Abstract
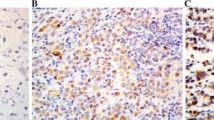
Eighty-two per cent of tumour sections from 105 patients with lung cancer showed positive immunocytochemical localization of an anti-carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) immunoglobulin free of antibody to normal cross-reacting antigen (NCA). The highest incidence was found in adenocarcinomas, and no association between staining and disease stage was found. There was a relationship between positive-staining tumours and preoperative and postoperative serum CEA levels of greater than or equal to 20 ng/ml, but the high incidence of CEA+, less than 20 ng/ml serum patients indicated that immunocytochemical localization was of little value in selecting patients for sequential serum monitoring. Staining for CEA was not prognostic but a preoperative serum CEA levels greater than or equal to 20 ng/ml was associated with a poor prognosis in patients undergoing radical surgery for lung cancer (P = 0.043). this prognostic effect of CEA was seen mainly in patients whose tumours showed the greatest immunocytochemical localization (P = 0.017) and in Stage III patients (P = 0.04).
Similar content being viewed by others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ford, C., Stokes, H. & Newman, C. Carcinoembryonic antigen and prognosis after radical surgery for lung cancer: Immunocytochemical localization and serum levels. Br J Cancer 44, 145–153 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1981.164
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1981.164
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Development and validation of a preoperative prognostic index independent of TNM stage in resected non-small cell lung cancer
BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2017)
-
History, molecular features, and clinical importance of conventional serum biomarkers in lung cancer
Surgery Today (2017)
-
Paper-based upconversion fluorescence resonance energy transfer biosensor for sensitive detection of multiple cancer biomarkers
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Brain metastasis development and poor survival associated with carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) level in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a prospective analysis
BMC Cancer (2009)
-
Carcinoembryonic antigen expression in gastric cancer as related to biological behaviour and prognosis
Chinese Journal of Cancer Research (1996)