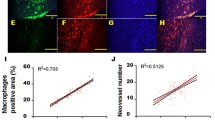
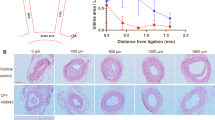
Abstract
We postulated that activation of a genetic program that tonicaiiy inhibits intimal cell death is a necessary condition for the pathogenesis of vascular disease. Studies of vascular lesions in humans and animal models documented increased expression of the anti-apoptotic gene product Bcl-xL within intimal cells. Downregulation of intimal cell bcl-xL expression with the use of antisense oligonucleotides induced apoptosis and acute regression of vascular lesions. These findings indicate that apoptosis regulatory genes such as bcl-xL are critical determinants of intimal lesion formation and that targeted apoptosis may be a novel therapy for intimal vascular disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Han, D.K.M. et al. Evidence for apoptosis in human atherogenesis and in a rat vascular injury model. Am. J. Pathol. 147, 267–277 (1995).
Geng, Y.J. & Libby, P. Evidence for apoptosis in advanced human atheroma: Colocalization with interleukin-1 β-converting enzyme. Am. J. Pathol. 147, 251–266 (1995).
Isner, J.M., Kearney, M., Bortman, S. & Passeri, J. Apoptosis in human atherosclerosis and restenosis. Circulation. 91, 2703–2711 (1995).
Bochaton-Piallat, M.L., Gabbiani, F., Redard, M., Desmouliere, A. & Cabbiani, G. Apoptosis participates in cellularity regulation during rat aortic intimal thickening. Am. J. Pathol. 146, 1059–1064 (1995).
Perlman, H., Maillard, L., Krasinski, K. & Walsh, K. Evidence for the rapid onset of apoptosis in medial smooth muscle cells after balloon injury. Circulation 95, 981–987(1997).
Sedlak, T.W. et al. Multiple Bcl-2 family members demonstrate selective dimeriza-tionswith Bax. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 7834–7838 (1995).
Gajewski, T.F. & Thompson, C.B. Apoptosis meets signal transduction: Elimination of a BAD influence. Cell 87, 589–592 (1996).
Golstein, P. Controlling cell death. Science 275, 1081 1082 (1997).
Cheng, E.H., Levine, B., Boise, L.H., Thompson, C.B. & Hardwick, J.M. Bax-inde-pendent inhibition of apoptosis by Bcl-XL. Nature 379, 554–556 (1996).
Zha, J. et al. BH3 domain of BAD is required for heterodimerization with BCL-XL and pro-apoptotic activity. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 24101–24104 (1997).
Chinnaiyan, A.M., O'Rourke, K., Lane, B.R. & Dixit, V.M. Interaction of CED-4 with CED-3 and CED-9: A molecular framework for cell death. Science 275, 122–126 (1997).
Motoyama, N. et al. Massive cell death of immature hematopoietic cells and neurons in bcl-x-deficient mice. Science 267, 1506–1510 (1995).
Schwartz, S.M., deBlois, D. & O'Brien, E.R. The intima: Soil for atherosclerosis and restenosis. Ore Res. 77, 445–465 (1995).
Morishita, R. et al. Single intraluminal delivery of antisense cdc2 kinase and prolifer-ating-cell nuclear antigen oligonucleotides results in chronic inhibition of neointimal hyperplasia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 8474–8478 (1993).
Mann, M. et al. Genetic engineering of vein grafts resistant to atherosclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 4502–4506 (1995).
Wagner, R.W. Gene inhibition using antisense oligonucleotides. Nature 372, 333–335 (1994).
Burgess, T.L. et al. The antiproliferative activity of c-myb and c-myc antisense oligonucleotides in smooth muscle cells is caused by a nonantisense mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 4051–4055 (1995).
Boise, L.H. et al. Bcl-x, a bcl-2-related gene that functions as a dominant regulator of apoptotic cell death. Cell 74, 597–608 (1993).
Minn, A.J., Boise, L.H. & Thompson, C.B. Bcl-x(S) antagonizes the protective effects of Bcl-x(L). J. Biol. Chem. 271, 6306–6312 (1996).
Faxon, D.P. et al. Acute effects of transluminal angioplasty in three experimental models of atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis 2, 125–133 (1982).
Shinomiya, M., Shirai, K., Saito, Y. & Yoshida, S. Inhibition of intimal thickening of the carotid artery of rabbits and of outgrowth of explants of aorta by probucol. Atherosclerosis 97, 143–148 (1992).
Morishita, R, et al. Intimal hyperplasia after vascular injury is inhibited by antisense cdk 2 kinase oligonucleotides. J. Clin. Invest. 93, 1458–1464 (1994).
Pollman, M.J., Yamada, T., Horiuchi, M. & Gibbons, G.H. Vasoactive substances regulate vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis: Countervailing influences of nitric oxide and angiotensin II. Circ. Res. 79, 748–756 (1996).
Gavrieli, Y., Sherman, Y. & Ben-Sasson, S.A. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J. Cell Biol. 119, 493–501 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pollman, M., Hall, J., Mann, M. et al. Inhibition of neointimal cell bcl-x expression induces apoptosis and regression of vascular disease. Nat Med 4, 222–227 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0298-222
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0298-222
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
Ferroptotic stress facilitates smooth muscle cell dedifferentiation in arterial remodelling by disrupting mitochondrial homeostasis
Cell Death & Differentiation (2023)
-
Different types of cell death in vascular diseases
Molecular Biology Reports (2021)
-
SRSF1 promotes vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation through a Δ133p53/EGR1/KLF5 pathway
Nature Communications (2017)
-
Nrf2/Keap1 system regulates vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis for vascular homeostasis: role in neointimal formation after vascular injury
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Migration of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Treated Rat Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells
Cardiovascular Toxicology (2016)