Abstract
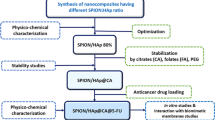
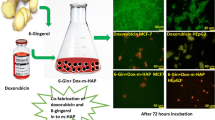
We performed an experimental study on slow releasing anticancer drug implantation treatment as a new therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hydroxyapatite (HAP) was chosen for the carrier material and doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX) for anticancer agent. DOX-HAP was produced by adsorbing DOX to porous HAP particles of 1375 +/- 125 microns diameter using the freeze drying method. In vitro experiments showed slow release of the drug resulting in the steady release of DOX from HAP for 1 month duration. In healthy white rabbits with DOX-HAP implantation in the liver, serum DOX was not detectable, and DOX release rate was stable at the implanted region after 7, 14, and 21 days. When DOX-HAP (DOX; 100 mg kg-1) was administered to mice with sarcoma 180, an improved survival rate was observed without acute toxicity. We also found that VX2 liver tumour growth on white rabbit was inhibited by implantation of DOX-HAP, without acute toxicity. We hope that DOX-HAP implantation therapy will open up new avenues for the treatment of hepatoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kunieda, K., Seki, T., Nakatani, S. et al. Implantation treatment method of slow release anticancer doxorubicin containing hydroxyapatite (DOX-HAP) complex. A basic study of a new treatment for hepatic cancer. Br J Cancer 67, 668–673 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1993.124
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1993.124
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Safety evaluation of nanodiamond-doxorubicin complexes in a Naïve Beagle canine model using hematologic, histological, and urine analysis
Nano Research (2022)
-
Preparation of microstructured hydroxyapatite microspheres using oil in water emulsions
Bulletin of Materials Science (2005)