Abstract
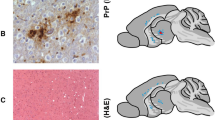
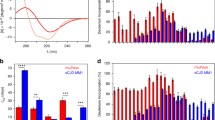
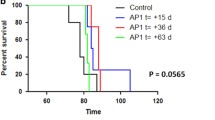
ACCUMULATION of the prion protein PrPSc, a pathological and protease-resistant isoform of the normal host protein PrPc, is a feature of prion disease such as scrapie1,2. It is still unknown whether scrapie pathology comes about by neurotoxicity of PrPSc, acute depletion of PrPc, or some other mechanism. Here we investigate this question by grafting neural tissue overexpressing PrPc into the brain of PrP-deficient mice which are scrapie-resistant and do not propagate infectivity3–5. After intracerebral inoculation with scrapie prions, the grafts accumulated high levels of PrPSc and infectivity and developed the severe histopathological changes characteristic of scrapie. Moreover, substantial amounts of graft-derived PrPSc migrated into the host brain. Even 16 months after inoculation no pathological changes were seen in PrP-deficient tissue, not even in the immediate vicinity of the grafts. Therefore, in addition to being resistant to scrapie infection, brain tissue devoid of PrPc is not damaged by exogenous PrPSc.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prusiner, S. B. A. Rev. Microbiol. 48, 655–686 (1994).
Weissmann, C. Trends Cell Biol. 4, 10–14 (1994).
Büeler, H. R. et al. Nature 356, 577–582 (1992).
Büeler, H. R. et al. Cell 73, 1339–1347 (1993).
Sailer, A., Büeler, H., Fischer, M., Aguzzi, A. & Weissmann, C. Cell 77, 967–968 (1994).
Fischer, M. et al. EMBO J. (in the press).
Taraboulos, A. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 7620–7624 (1992).
Isenmann, S., Brandner, S., Sure, U. & Aguzzi, A. Neuropathol. appl. Neurobiol. (in the press).
Jeffrey, M. et al. Neurosci. Lett. 174, 39–42 (1994).
Manson, J. C. et al. Molec. Neurobiol. 8, 121–127 (1994).
Jeffrey, M. et al. Brain Res. 656, 329–343 (1994).
Forloni, G. et al. Nature 362, 543–546 (1993).
Müller, W. E. et al. Eur. J. Pharmac. 246, 261–267 (1993).
Collinge, J. et al. Lancet 336, 7–9 (1990).
Hayward, P. A., Bell, J. E. & Ironside, J. W. Neuropath. appl. Neurobiol. 20, 375–383 (1994).
Shyng, S. L., Huber, M. T. & Harris, D. A. J. biol. Chem. 268, 15922–15928 (1993).
Büeler, H. et al. Molec. Med. 1, 19–30 (1994).
Manson, J. C., Clarke, A. R., McBride, P. A., McConnell, I. & Hope, J. Neurodegeneration 3, 331–340 (1994).
Collinge, J. et al. Lancet 346, 569–570 (1995).
Reed, J. & Muench, H. Am. J. Hyg. 27, 493–497 (1938).
Prusiner, S. B. et al. Ann. Neurol. 11, 353–358 (1982).
Farquhar, C. F., Somerville, R. A. & Ritchie, L. A. J. virol. Meth. 24, 215–221 (1989).
Schaeren-Wiemers, N. & Gerfin-Moser, A. Histochemistry 100, 431–440 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brandner, S., Isenmann, S., Raeber, A. et al. Normal host prion protein necessary for scrapie-induced neurotoxicity. Nature 379, 339–343 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/379339a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/379339a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Genetically engineered cellular models of prion propagation
Cell and Tissue Research (2023)
-
Extracellular vesicles with diagnostic and therapeutic potential for prion diseases
Cell and Tissue Research (2023)
-
Mechanisms of prion-induced toxicity
Cell and Tissue Research (2023)
-
A conformational switch controlling the toxicity of the prion protein
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2022)
-
Non-cell autonomous astrocyte-mediated neuronal toxicity in prion diseases
Acta Neuropathologica Communications (2021)