.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weggen, S. et al. Nature 414, 212–216 (2001).
Lim, G.P. et al. J. Neurosci. 20, 5709–5714 (2000).
Jantzen, P.T. et al. J. Neurosci. 22, 2246–2254 (2002).
Yan, Q. et al. J. Neurosci. 23, 7504–7509 (2003).
Eriksen, J.L. et al. J. Clin. Invest. 112, 440–449 (2003).
Weggen, S. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 31831–31837 (2003).
Berezovska, O. et al. J. Neurosci. 23, 4560–4566 (2003).
Annaert, W.G. et al. Neuron 32, 579–589 (2001).
Kornilova, A.Y., Das, C. & Wolfe, M.S. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 16470–16473 (2003).
Esler, W.P. et al. Nat. Cell Biol. 2, 428–434 (2000).
Berezovska, O. et al. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 69, 273–280 (1999).
Fukumoto, H. et al. Am. J. Pathol. 164, 719–725 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We thank T. Südhof (University of Texas, Southwestern Medical Center) for the APP-Gal4 constructs, D. Selkoe and M. Wolfe (Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts) for PS1 antibodies, and WPE-III-31C and DAPT and H. Fukumoto (Takeda Industries, Osaka, Japan) for assistance with the Aβ ELISAs. This study was supported by US National Institutes of Health AG15379, a Pioneer Award from the Alzheimer Association (B.T.H.), a Hoffmann Fellowship (A.L.), NIH EB00768 (B.J.B.) and a Paul Beeson Physician Faculty Scholar in Aging Research Award (M.P.F).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Effects of NSAIDs on Aβ secretion. (PDF 366 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
NSAIDs do not inhibit BACE or γ-secretase. (PDF 361 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
FLIM assay of proximity between APP and PS1. (PDF 305 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
Some NSAIDs change PS1 conformation assessed by FLIM. (PDF 21 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lleó, A., Berezovska, O., Herl, L. et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs lower Aβ42 and change presenilin 1 conformation. Nat Med 10, 1065–1066 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1112
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1112
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
Targeting Common Signaling Pathways for the Treatment of Stroke and Alzheimer’s: a Comprehensive Review
Neurotoxicity Research (2021)
-
Novel botanical drug DA-9803 prevents deficits in Alzheimer’s mouse models
Alzheimer's Research & Therapy (2018)
-
Dynamic Nature of presenilin1/γ-Secretase: Implication for Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis
Molecular Neurobiology (2018)
-
Dynamic presenilin 1 and synaptotagmin 1 interaction modulates exocytosis and amyloid β production
Molecular Neurodegeneration (2017)
-
Identification of the novel activity-driven interaction between synaptotagmin 1 and presenilin 1 links calcium, synapse, and amyloid beta
BMC Biology (2016)