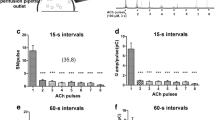
Abstract
The clostridial neurotoxins tetanus and botulinum toxin type A are known to block transmitter release from nerve terminals1–3, probably by interfering with some essential process controlling exocytosis3,4 after the entry of Ca2+ ions. Although exocytosis occurs in many secretory cells, these toxins show a high specificity for neurones and the secretory response of cultured bovine adrenal medullary cells is not inhibited by exposure to medium containing tetanus or botulinum toxin type A (although it is by botulinum toxin type D)4. Here we report that when tetanus toxin and botulinum neurotoxin type A are injected intracellularly into chromaffin cells they strongly inhibit secretion, as revealed by the measurement of cell capacitance5. These results indicate that these toxins are normally ineffective in chromaffin cells because they are not bound and internalized, so do not reach their site of action. Furthermore, we have localized the secretion-blocking effects of the toxin to a fragment comprising the light chain covalently linked to part of the heavy chain, suggesting that this part of the molecule contains the active site.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mellanby, J. J. Neurosci. 11, 29–34 (1984).
Simpson, L. L. A. Rev. Pharmac. Tox. 26, 427–453 (1986).
Habermann, E. & Dreyer, F. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immun. 129, 93–179 (1986).
Knight, D. E., Tonge, D. A. & Baker, P. F. Nature 317, 719–721 (1985).
Neher, E. & Marty, A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 6712–6716 (1982).
Fenwick, E. M., Fajdiga, P. B., Howe, N. B. S. & Livett, B. G. J. Cell Biol. 76, 12–30 (1978).
Hamill, O. P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B. & Sigworth, F. J. Pfl&ügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 391, 85–100 (1981).
Dreyer, F. & Schmitt, A. Neurosci. Lett. 26, 307–311 (1981).
Dreyer, F. et al. J. Physiol. (Paris) 79, 252–258 (1984).
Schmitt, A., Dreyer, F. & John, Chr. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archs Pharmak. 317, 326–330 (1981).
Morris, N. P. et al. J. biol. Chem. 255, 6071–6076 (1980).
Goldberg, R. L., Costa, T., Habig, W. H., Kohn, L. D. & Hardegree, M. C. Molec. Pharmac. 20, 565–570 (1981).
Weller, U., Taylor, C. F. & Habermann, E. Toxicon (in the press).
Habermann, E., Wellhöner, H. H. & Räker, K. O. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archs Pharmak. 299, 187–196 (1977).
Baker, P. F. & Knight, D. E. Nature 276, 620–622 (1978).
Dunn, L. A. & Holz, R. W. J. biol. Chem. 258, 4989–4993 (1983).
Wilson, S. P. & Kirshner, N. J. biol. Chem. 258, 4994–5000 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Penner, R., Neher, E. & Dreyer, F. Intracellularly injected tetanus toxin inhibits exocytosis in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature 324, 76–78 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/324076a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/324076a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Association of SNAREs and Calcium Channels with the Borders of Cytoskeletal Cages Organizes the Secretory Machinery in Chromaffin Cells
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2010)
-
Protein kinase C and clostridial neurotoxins affect discrete and related steps in the secretory pathway
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (1993)