Abstract
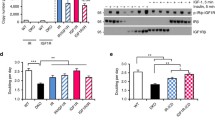
The cell surface receptors for insulin and epidermal growth factor (EGF) appear to share a common evolutionary origin, as suggested by structural similarity of cysteine-rich regions in their extracellular domains and a highly conserved tyrosine-specific protein kinase domain1-3. Only minor similarity is found outside this catalytic domain, as expected for receptors that have different ligand specificities and generate different biological signals4,5. The EGF receptor is a single polypeptide chain6 but the insulin receptor consists of distinct α and β summits7 that function as an α2β2 heterotetrameric receptor complex8-11. Provoked by this major structural difference in two receptors that carry out parallel functions, we have designed a chimaeric receptor molecule comprising the extracellular portion of the insulin receptor joined to the transmembrane and intracellular domains of the EGF receptor to investigate whether one ligand will activate the tyrosine kinase domain of the receptor for the other ligand. We show here that the EGF receptor kinase domain of the chimaeric protein, expressed transiently in simian cells, is activated by insulin binding. This strongly suggests that insulin and EGF receptors employ closely related or identical mechanisms for signal transduction across the plasma membrane.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ullrich, A. et al. Nature 309, 418–425 (1984).
Ullrich, A. et al. Nature 313, 756–761 (1985).
Ebina, Y. et al. Cell 40, 747–758 1985).
Kahn, C.R. A. Rev. Med. 36, 429–451 (1985).
Herschman, H. R. in Control of Animal Cell Proliferation (eds Boynton, A. L. & Leffert, H. L.) 169–199 (Academic, New York, 1985).
Cohen, S., Fava, R. A. & Sawyer, S. T. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 6237–6241 1982).
Kasuga, M., Hedo, J. A., Yamada, K. M. & Kahn, C. R. J. biol Chem. 257, 10392–10399 (1982).
Hedo, J. A., Kasuga, M., Van Obberghen, E., Roth, J. & Kahn, C. R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 4791–4795 (1981).
Massague, J., Pilch, P. F. & Czech, M. P. J. biol. Chem. 256, 3182–3190 (1981).
Van Obberghen, E. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 1052–1056 (1981).
Fujita-Yamaguchi, Y. J. biol. Chem. 259, 1206–1211 (1984).
Kasuga, M., Kahn, C. R., Hedo, J. A., Van Obberghen, E. & Yamada, K. M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 6917–6921 (1981).
Reed, B. C., Ronnett, G. V. & Lane, D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 2908–2912 (1981)
Deutsch, P. J., Wan, C. F., Rosen, O. M. & Rubin, C. S. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 133–136 (1983).
White, M. F., Haring, H.-U., Kasuga, M. & Kahn, C. R. J. biol. Chem. 259, 255–264 (1984).
Petruzelli, L., Herrera, R. & Rosen, O. M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 3327–3331 (1984).
Erneux, C., Cohen, S. & Garbers, D. J. biol. Chem. 258, 4137–4142 (1983).
Massague, J. & Czech, M. P. J. biol. Chem. 257, 5038–5045 (1982).
Simonsen, C. C. & Levinson, A. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 2495–2499 (1983).
Lusky, M. & Botchan, M. Nature 293, 79–81 (1981).
Graham, F. L. & van der Eb, A. J. Virology 52, 456–467 (1973).
Ganguly, S., Petruzzelli, L. M., Herrera, R., Stadtmauer, L. & Rosen, O. M. Curr. Top. cell. Regul. 27, 83–94 (1985).
Waterfield, M. D. et al. J. cell Biochem. 20, 149–161 (1982).
Kris, R. M. et al. Cell 40, 619–625 (1985).
Laemmli, U. K. Nature 227, 680–685 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riedel, H., Dull, T., Schlessinger, J. et al. A chimaeric receptor allows insulin to stimulate tyrosine kinase activity of epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature 324, 68–70 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/324068a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/324068a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
The discovery of receptor tyrosine kinases: targets for cancer therapy
Nature Reviews Cancer (2004)
-
Antigen Responsive Antibody–Receptor Kinase Chimera
Bio/Technology (1992)
-
Structure and function of tyrosine kinase receptors
Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes (1991)