Abstract
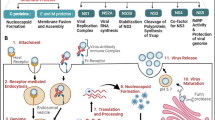
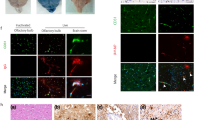
MANY people infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) develop neurological complications that can culminate in dementia and paralysis1. The discrepancy between the severity of impairment and the paucity of detectable HIV-1 within neurons has led to an intense search for diffusible virus- and host-derived factors that might be neurotoxic (see ref. 2 for review). The HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp120 is an extracellular protein that is shed from infected cells3 and so has the potential to diffuse and interact with distant uninfected brain cells. Studies on cultured immature cells suggest that gp120 induces neurotoxicity (reviewed in refs 2, 4), and systemic injection of gp120 in neonatal rats5 and intracerebroventricular injection in adult rats results in deleterious effects on the brain6,7. To assess the pathogenic potential of gp120 in the intact brain, we have now produced gp120 in the brains of transgenic mice and found a spectrum of neuronal and glial changes resembling abnormalities in brains of HIV-1-infected humans. The severity of damage correlated positively with the brain level of gp120 expression. These results provide in vivo evidence that gp120 plays a key part in HIV-1-associated nervous system impairment. This model should facilitate the evaluation and development of therapeutic strategies aimed at HIV–brain interactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Working Group of the American Academy of Neurology AIDS Task Force. Neurology 41, 778–785 (1991).
Spencer, D. C. & Price, R. W. A. Rev. Microbiol. 46, 655–693 (1992).
Schneider, J., Kaaden, O., Copeland, T. D., Oroszlan, S. & Hunsmann, G. J. gen. Virol. 67, 2533–2538 (1986).
Epstein, L. G. & Gendelman, H. E. Ann. Neurol. 33, 429–436 (1993).
Hill, J. M., Mervis, R. F., Avidor, R., Moody, T. W. & Brenneman, D. E. Brain. Res. 603, 222–223 (1993).
Kimes, A. S., London, E. D., Szabo, G., Raymon, L. & Tabakoff, B. Expl Neurol. 112, 224–228 (1991).
Glowa, J. R. et al. Brain Res. 570, 49–53 (1992).
Mucke, L., Oldstone, M. B. A., Morris, J. C. & Nerenberg, M. I. New Biol. 3, 465–474 (1991).
Mucke, L. et al. Neurobiol. Aging 13, Suppl. 1, S101 (1992).
Campbell, I. L. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 10061–10065 (1993).
Masliah, E. et al. Ann. Neurol. 32, 321–329 (1992).
Wiley, C. A. et al. Ann. Neurol. 29, 651–657 (1991).
Lipton, S. A. NeuroReport 3, 913–915 (1992).
Giulian, D., Wendt, E., Vaca, K. & Noonan, C. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 2769–2773 (1993).
Eddleston, M. P. & Mucke, L. Neuroscience 54, 15–36 (1993).
Budka, H. Brain. Path. 1, 163–175 (1991).
Abraham, C. R., Kanemaru, K. & Mucke, L. Brain Res. 621, 222–232 (1993).
Mucke, L. & Eddleston, M. FASEB J. 7, 1226–1232 (1993).
Dickson, D. W., Lee, S. C., Mattiace, L. A., Yen, S.-H. C. & Brosnan, C. Glia 7, 75–83 (1993).
Mucke, L. & Rockenstein, E. M. Transgene 1, 3–9 (1993).
Campbell, I. L., Mucke, L. & Sandberg, K. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 19, 98.2 (1993).
Freed, E. O., Myers, D. J. & Risser, R. J. Virol. 63, 4670–4675 (1989).
Miura, M., Tamura, T. & Mikoshiba, K. J. Neurochem. 55, 1180–1188 (1990).
McCune, J. M. et al. Cell 53, 55–67 (1988).
Haass, C., Hung, A. Y. & Selkoe, D. J. J. Neurosci. 11, 3783–3793 (1991).
Ratner, L. et al. AIDS. Res. hum. Retroviruses 3, 57–69 (1987).
Banker, G. A. & Cowan, W. M. Brain. Res. 126, 397–420 (1977).
Wilson, M. C. & Higgins, E. A. in Neuromethods: Molecular Neurobiological Techniques Vol. 16 (eds Boulton, A. A., Bake, G. B. & Campagnoni, A. T.) 239–284 (Humana, Clifton, New Jersey, 1989).
Masliah, E. et al. Lab. Invest 66, 285–291 (1992).
Masliah, E. et al. Expl Neurol. 113, 131–142 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toggas, S., Masliah, E., Rockenstein, E. et al. Central nervous system damage produced by expression of the HIV-1 coat protein gpl20 in transgenic mice. Nature 367, 188–193 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/367188a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/367188a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
The Impact of Cannabis Use on Cognition in People with HIV: Evidence of Function-Dependent Effects and Mechanisms from Clinical and Preclinical Studies
Current HIV/AIDS Reports (2024)
-
Kynurenic acid blunts A1 astrocyte activation against neurodegeneration in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2023)
-
Mechanisms underlying HIV-associated cognitive impairment and emerging therapies for its management
Nature Reviews Neurology (2023)
-
GP120 and tenofovir alafenamide alter cannabinoid receptor 1 expression in hippocampus of mice
Journal of NeuroVirology (2023)
-
Progress in Pathological and Therapeutic Research of HIV-Related Neuropathic Pain
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2023)