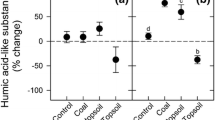
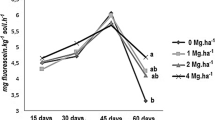
Abstract
SUBSOIL acidity is a serious problem in many tropical and sub-tropical soils1–3. The high acidity, low calcium contents and often toxic levels of soluble and/or exchangeable aluminium severely impair plant-root development in these soils1–3. The relative immobility of surface-applied liming materials limits their ability to reduce subsoil acidity. Recently, the use of gypsum or phosphogyp-sum has been advocated as an alternative to lime3–7. On the other hand, it is well known that humic substances can mobilize and form complexes with metals in soils8–11. Here we report that a newly available, coal-derived calcium-fulvate is highly efficient as a carrier of calcium in the soil profile. Moreover, subsoil pH was considerably higher when calcium-fulvate was applied to the soil surface, than when gypsum, calcium-EDTA, Ca(OH)2 or CaCO3 were applied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouldin, D. R. Cornell Int. Agria. Bull. No. 34 (1979).
Haynes, R. J. Adv. Agron. 37, 249–315 (1984).
Shainberg, I. et al. Adv. Soil Sci. 9, 1–111 (1989).
Reeve, N. G. & Sumner, M. E. Agrochemophysica 4, 1–6 (1972).
Farina, M. P. W. & Channon, P. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 52, 175–180 (1988).
Pavan, M. A., Bingham, F. T. & Pratt, P. F. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 46, 1201–1207 (1982).
Oates, K. M. & Caldwell, A. G. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 49, 915–918 (1985).
Gregor, J. E., Powell, H. K. T. & Town, R. M. J. Soil Sci. 40, 661–673 (1989).
Saar, R. A. & Weber, J. H. Environ. Sci. Tech. 16, 510A–517A (1982).
Stevenson, F. J. Humus Chemistry: Genesis, Composition Reactions (Wiley, New York, 1982).
Aiken, R. A., McKnight, D. M., Wershae, R. L. & MacCarthy, P. (eds) Humic Substances in Soil, Sediment, and Water (Wiley, New York, 1985).
Cronje, I. J. Process for the Oxidation of Coal. S. Afr. Patent 88/4770 (1988).
Lindsay, W. L. Chemical Equilibria in Soils (Wiley, New York, 1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Watt, H., Barnard, R., Cronje, I. et al. Amelioration of subsoil acidity by application of a coal-derived calcium fulvate to the soil surface. Nature 350, 146–148 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1038/350146a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/350146a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Impact of novel materials on alkalinity movement down acid soil profiles when combined with lime
Journal of Soils and Sediments (2021)
-
Soil properties and subsoil constraints of urban and peri-urban agriculture within Mahikeng city in the North West Province (South Africa)
Journal of Soils and Sediments (2018)
-
Ameliorating subsoil acidity by surface application of calcium fulvates derived from common organic materials
Biology and Fertility of Soils (1996)