Abstract
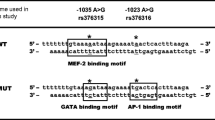
Genetic studies have shown linkages for asthma to the chromosomal region 5q31–q33 in humans that includes the IL-9 gene. An A-to-G base substitution has been identified at bp −351 in the IL-9 promoter. The role of this polymorphism in IL-9 promoter function was assessed utilizing CD4+ T cells purified from individuals with one or two of the G alleles in comparison to those homozygous for the wild-type A. The presence of an A at –351 (A allele) increased mitogen-stimulated IL-9 transcription twofold in comparison to subjects with one or two G alleles at this position. Binding of nuclear extract proteins from IL-9-producing human cell lines to DNA sequences including this base exchange demonstrated specific binding of the transcription factor NF-κB. Binding of NF-κB to the IL-9 promoter was confirmed in vivo using the chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. Recombinant NF-κB bound to a promoter fragment with the A allele with fivefold higher affinity than it did to a promoter with the G allele. Individuals carrying the A allele of the IL-9 promoter display increased synthesis of IL-9, which may result in strong Th2 immune responses and a modulation of their susceptibility to infectious, neoplastic, parasitic or atopic disease.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borish LC, Steinke JW . Cytokines and chemokines. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003; 111: S460–S475.
Hultner L, Moeller J . Mast cell growth-enhancing activity (MEA) stimulates interleukin 6 production in a mouse bone marrow-derived mast cell line and a malignant subline. Exp Hematol 1990; 18: 873–877.
Renauld J-C, Kermouni A, Vink A, Louahed J, Van Snick J . Interleukin-9 and its receptor: involvement in mast cell differentiation and T cell oncogenesis. J Leukoc Biol 1995; 57: 353–360.
Louahed J, Kermouni A, Van Snick J, Renauld J-C . IL-9 induces expression of granzymes and high-affinity IgE receptor in murine T helper clones. J Immunol 1995; 154: 5061–5070.
Hultner L, Druez C, Moeller J, Uyttenhove C, Schmitt E, Rüde E et al. Mast cell growth-enhancing activity (MEA) is structurally related and functionally identical to the novel mouse T cell growth factor P40/TCGFIII (interleukin 9). Eur J Immunol 1990; 20: 1413–1416.
Gounni AS, Gregory B, Nutku E, Aris F, Latifa K, Minshall E et al. Interleukin-9 enhances interleukin-5 receptor expression, differentiation, and survival of human eosinophils. Blood 2000; 96: 2163–2171.
Erpenbeck VJ, Hohlfeld JM, Volkmann B, Hagenberg A, Geldmacher H, Braun A et al. Segmental allergen challenge in patients with atopic asthma leads to increased IL-9 expression in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid lymphocytes. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003; 111: 1319–1327.
Dong Q, Louahed J, Vink A, Sullivan CD, Messler CJ, Zhou Y et al. IL-9 induces chemokine expression in lung epithelial cells and baseline airway eosinophilia in transgenic mice. Eur J Immunol 1999; 29: 2130–2139.
Louahed J, Toda M, Jen J, Hamid Q, Renauld JC, Levitt RC et al. Interleukin-9 upregulates mucus expression in the airways. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2000; 22: 649–656.
Merz H, Houssiau FA, Orscheschek K, Renauld JC, Fliedner A, Herin M et al. Interleukin-9 expression in human malignant lymphomas: unique association with Hodgkin's disease and large cell anaplastic lymphoma. Blood 1991; 78: 1311–1317.
Bleeker ER, Amelung PJ, Levitt RC, Postma DS, Meyers DA . Evidence for linkage of total serum IgE and bronchial hyperresponsiveness to chromosome 5q: a major regulatory locus important in asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 1995; 25: S84–S88.
Doull IJ, Lawrence S, Watson M, Begishvili T, Beasley RW, Lampe F et al. Allelic association of gene markers on chromosomes 5q and 11q with atopy and bronchial hyperreponsiveness. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996; 153: 1280–1284.
Nicolaides NC, Holroyd KJ, Ewart SL, Eleff SM, Kiser MB, Dragwa CR et al. Interleukin 9: a candidate gene for asthma. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1997; 94: 13175–13180.
Marsh DG, Neely JD, Breazeale DR, Ghosh B, Freidhoff LR, Ehrlich-Kautzky E et al. Linkage analysis of IL4 and other chromosome 5q31.1 markers and total serum immunoglobulin E concentrations. Science 1994; 264: 1152–1156.
Hobbs K, Negri J, Klinnert M, Rosenwasser LJ, Borish L . Interleukin-10 and transforming growth factor-beta promoter polymorphisms in allergies and asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998; 158: 1958–1962.
Steinke JW, Barekzi E, Hagman J, Borish L . Functional analysis of −571 IL-10 promoter polymorphism reveals a repressor element controlled by Sp1. J Immunol 2004; 173: 3215–3222.
Rosenwasser LJ, Klemm DJ, Dresback JK, Inamura H, Mascali JJ, Klinnert M et al. Promoter polymorphisms in the chromosome 5 gene cluster in asthma and atopy. Clin Exp Allergy 1995; 25 (Suppl. 2): 74–78.
Song Z, Casolaro V, Chen R, Georas SN, Monos D, Ono SJ . Polymorphic nucleotides within the human IL-4 promoter that mediate overexpression of the gene. J Immunol 1996; 156: 424–429.
LeVan TD, Bloom JW, Bailey TJ, Karp CL, Halonen M, Martinez FD et al. A common single nucleotide polymorphism in the CD14 promoter decreases the affinity of Sp protein binding and enhances transcriptional activity. J Immunol 2001; 167: 5838–5844.
Nickel RG, Caslaro V, Wahn U, Beyer K, Barnes KC, Plunkett BS et al. Atopic dermatitis is associated with a functional mutation in the promoter of the C-C chemokine RANTES. J Immunol 2000; 164: 1612–1616.
Yao T, Kuo M, See L, Chen LC, Yan DC, Ou LS et al. The RANTES promoter polymorphism: A genetic risk factor for near-fatal asthma in Chinese children. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003; 111: 1285–1292.
Mormann M, Rieth H, Hua TD, Assohou C, Roupelieva M, Hu SL et al. Mosaics of gene variations in the interleukin-10 gene promoter affect interleukin-10 production depending on the stimulation used. Genes Immun 2004; 5: 246–255.
Steinke JW, Barekzi E, Huyett P, Borish L . Differential interleukin-10 production stratified by −571 promoter polymorphism in purified human immune cells. Cell Immunol 2007; 249: 101–107.
Stassen M, Muller C, Arnold M, Hültner L, Klein-Hessling S, Neudörfl C et al. IL-9 and IL-13 production by activated mast cells is strongly enhanced in the presence of lipopolysaccharide: NF-κB is decisively involved in the expression of IL-9. J Immunol 2001; 166: 4391–4398.
Baldwin Jr AS . The NF-κB and IκB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol 1996; 14: 649–681.
Kuriyan J, Thanos D . Structure of the NF-κB transcription factor: a holistic interaction with DNA. Structure 1995; 3: 135–141.
Shimbara A, Christodoulopoulos P, Soussi-Gounni A, Olivenstein R, Nakamura Y, Levitt RC et al. IL-9 and its receptor in allergic and nonallergic disease: increased expression in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2000; 105: 108–115.
Tsicopoulos A, Shimbara A, de Nadai P, Aldewachi O, Lamblin C, Lassalle P et al. Involvement of IL-9 in the bronchial phenotype of patients with nasal polyposis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004; 113: 462–469.
Faulkner H, Humphreys N, Renauld JC, Van Snick J, Grencis R . Interleukin-9 is involved in host protective immunity to intestinal nematode infection. Eur J Immunol 1997; 27: 2536–2540.
Gilmelius I, Edstrom A, Amini RM, Fischer M, Nilsson G, Sundström C et al. IL-9 expression contributes to the cellular composition in Hodgkin lymphoma. Eur J Haematol 2006; 76: 278–283.
Wang TN, Chen WY, Huang YF, Shih NH, Feng WW, Tseng HI et al. The synergistic effects of the IL-9 gene and environmental exposures on asthmatic Taiwanese families as determined by the transmission/disequilibrium test. Int J Immunogenet 2006; 33: 105–110.
Steinke JW, Crouse CD, Bradley D, Hise K, Lynch K, Kountakis SE et al. Characterization of interleukin-4 stimulated nasal polyp fibroblasts. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2004; 30: 212–219.
Hagman J, Travis A, Grosschedl R . A novel lineage-specific nuclear factor regulates mb-1 gene transcription at the early stages of B cell differentiation. EMBO J 1991; 10: 3409–3417.
Fitzsimmons D, Hodson W, Wheat W, Maira SM, Wasylyk B, Hagman J . Pax-5 (BSAP) recruits Ets proto-oncogene family proteins to form functional ternary complexes on a B-cell-specific promoter. Genes Dev 1996; 10: 2198–2211.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH AI01793.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Early, S., Huyett, P., Brown-Steinke, K. et al. Functional analysis of −351 interleukin-9 promoter polymorphism reveals an activator controlled by NF-κB. Genes Immun 10, 341–349 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2009.28
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2009.28
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Regulatory T cells and immune regulation of allergic diseases: roles of IL-10 and TGF-β
Genes & Immunity (2014)
-
NF-κB in immunobiology
Cell Research (2011)
-
A new association between polymorphisms of the SLC6A7 gene in the chromosome 5q31–32 region and asthma
Journal of Human Genetics (2010)