Abstract
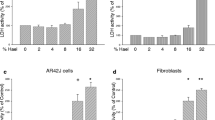
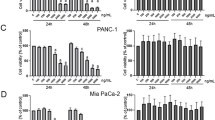
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) has been shown to have an inhibitory effect on the growth of several pancreatic cancer cell lines in vitro. This study investigates the mechanism of growth inhibition and cytotoxicity of EPA on the pancreatic cancer cell line MIA PaCa-2. Cells were analysed for cell count, viability, cell cycle distribution and ultrastructural changes. There was a time- and dose-dependent decrease in cell count and viability in cultures of pancreatic cancer cells supplemented with EPA. Flow cytometric DNA analysis of MIA PaCa-2 cells incubated with EPA demonstrated the presence of sub G1 populations corresponding to the presence of apoptotic cells and the blockade of cell cycle progression in S-phase and G2/M-phase. The presence of apoptosis in EPA-supplemented cultures was further confirmed by DNA fragmentation and ultrastructural changes associated with apoptosis. Therefore, we conclude that EPA mediates its effect on the pancreatic cancer cell line MIA PaCa-2, at least in part, via cell cycle arrest and the induction of apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, P., Ross, J., Fearon, K. et al. Cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells exposed to eicosapentaenoic acid in vitro. Br J Cancer 74, 1375–1383 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1996.552
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1996.552
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Krill oil extract suppresses cell growth and induces apoptosis of human colorectal cancer cells
BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine (2016)
-
Effects of n-3 PUFAs on breast cancer cells through their incorporation in plasma membrane
Lipids in Health and Disease (2011)
-
Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation in Cancer Therapy
Strahlentherapie und Onkologie (2011)
-
The inhibitory action of long‐chain fatty acids on the DNA binding activity of p53
Lipids (2006)