Abstract
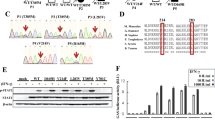
SEVERE combined immune deficiency (SCID) represents a hetero-genous group of hereditary diseases. Mutations in the common γ-chain (γc), which is part of several cytokine receptors including those for interleukin (IL)-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9 and FL-15, are responsible for X-linked SCID1,2, which is usually associated with a lack of circulating T cells and the presence of B lymphocytes (T- B+ SCID). The gene(s) responsible for autosomal recessive T- B+ SCID is still unknown. The Jak-3 protein kinase3,4 has been found to associate with the γc-chain-containing cytokine receptors4–9. Therefore Jak-3 or other STAT proteins with which it interacts10,11 are candidate genes for autosomal recessive T- B+SCID7. Here we investigate two unrelated T- B+SCID patients (both from consanguineous parents) who have homozygous mutations in the gene for Jak-3. One patient carries a mutation (TyrlOO→Cys) in a conserved tyrosine residue in the JH7 domain of Jak-3 which is absent in more than 150 investigated chromosomes. The other patient carries a homozygous 151-base-pair deletion in the kinase-like domain, leading to a frameshift and premature termination. Both mutations resulted in markedly reduced levels of Jak-3. These findings show that abnormalities in the Jak/STAT signalling pathway can account for SCID in humans.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Noguchi, M. et al. Cell 73, 147–157 (1993).
Schmaistieg, F. C. et al. J. clin. Invest. 95, 1169–1173 (1995).
Kawamura, M. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91, 6374–6378 (1994).
Witthuhn, B. A. et al. Nature 370, 153–157 (1994).
Johnston, J. A. et al. Nature 370, 151–153 (1994).
Boussiotis, V. A. et el. Science 266, 1039–1042 (1994).
Russell, S. M. Science 266, 1042–1045 (1994).
Myazaki, T. et al. Science 266, 1045–1047 (1994).
Musso, T. et al. J. exp. Med. 181, 1425–1431 (1995).
Darnell, J. E., Kerr, I. M. & Start, G. R. Science 264, 1415–1421 (1994).
Ihle, J. N. & Kerr, I. M. Trends Genet. 11, 69–74 (1995).
Cao, X. et al. Immunity 2, 223–238 (1995).
Di Santo, J. P., Muller, W., Guy-Grand, D., Fischer, A. & Rajewsky, K. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93, 377–381 (1995).
Gougeon, M.-L. et al. J. Immun. 145, 2873–2877 (1990).
Wengler, G. S., Allen, R. C., Parolini, O., Smith, H. & Conley, M. E. J. Immun. 150, 700–704 (1993).
Puck, J. M., Nussbaum, R. L. & Conley M. E. J. clin. Invest. 79, 1395–1400 (1987).
Conley, M. E. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 3090–3094 (1988).
Chomczynski, P. & Sacchi, N. Analyt. Biochem. 162, 156–159 (1987).
Villa, A. et al. Nature Genet. 9, 414–417 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Macchi, P., Villa, A., Giliani, S. et al. Mutations of Jak-3 gene in patients with autosomal severe combined immune deficiency (SCID). Nature 377, 65–68 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/377065a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/377065a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Does baricitinib reduce disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Clinical Rheumatology (2024)
-
Double-edged sword of JAK/STAT signaling pathway in viral infections: novel insights into virotherapy
Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
A review of Janus kinase inhibitors for the treatment of Covid-19 pneumonia
Inflammation and Regeneration (2023)
-
JAKs and STATs from a Clinical Perspective: Loss-of-Function Mutations, Gain-of-Function Mutations, and Their Multidimensional Consequences
Journal of Clinical Immunology (2023)
-
Janus kinase-targeting therapies in rheumatology: a mechanisms-based approach
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2022)