Abstract
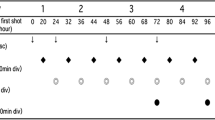
A phase I study was designed to assess whether dose intensity of an 'accelerated' cyclophosphamide-doxorubicin-etoposide (CDE) regimen plus granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) could be increased further, in an outpatient setting, by escalating the dose of each single drug of the regimen. Patients with previously untreated small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) received escalating doses of cyclophosphamide (C) 1100-1300 mg m-2 intravenously (i.v.) on day 1, doxorubicin (D) 50-60 mg m-2 i.v. on day 1, etoposide (E) 110-130 mg m-2 i.v. on days 1, 2, 3 and every 14 days for at least three courses. Along with chemotherapy, G-CSF (filgastrim) 5 micrograms kg-1 from day 5 to day 11 was administered subcutaneously (s.c.) to all patients. Twenty-five patients were enrolled into the study. All patients at the first dose level (C 1100, D 50, E 110 x 3) completed three or more cycles at the dose and schedule planned by the protocol and no 'dose-limiting toxicity' (DLT) was seen. At the second dose level (C 1200, D 55, E 120 x 3) three out of five patients had a DLT consisting of 'granulocytopenic fever' (GCPF). Another six patients were treated at this dose level with the addition of ciprofloxacin 500 mg twice a day and only two patients had a DLT [one episode of documented oral candidiasis and one of 'fever of unknown origin' (FUO) with generalised mucositis]. Accrual of patients proceeded to the third dose level (C 1300, D 60, E 130 x 3) with the prophylactic use of ciprofloxacin. Four out of six patients experienced a DLT consisting of GCPF or documented non-bacterial infection. Accrual of patients at the third dose level was then resumed adding to ciprofloxacin anti-fungal prophylaxis (fluconazole 100 mg daily) and anti-viral prophylaxis (acyclovir 800 mg twice a day) from day 5 to 11. Out of five patients treated three experienced a DLT consisting of severe leucopenia and fever or infection. With a simultaneous dose escalation and schedule acceleration it is indeed possible to take maximum advantage of G-CSF activity and to increase CDE dose intensity by a factor 1.65-1.80 for a maximum of 3-4 courses. The role of antimicrobial prophylaxis in this setting deserves to be investigated further.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ardizzoni, A., Pennucci, M., Danova, M. et al. Phase I study of simultaneous dose escalation and schedule acceleration of cyclophosphamide-doxorubicin-etoposide using granulocyte colony-stimulating factor with or without antimicrobial prophylaxis in patients with small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 74, 1141–1147 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1996.504
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1996.504
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
A systematic review of dental disease management in cancer patients
Supportive Care in Cancer (2018)
-
A systematic review of dental disease in patients undergoing cancer therapy
Supportive Care in Cancer (2010)