Abstract
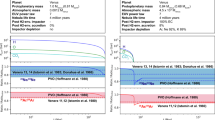
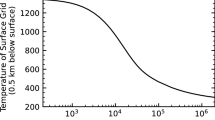
High-velocity impacts of planetesimals onto a growing planet result in the impact-degassing of volatiles and the formation of an impact-induced atmosphere. Because of the blanketing effect of such an atmosphere, it is likely that the surface of the proto-Venus melted once the radius exceeded ∼40% of the final radius. The final mass of H2O in the impact-generated atmosphere, predicted to be ∼1021 kg on the basis of thermal evolution models of the growing proto-Venus, does not depend on the initial water content of the Venus-forming planetesimals and is almost identical to the present mass of the Earth's oceans. We show here that an impact-induced H2O atmosphere of ∼1021 kg mass probably formed on both Venus and Earth during accretion, but that whereas H2O in the proto-atmosphere of the Earth could condense to form a hot (∼600 K) ocean, such condensation probably did not occur on Venus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe, Y. & Matsui, T. J. geophys. Res. 90, C545–C559 (1985).
Matsui, T. & Abe, Y. Nature 319, 303–305 (1986).
Donahue, T. M. et al. Science 216, 630–633 (1982).
Tomasko, M. G. et al. J. geophys. Res. 85, 8167–8186 (1980).
Kasting, J. F. & Pollack, J. B. Icarus 53, 479–508 (1983).
Oskvarek, J. D. & Perry, E. C. Jr Nature 259, 192–194 (1976).
Sagan, C. & Mullen, G. Science 177, 52–56 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsui, T., Abe, Y. Impact-induced atmospheres and oceans on Earth and Venus. Nature 322, 526–528 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/322526a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/322526a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
A cool runaway greenhouse without surface magma ocean
Nature (2023)
-
Synergies Between Venus & Exoplanetary Observations
Space Science Reviews (2023)
-
Predicted diversity in water content of terrestrial exoplanets orbiting M dwarfs
Nature Astronomy (2022)
-
Brightness modulations of our nearest terrestrial planet Venus reveal atmospheric super-rotation rather than surface features
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Formation and Evolution of Protoatmospheres
Space Science Reviews (2016)