Abstract
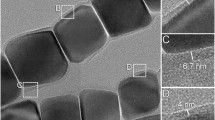
IN all magnetotactic microorganisms studied so far, the geomagnetic field is detected by magnetic particles with a permanent magnetic moment. These are crystallites enveloped by a membrane that forms the magnetosome, a specialized organelle common to magnetotactic cells1,2. To date, the magnetic crystallite of magnetotactic bacteria has been found to be magnetite, an iron-oxygen mineral3–7. Here we report the discovery of magnetic iron-sulphur crystals in a highly motile multicellular aggregate of bacteria found in brackish water with sulphide-rich sediments. The iron sulphide crystals are enveloped by amorphous or weakly crystalline regions rich in iron and oxygen, and these regions are surrounded by a membrane forming the magnetosome. The oxygen-rich region may be involved in growth of the iron sulphide crystals. The magnetosomes are found in planar groups inside the cytoplasm of each cell in the aggregate. Magnetic iron sulphide such as we describe here, which is probably pyrrhotite, may be a source of remnant magnetization in sediments and soils.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blakemore, R. P. Science 190, 377–379 (1975).
Frankel, R. B., Blakemore, R. P. & Wolfe, R. S. Science 203, 1355–1356 (1979).
Matsuda, T., Endo, J., Osakabe, N., Tonomura, A. & Arii, T. Nature 302, 411–412 (1983).
Towe, K. M. & Moench, T. T. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 52, 213–220 (1981).
Mann, S., Frankel, R. B. & Blakemore, R. P. Nature 310, 405–407 (1984).
Bazylinski, D. A., Frankel, R. B. & Jannasch, H. W. Nature 334, 518–519 (1988).
Blakemore, R. P. A Rev. Microbiol. 36, 217–238 (1982).
Farina, M., Lins de Barros, H. G. P., Esquivel, D. M. S. & Danon, J. Biol. Cell. 48, 85–86 (1983).
Lins de Barros, H. G. P. & Esquivel, D. M. S. in Magnetite Biomineralization and Magnetoreception in Organisms (eds Kirschvink, J. L. et al.) 289–309 (Plenum, New York, 1985).
Esquivel, D. M. S., Lins de Barros, H. G. P., Farina, M., Aragão, P. H. A. & Danon, J. Biol. Cell. 47, 227–234 (1983).
Farina, M., Sollorzano, G. & Vieira, G. J. Proc. Xlth Int. Cong. on Electron Microscopy, Kyoto 3369–3370 (1986).
Reimer, L., Fromm, J. & Rennekam, R. Ultramicroscopy 24, 339–354 (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1988).
Inorganic Index to the Powder Diffraction File (Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards, 1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farina, M., Esquivel, D. & de Barros, H. Magnetic iron-sulphur crystals from a magnetotactic microorganism. Nature 343, 256–258 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/343256a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/343256a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Textures, trace element compositions, and sulfur isotopes of pyrite from the Honghai volcanogenic massive sulfide deposit: Implications for ore genesis and mineral exploration
Science China Earth Sciences (2023)
-
Correlative SIP-FISH-Raman-SEM-NanoSIMS links identity, morphology, biochemistry, and physiology of environmental microbes
ISME Communications (2022)
-
Occurrence of south- and north-seeking multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes in a coastal lagoon in the South Hemisphere
International Microbiology (2022)
-
Swimming behavior of the multicellular magnetotactic prokaryote ‘Candidatus Magnetoglobus multicellularis’ near solid boundaries and natural magnetic grains
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (2021)
-
Magnetosomes: biogenic iron nanoparticles produced by environmental bacteria
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2019)