Abstract
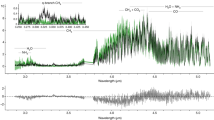
The planet in the system HD209458 is the first one for which repeated transits across the stellar disk have been observed1,2. Together with radial velocity measurements3, this has led to a determination of the planet's radius and mass, confirming it to be a gas giant. But despite numerous searches for an atmospheric signature4,5,6, only the dense lower atmosphere of HD209458b has been observed, through the detection of neutral sodium absorption7. Here we report the detection of atomic hydrogen absorption in the stellar Lyman α line during three transits of HD209458b. An absorption of 15 ± 4% (1σ) is observed. Comparison with models shows that this absorption should take place beyond the Roche limit and therefore can be understood in terms of escaping hydrogen atoms.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Henry, G. W., Marcy, G. W., Butler, R. P. & Vogt, S. S. A transiting “51 Peg-like” planet. Astrophys. J. 529, L41–L44 (2000)
Charbonneau, D., Brown, T. M., Latham, D. W. & Mayor, M. Detection of planetary transits across a Sun-like star. Astrophys. J. 529, L45–L48 (2000)
Mazeh, T. et al. The spectroscopic orbit of the planetary companion transiting HD 209458. Astrophys. J. 532, L55–L58 (2000)
Bundy, K. A. & Marcy, G. W. A search for transit effects in spectra of 51 Pegasi and HD 209458. Proc. Astron. Soc. Pacif. 112, 1421–1425 (2000)
Rauer, H., Bockelée-Morvan, D., Coustenis, A., Guillot, T. & Schneider, J. Search for an exosphere around 51 Pegasi B with ISO. Astron. Astrophys. 355, 573–580 (2000)
Moutou, C. et al. Search for spectroscopical signatures of transiting HD 209458b's exosphere. Astron. Astrophys. 371, 260–266 (2001)
Charbonneau, D., Brown, T. M., Noyes, R. W. & Gilliland, R. L. Detection of an extrasolar planet atmosphere. Astrophys. J. 568, 377–384 (2002)
Vidal-Madjar, A. Evolution of the solar lyman alpha flux during four consecutive years. Sol. Phys. 40, 69–86 (1975)
Lemaire, P. et al. in Proc. Symp. SOHO 11, From Solar Min to Max: Half a Solar Cycle with SOHO (ed. Wilson, A.) 219–222 (ESA SP-508, ESA Publications Division, Noordwijk, 2002)
Prinz, D. K. The spatial distribution of Lyman alpha on the Sun. Astrophys. J. 187, 369–375 (1974)
Paczynski, B. Evolutionary processes in close binary systems. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 9, 183–208 (1971)
Cumming, A., Marcy, G. W., Butler, R. P. & Vogt, S. S. The statistics of extrasolar planets: Results from the Keck survey. Preprint astro-ph/0209199 available at 〈http://xxx.lanl.gov〉 (2002).
Konacki, M., Torres, G., Jha, S. & Sasselov, D. D. An extrasolar planet that transits the disk of its parent star. Nature 421, 507–509 (2003)
Acknowledgements
This work is based on observations with the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, obtained at the Space Telescope Science Institute, which is operated by AURA, Inc. We thank M. Lemoine, L. Ben Jaffel, C. Emerich, P. D. Feldman and J. McConnell for comments, J. Herbert and W. Landsman for conversations on STIS data reduction, and J. Valenti for help in preparing the observations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vidal-Madjar, A., des Etangs, A., Désert, JM. et al. An extended upper atmosphere around the extrasolar planet HD209458b. Nature 422, 143–146 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01448
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01448
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
The Colorado Ultraviolet Transit Experiment (CUTE) signal to noise calculator
Astrophysics and Space Science (2023)
-
Indian spectroscopic and imaging space telescope (INSIST): An optics design trade-off study
Journal of Astrophysics and Astronomy (2023)
-
The escape mechanisms of the proto-atmosphere on terrestrial planets: “boil-off” escape, hydrodynamic escape and impact erosion
Acta Geochimica (2022)
-
The search for living worlds and the connection to our cosmic origins
Experimental Astronomy (2022)
-
Closing gaps to our origins
Experimental Astronomy (2022)