Abstract
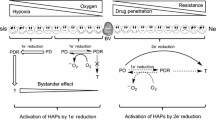
SR 4233 (3-amino-1,2,4-benzotriazine 1,4-dioxide, WIN 59075, tirapazamine) is the lead compound in a new class of bioreductive anticancer drugs, the benzotriazine di-N-oxides. It is currently undergoing Phase I clinical testing. The preferential tumour cell killing of SR 4233 is a result of its high specific toxicity to cells at low oxygen tensions. Such hypoxic cells are a common feature of solid tumours, but not normal tissues, and are resistant to cancer therapies including radiation and some anticancer drugs. The killing of these tumour cells by SR 4233, particularly when given on multiple occasions, can increase total tumour cell killing by fractionated irradiation by several orders of magnitude without increasing toxicity to surrounding normal tissues. Topics covered in this review include the rationale for developing a hypoxic cytotoxic agent, the cytotoxicity of SR 4233 as a function of oxygen concentration, the mechanism of action of the drug and its intracellular target and the in vivo evidence that the drug may be useful as an adjunct both to radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Finally, the major unanswered questions on the drug are outlined.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brown, J. SR 4233 (Tirapazamine): a new anticancer drug exploiting hypoxia in solid tumours. Br J Cancer 67, 1163–1170 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1993.220
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1993.220
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Electronic structure and reactivity of tirapazamine as a radiosensitizer
Journal of Molecular Modeling (2021)
-
A rat toxicological study of intra-arterial injection of Tirapazamine, a hypoxia-activating Cancer therapeutic agent, followed by hepatic artery ligation
Investigational New Drugs (2021)
-
Perfluorocarbon regulates the intratumoural environment to enhance hypoxia-based agent efficacy
Nature Communications (2019)
-
A microfluidic chip of multiple-channel array with various oxygen tensions for drug screening
Microfluidics and Nanofluidics (2016)